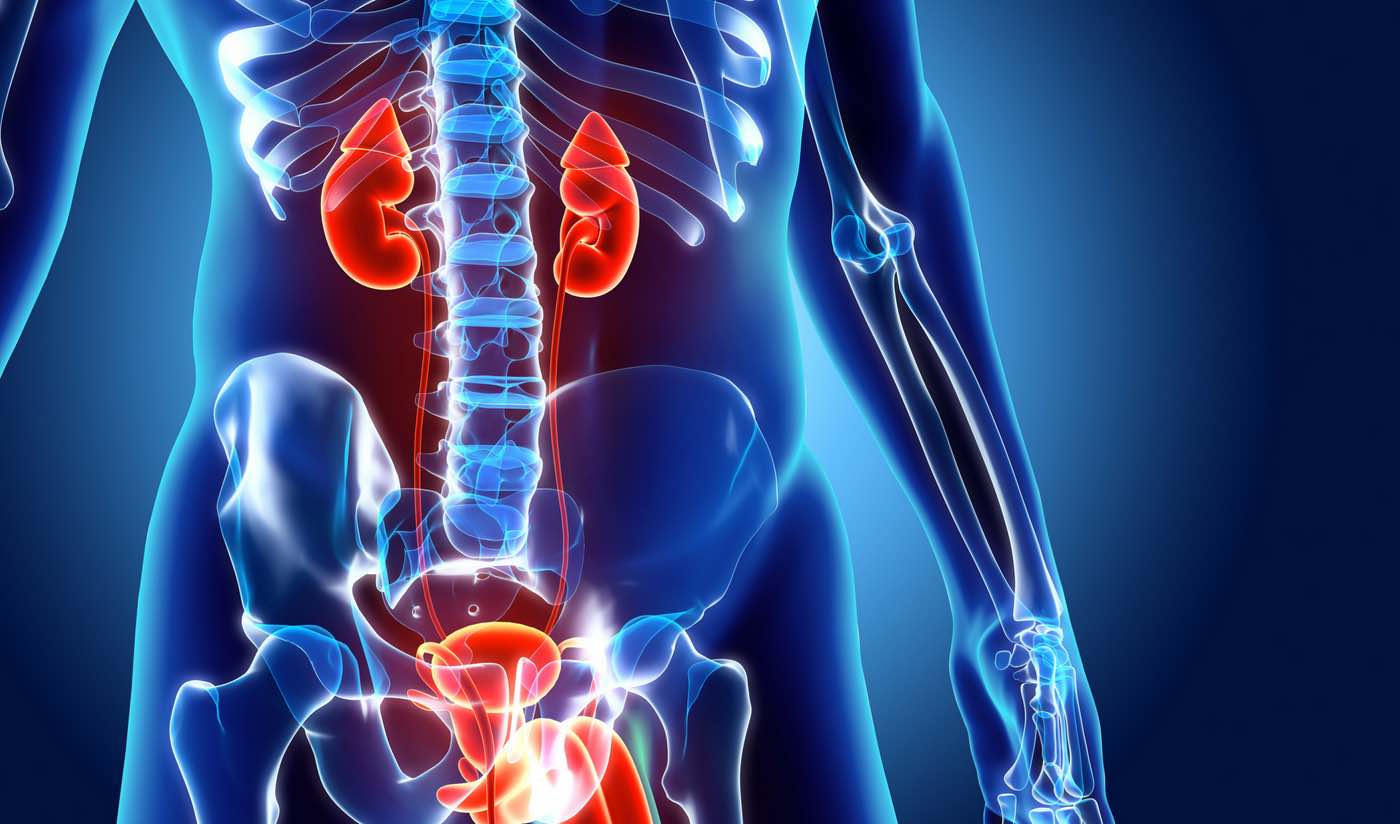
مثانه نوروژنیک ، همچنین به عنوان اختلال عملکرد دستگاه ادراری تحتانی نوروژنیک (NLUTD) شناخته می شود، وضعیتی است که زمانی رخ می دهد که آسیب عصبی ارتباط بین مغز و مثانه را مختل کند. این می تواند باعث ایجاد مشکلاتی در کنترل مثانه شود، از جمله بی اختیاری ادرار، تکرر ادرار و فوریت ادرار.
دلایل مختلفی برای مثانه نوروژنیک وجود دارد، از جمله:
- آسیب نخاعی: این شایع ترین علت مثانه نوروژنیک است. آسیب های نخاعی می تواند به اعصابی که عملکرد مثانه را کنترل می کنند آسیب برساند.
- مولتیپل اسکلروزیس (MS): ام اس بیماری است که به غلاف میلین که رشته های عصبی را احاطه کرده است آسیب می رساند. این می تواند انتقال سیگنال های عصبی به مثانه را مختل کند.
- بیماری پارکینسون: بیماری پارکینسون یک اختلال عصبی است که بر سیستم عصبی تأثیر می گذارد. It can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
- Stroke: Stroke can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
- Brain tumors: Brain tumors can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
- Spinal cord tumors: Spinal cord tumors can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
- Birth defects: Birth defects of the spinal cord, such as spina bifida, can damage the nerves that control bladder function.
Symptoms of neurogenic bladder
Symptoms of this disease can be different depending on the cause and severity of the disease. Some common symptoms are:
- Urinary incontinence: is the involuntary loss of urine. Urinary incontinence can be caused by bladder muscle weakness, bladder muscle overactivity, or problems with the sphincter muscles that control the flow of urine. Urinary frequency: This is the need to urinate more than usual. It can be caused by weakness of the bladder muscle, excessive activity of the bladder muscle or difficulty in feeling the bladder full. Urinary urgency: This is a sudden and strong need to urinate. This can be caused by overactivity of the bladder muscle or difficulty in feeling the bladder full. Urinary retention: inability to pass urine. This can be caused by bladder muscle weakness, bladder muscle overactivity, or problems with the sphincter muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): UTIs are more common in people with neurogenic bladder. This is because the bladder is less able to empty completely, which can allow bacteria to grow.
The doctor diagnoses neurogenic bladder based on medical history, physical examination and diagnostic tests:
- Urinalysis: This test checks for signs of infection or other urinary problems.
- Urine culture: This test checks the presence of bacteria in the urine.
- Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to create images of the bladder and kidneys.
- Cystorenteroscopy: This test involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the bladder to check for problems inside the bladder and urethra.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of the muscles of the bladder and urethra.
treatment methods
The treatment of neurogenic bladder depends on the cause and severity of the disease. The goal of treatment is to improve bladder control and prevent complications such as urinary incontinence.
Treatment options for neurogenic bladder may include:
- Medications: There are several medications that can be used to treat neurogenic bladder, including anticholinergics, beta blockers, and muscle relaxants.
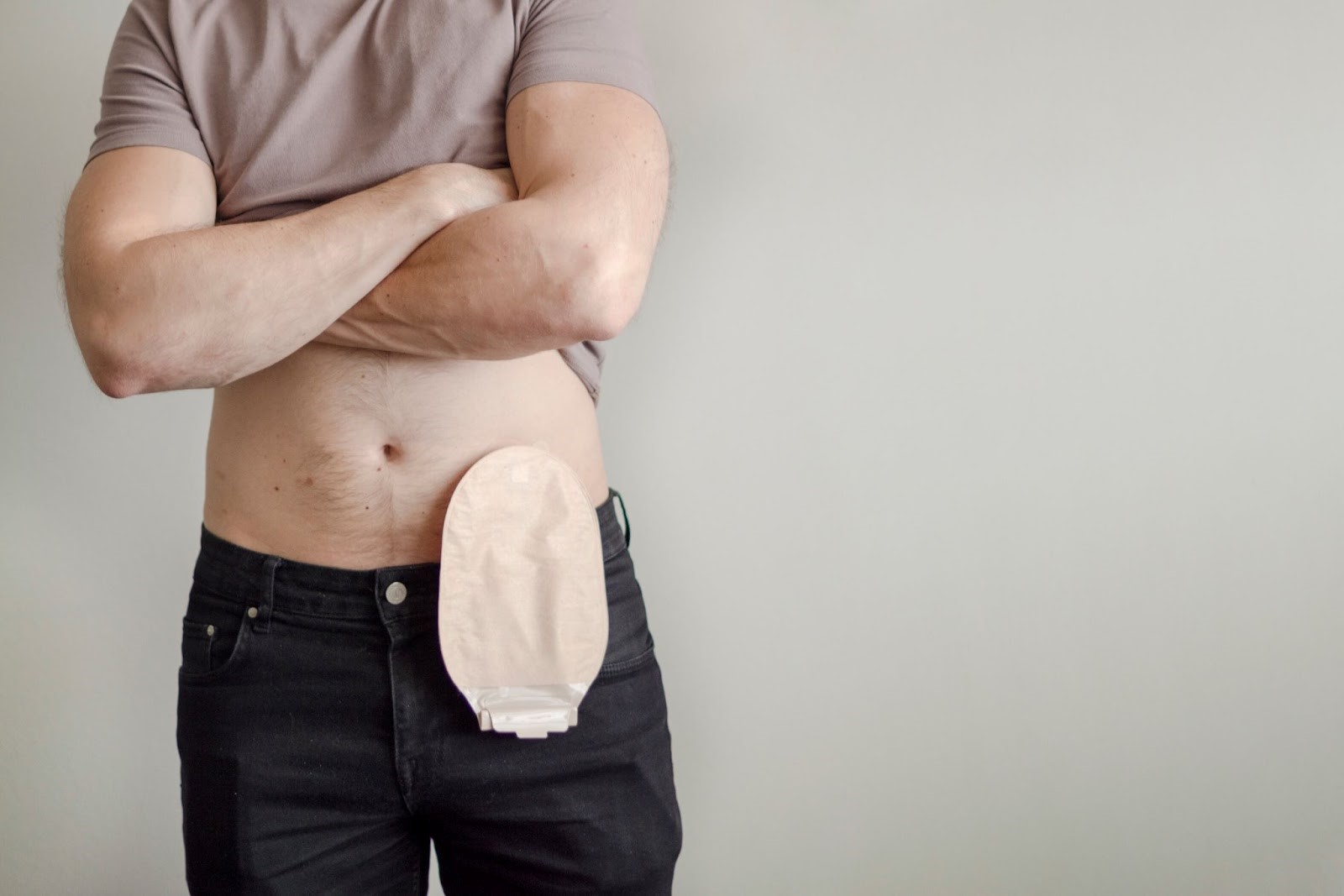
- Catheters: A catheter is a thin tube that is inserted into the bladder to drain urine. Catheters can be used temporarily or long-term.
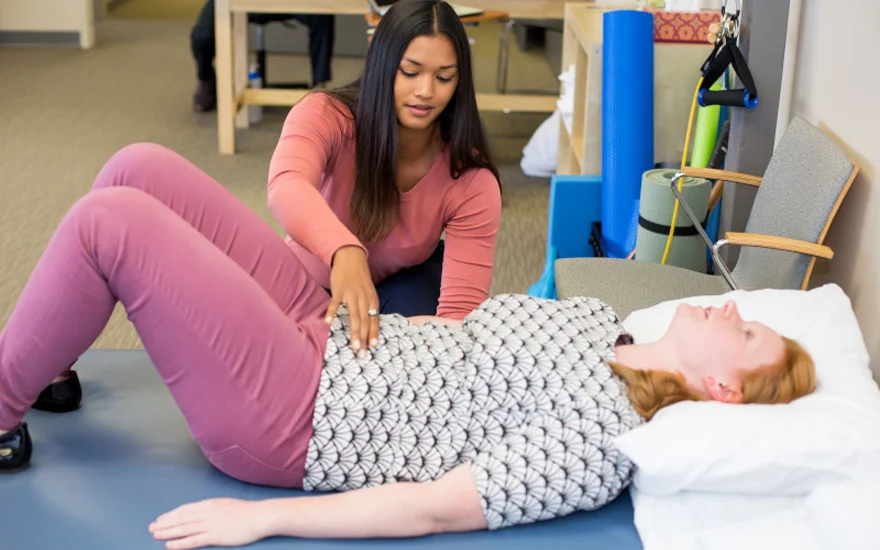
- Bladder training: Bladder training under expert supervision Pelvic floor physiotherapy is a treatment that teaches people How to control their bladder muscles.
- Electrical stimulation: Electrical stimulation can be used to help relax the bladder muscles or stimulate the nerves that control bladder function.
- Surgery: Surgery may be an option for people who do not respond to other treatments.