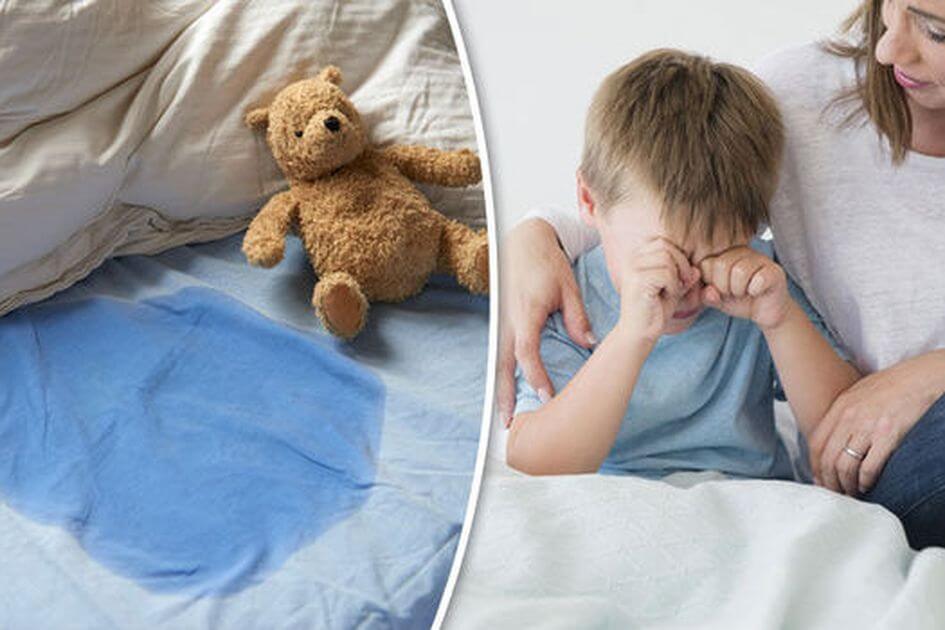
شب ادراری در کودکان، ترشح غیرارادی ادرار در هنگام خواب در کودکان پنج سال و بالاتر است. این یک بیماری شایع دوران کودکی است که بسته به گروه سنی، شیوع متفاوتی دارد. حدود 15 درصد از کودکان پنج ساله، 5 درصد از کودکان ده ساله و 1-2 درصد از نوجوانان هنوز شب ادراری را تجربه می کنند. اگرچه معمولاً به خودی خود برطرف می شود، اما می تواند باعث ناراحتی و خجالت قابل توجهی برای کودکان و نگرانی والدین شود.
بیشتر بخوانید : یبوست در کودکان
علل شب ادراری در کودکان
علل شب ادراری می تواند چند عاملی باشد که اغلب شامل ترکیبی از عوامل ژنتیکی، رشدی، روانی و فیزیولوژیکی است. درک این موارد می تواند به ایجاد درمان های موثرتر کمک کند.
1. عوامل ژنتیکی
سابقه خانوادگی نقش مهمی در شب ادراری دارد. مطالعات نشان داده است که کودکانی که والدینشان شب ادراری داشته اند، احتمالاً خودشان تخت را خیس می کنند. اگر پدر و مادر هر دو در کودکی رختخواب را خیس کنند، 77 درصد احتمال دارد که فرزندشان نیز شب ادراری را تجربه کند.
2. Growth factors Delayed bladder development can contribute to bedwetting. Some children's bladders may grow more slowly, resulting in a reduced capacity to hold urine during the night or a delayed need to urinate.
3. Sleep patterns Children who wet their beds often exhibit deep sleep patterns and may not wake up when their bladders are full. This deep sleep can prevent the recognition of the signal to wake up and urinate. 4. Hormonal factors Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) regulates urine production during sleep. Children who produce insufficient levels of ADH at night may produce more urine than their bladder can handle, leading to enuresis. 5. Urinary tract infections (UTIs). A UTI can cause frequent urination, pain, and bedwetting. If a child suddenly develops nocturnal enuresis and also shows symptoms such as pain during urination, it is essential to consult a health care provider. 6. Psychological factors Stress and anxiety can contribute to bedwetting. Major life changes such as moving to a new home, parents divorcing, or starting a new school can be stressful, which may lead to or exacerbate bedwetting. 7. Constipation Chronic constipation can put pressure on the bladder and reduce its capacity, potentially causing bedwetting. Treating constipation can often reduce the symptoms of bedwetting.Treatment approaches
Treatment of bedwetting in children includes a wide range of strategies, from behavior modification to medical interventions. Here are some common approaches:
1. Behavioral interventionsBehavioral interventions are often the first line of treatment and can include:
Bladder training: encouraging the child to delay urinating during the day to increase bladder capacity.
Bedwetting alarms: devices that wake up a child at the first sign of wetting and help them learn to respond to a full bladder.
Positive reinforcement: rewarding dry nights to motivate the child.
In some cases, medical treatments may be necessary:
Desmopressin: synthetic form of ADH to reduce urine output at night.
Anticholinergic drugs: to relax the bladder and increase its capacity.
Treatment of underlying diseases such as constipation or UTI can eliminate or significantly reduce bedwetting. 4. Psychological support Counseling or therapy may be helpful for children who experience stress, anxiety, or other psychological factors contributing to bedwetting.
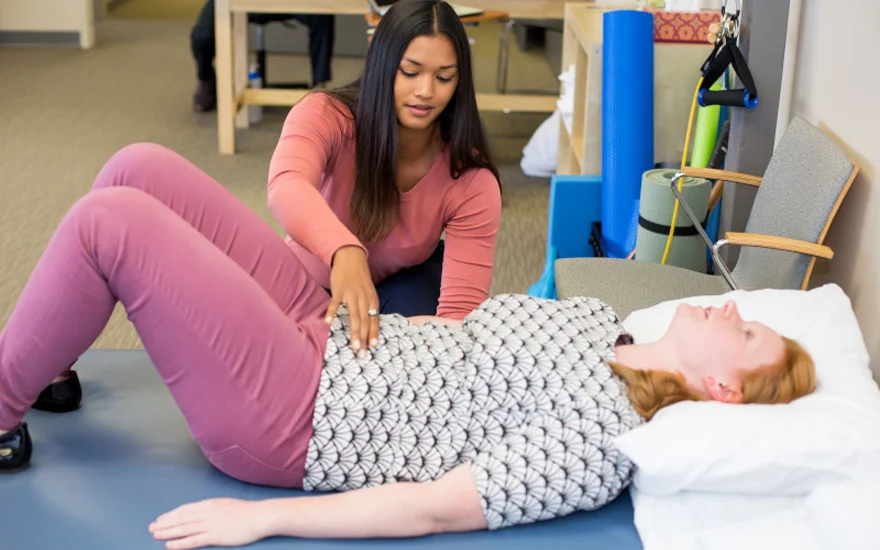
The role of pelvic floor physiotherapy in treating nocturnal enuresis in children
Pelvic floor physiotherapy as an approach It is emerging as a promising treatment for enuresis. This type of treatment focuses on the muscles, ligaments and connective tissues of the pelvic floor, which play an important role in urine control.The pelvic floor is a group of muscles that support the bladder, rectum and genitals. These muscles help to control the secretion of urine and feces by contracting and relaxing. Dysfunction or weakness in these muscles can contribute to incontinence and bedwetting.
Pelvic floor physiotherapy aims to strengthen and rehabilitate pelvic floor muscles through different techniques:
Biofeedback: This technique uses electronic monitoring to help children become aware of their pelvic floor muscles and learn how to control them.
Pelvic floor exercises: Exercises such as Kegels can strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Children are taught how to properly contract and relax these muscles.
Behavioral techniques: Helping children develop better bladder habits, including scheduled urination and avoiding bladder irritants.
Manual therapy: practical techniques to reduce tension and improve muscle function.
Benefits of pelvic floor physiotherapy for bedwetting
Pelvic floor physiotherapy can have several benefits for children who struggle with bedwetting:
- Improving muscle strength: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles increases bladder control.
- Better awareness: Children learn to recognize their bladder signals, improving their ability to wake up when they need to urinate.
- Decreasing the frequency: increasing muscle control can reduce the frequency of bedwetting.