بیماری صرع و درمان آن
تشخیص بیماری صرع
پزشک برای این منظور علائم و سابقه شما را بررسی میکند و تستهایی را برای تشخیص و تعیین علت صرع تجویز میکند. تشخیص مناسب شانس پیداکردن درمان بهینه را بالا میبرد.
تست نورولوژیک: پزشک، رفتار، توانایی حرکتی، عملکرد ذهنی و دیگر نواحی را برای تشخیص و تعیین نوع صرع میآزماید.
تستهای خونی: ممکن است جهت بررسی نشانههای عفونت، بیماریهای ژنتیکی و دیگر بیماریهای همراه از شما نمونه خونی گرفته شود.
همچنین ممکن است تستهایی برای تعیین ناهنجاریهای مغزی توصیه شود؛ مانند:
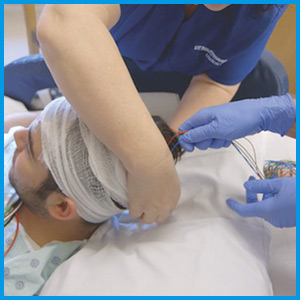
الکتروانسفالوگرام (EEG): رایجترین تست برای تشخیص صرع است. الکترودهایی به سر شما وصل شده و فعالیت الکتریکی مغز شما را ضبط میکنند. اگر مبتلا به صرع باشید عموما تغییراتی در الگوی امواج مغزیتان دیده میشود، حتی زمانیکه تشنج نداشته باشید. این تست میتواند در تعیین نوع صرع و رد دیگر بیماریها کمک کننده باشد.
EEGبا تراکم بالا: در این تست فاصله الکترودها نسبت به نوع مرسوم نزدیکتر است و به پزشک کمک میکند دقیقتر متوجه شود چه ناحیهای از مغز درگیر است.
CTاسکن: در این روش با استفاده از اشعه X تصویر مقطعی از مغز شما تهیه میشود. این روش قادر به شناسایی ناهنجاریهای ساختاری مغز است که موجب صرع شدهاند؛ مانند تومور، خونریزی و کیست.
MRI: این روش از مگنتهای قوی و امواج رادیویی برای ایجاد نمای جزئی از مغز، استفاده میکند. In this method, lesions and abnormalities that cause epilepsy can be traced.
fMRI: This method measures blood flow changes during the activity of a certain part of the brain.
PET: Uses intravenous injection of a small amount of radioactive material with a low dose to help image the brain's metabolic activity and determine abnormalities. Areas of the brain that have little metabolic activity may indicate the occurrence of epilepsy.
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT): This test is used if MRI and EEG are not able to determine the origin of epilepsy. In this test, a three-dimensional image of the blood flow activity in the brain during a seizure is prepared, and the areas with more blood flow indicate the affected areas.
Neuropsychological tests: In these tests, the doctor evaluates your thinking, memory and speech. The results help to identify the areas involved in the brain.Besides these tests, there is a combination of analysis techniques to identify the starting point of epilepsy.
Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM): It is a way to compare areas with high blood flow in the brain during a seizure with a normal brain.
Electric source imaging (ESI): is a method that receives EEG data and projects it onto MRI.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG): measures the magnetic field produced by brain activity.
Treatment of epilepsy
Doctors generally start the treatment with drugs and if the patient does not respond, they suggest surgery or other methods.
Drugs for epilepsy
Most of the patients recover completely by taking one drug, and others receive a combination of drugs, the frequency and severity of their epilepsy decreases.
Many children who do not have epilepsy symptoms can finally stop taking the medicine, and many adults can also stop taking the medicine after two or more years of symptoms; The doctor will help you in this matter.
Your doctor will choose the right medicine according to the type of disease, frequency of seizures, age and other factors, and will also check drug interactions.
He will probably prescribe a drug with a low dose at first and then gradually increase the dose until your disease is under control.
There are more than 20 types of antiepileptic drugs. Their mild side effects include: fatigue, dizziness, weight loss, bone density reduction, skin rash, imbalance, speech problems, memory and thinking problems, and mood changes.
Severe but rare side effects include: depression, suicidal thoughts, severe rash and inflammation of organs such as the liver.
Note that in case of side effects, be sure to consult your doctor and never stop taking the medicine without his knowledge.
We have two types of surgery
Reductive surgery: the surgeon removes the part of the brain that causes seizures. This method is usually used when the involved area is very small, has precise boundaries and is not responsible for controlling actions such as speech, movement, vision and hearing.
Cutting surgery: instead of removing a part of the brain, the surgeon cuts the communication path between the nerves involved in epilepsy.
Although most people need to take medication to prevent seizures after successful surgery, the dose and amount of these medications may be reduced.
In few cases, these surgeries cause complications, for example, they may permanently change your cognitive abilities.
Ketogenic diet
This diet is high in fat and low in carbohydrates and has been successful in reducing seizures especially in children. Studies show that it is also effective for adults. The doctor may suggest this diet based on the type of epilepsy, but you should not start it without consulting him. At first, you may feel lazy, and its side effects include dehydration, constipation, reduced growth due to lack of nutrition, kidney stones, weight loss, and bone fractures, which, of course, are very uncommon if the diet and medication are appropriate.
Neural stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation: The doctor places pieces called a vagus nerve stimulator under the skin of your chest, which is similar to a heart pacemaker and sends electrical waves to the brain through the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve is responsible for involuntary activities such as heartbeat. It is not clear how this piece reduces seizures, but a 20-40% reduction has been observed.
Deep brain stimulation: In this method, electrodes are placed in a certain part of the brain, which is generally the thalamus, and this electrode is connected to a generator in the chest. This generator sends electrical pulses to the brain at intervals and can reduce seizures.
Reactive neuron stimulation: In this method, a small gadget called a neuron stimulator is placed in the skull. This piece detects the brain patterns that initiate the seizure and as soon as it is observed, it sends a small pulse to disrupt it. Studies show that this method has few side effects and can be used in the long term.
Lifestyle
Timely use of medicines, having enough sleep and exercise can be very useful. It is also very important to reduce stress and quit smoking and alcohol.
Uncontrollable seizures can make life difficult and lead to depression. It's important not to let seizures take you away from life. Teaching family and friends to understand better, ignore negative reactions from the surrounding environment and lead an independent life as much as possible can improve social life conditions. Even if the disease is such that you cannot work outside the home, it is better to follow work and social activities from home.Resources
https://www.webmd.com/epilepsy/guide/treating-epilepsy