سکته مغزی: علائم و درمان آن
سکته مغزی عارضهای بسیار جدی و مرگبار است که در اثر عدم خونرسانی به بخشی از مغز و تنگی عروق مغزی رخ میدهد. سکته مغزی موردی اورژانسی است و نیاز به درمان فوری دارد، چرا که با درمان هر چه سریعتر بیمار میتوان میزان آسیب دیدگی را کاهش داد نیز در ادامه به بحث ضربه مغزی نیز میپردازیم.
در روش درمانی بیوفیدبک به بیماران آموزش داده میشود که با استفاده از سیگنالهای به دست آمده از بدنشان، سلامت خود را بهبود دهند. متخصصین طب فیزیکی از روش بیوفیدبک برای بیماران سکتهی مغزی استفاده میکنند تا به آنها کمک کنند دوباره عضلات فلج خود را به حرکت دربیاورند.
زخم بستر که با نامهای زخم فشاری، دکوبیتوس اولسر، اولسر فشاری نیز شناخته میشود، یکی از چندین نشانۀ اهمال در نگهداری بیماران در اسایشگاه و عدم توجه به وضعیت جسمی بیماران ناتوان حرکتی در بیمارستان هاست. A bed sore occurs when there is constant pressure on the skin, and this condition can cause serious health problems such as infections or other threatening injuries.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptoms of a stroke can be remembered with the keyword FAST, which stands for face, arm, speech and time in English.
• Face - the patient sometimes faces drooping of one side of the face and cannot smile, or faces drooping of the mouth or eyes, and there is a possibility of nervous tics in the person.
• Arms - a person suspected of having a stroke usually cannot raise both arms and hold them up due to weakness or numbness in one arm.
• Speech - the patient's speech is unintelligible or slurred, or the patient cannot speak at all despite being intelligent.
• Time - If you see the above signs and symptoms, contact the emergency medical center immediately.
Causes and Reasons
The proper functioning of the brain, like any other organ, is dependent on receiving nutrients and oxygen through the blood stream. If the blood supply is limited or stopped, the death of brain cells starts and leads to brain damage, disability and eventually death.
There are two main reasons for a stroke:
Ischemic: When the blood supply to the brain is stopped due to the formation of a blood clot. 85% of all cases of cerebral strokes occur for this reason.
Hemorrhage: If a weak blood vessel responsible for blood supply to the brain is torn.
There is also a related complication called Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), in which blood supply to the brain is temporarily interrupted, causing a mild or small stroke that lasts between 30 minutes and several hours. Do not take this attack lightly and be sure to treat it, because it is often a warning sign that informs you of the risk of a complete stroke in the near future.
Individuals at risk
Stroke is a serious problem that many people suffer from every year and it is the third cause of death after heart disease and cancer. Brain damage caused by stroke is one of the common causes of disability in adults.
Older people are more prone to stroke than others, although anyone of any age, even children, can fall victim to this deadly complication.
This is partially rooted in the tendency to suffer from high blood pressure, a complication of which stroke is one of its results.
Smoking, overweight, lack of exercise and improper diet, as well as high cholesterol, atrial fibrillation and diabetes are risk factors for stroke.
Complications
About one in four strokes result in death, and those who survive suffer long-term complications from brain damage.
Some patients regain their former independence after a long period of time has passed, but unfortunately, many never fully recover and inevitably make changes in their lifestyle or become somewhat dependent on the people around them.
About half of stroke victims depend on others to perform daily activities and take care of themselves.
The rehabilitation process is different for each patient and depends on their symptoms and severity. In this clinic, a group of experienced specialists, such as physiotherapists, psychologists, occupational therapists, speech therapists and other trained nurses and doctors are ready to provide treatment services to patients.
Ways and methods of treatment
From the methods of stroke treatment, it can be said that the treatment depends on the type of stroke, for example, which part of the brain was damaged and what was the cause of the stroke.
Stroke is often treated with medicine. The main role of these drugs is to prevent the formation of blood clots and destroy these clots, lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels.
In case of swelling of the brain, brain vascular surgery is necessary to eliminate the swelling and reduce the possibility of re-bleeding in hemorrhagic strokes.
Physiotherapy
Since the brain cannot produce new cells to replace damaged cells, the patient's recovery depends on the brain's ability to organize healthy cells and compensate for lost cells, this ability is called neuroplasticity. Stroke physiotherapy helps the patient by providing practical and specialized guidance. Physiotherapy specialists often interact with other members of the stroke treatment group by providing post-stroke exercises and do their best to eliminate complications caused by stroke.
Physiotherapist helps the patient by considering the needs of the patient in the following cases:
• Preparing a patient care plan in order to improve conditions and prevent complications that prolong the recovery period
• Providing useful recommendations regarding the correct posture when sitting or lying down and the pause between movement times
• Determining the right time to get up from the sick bed and start walking and, if necessary, determine the necessary equipment and tools to move or support the patient.
• Encouraging the patient to actively participate in physical therapy sessions to retrain the natural pattern of movement
• Providing treatments to strengthen the body parts and teaching how to move the body again with the maximum possible independence
A number of treatment methods in stroke physiotherapy are described below. Physiotherapy is also used to treat cerebral palsy. Physiotherapy of cerebral palsy helps patients to get the strength and power of movement suitable for activity in the best possible state in all stages of their life.
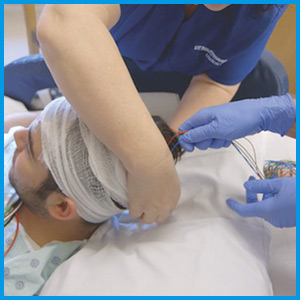
Magnetic Brain Stimulation (TMS)
Magnetic brain stimulation is one of the most important and effective therapeutic modalities in stroke physiotherapy.
Magnetic brain stimulation is a completely safe and non-invasive treatment for rehabilitation after stroke. In this method, by applying magnetic stimulation to the damaged networks and structures, a significant improvement is made in the patient's condition. TMS is an outpatient procedure that does not require hospitalization or anesthesia, the patient tolerates it well and usually does not face any side effects.
The patient sits on a special chair during the TMS session. In the first session, several measures are taken to ensure that the TMS coil is correctly placed on the patient's head.
Then the coil is brought forward to the anterior region of the patient's brain and the treatment begins. During the treatment, the patient hears a series of click-like sounds and feels small shocks under the coil.
This treatment method is usually performed in several sessions of approximately 40 minutes, 5 days a week for 4 to 6 weeks. Of course, the number of sessions depends on the patient's response to the treatment.
One side of the brain becomes hyperactive after a stroke and excessive load is imposed on its circuits. We recommend that you try TMS therapy to most likely restore the balance between the two sides of the brain. In the following, we will explain that rehabilitation exercises are useful for the treatment of concussions and strokes.
Rehabilitation exercises
Passive range of motion: In this method, instead of the patient moving his body by his own will, an external force is applied to move a part of the body. For example, a patient moves a weak or paralyzed arm with a strong arm, a specialist or nurse moves an injured arm or leg, or the body is made to move by a device. Passive range of motion helps keep joints flexible and prevent joint stiffness. Joint stiffness occurs when structural changes occur in soft tissues, for example, movement is limited due to stiffness or shortening of muscles and tendons. Do passive range-of-motion exercises even in the case of complete paralysis, because the contraction leads to skin breakdown, tissue irritation, pain, decreased blood flow, and even when muscle function is restored, it prevents arm or leg movement.
Dr. Hamidreza Torabi, neurologist