جراحی دیسک کمر در مواقعی انجام میشود که دیسک ستون فقرات به دلایل مختلفی بیرون زده باشند. A herniated disc occurs most often at the end of the spine, although it can also occur in other parts of the spine. Each bone of the spine has a disc that protects the vertebral column from shocks and prevents shock absorption to prevent damage to the vertebrae. But in some cases, lumbar discs may protrude or dislocate, necessitating lumbar disc surgery. In the following, we discuss tips about lumbar disc surgery and necessary care after it.

Lumbar disc herniation
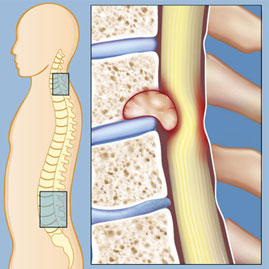
The water content of the intervertebral discs and their elasticity decreases with age and due to the increase in physical struggle, also the structure of the discs changes and the discs are gradually worn. As a result, the fibrous wall of the disc becomes weak, in this case, the disc wall may bulge. After all, there is also the possibility of tearing the disc wall, in this case, there is a possibility that the elastic material inside the disc will come out of the gap created in the disc wall and cause a disc herniation. Bulging or disc herniation causes narrowing of the space Damage to the disc in the long term causes the loss of communication between the vertebrae, which may be accompanied by other injuries. In severe cases, a lumbar disc surgeon or a neurosurgeon uses surgery to treat disc herniation. A neurosurgeon diagnoses and treats disorders involving the nervous system. Drying of spongy disc fluid in the spine can cause them to protrude from their original location and gradually lead to their wear and tear, which is known as a bulging disc or lumbar disc. Among the symptoms of lumbar disc protrusion are intermittent back pain, back muscle spasm, sciatica pain, muscle weakness and numbness in the legs, decreased knee and ankle reflexes, changes in bladder function, muscle weakness, and tingling in the lower limbs. For the treatment of lumbar disc, various non-surgical methods are used, which include changes in lifestyle, attention to body posture and ergonomics, physical therapy, drug therapy, and the use of platelet-rich plasma are recommended. If non-surgical treatments have no effect in reducing the problems caused by the lumbar disc, the doctor can turn to lumbar disc surgery. Lumbar disc surgery is performed in two ways, and we will discuss each of them below. Open lumbar disc surgery is one of the oldest and most common treatment methods for patients who have severe disc protrusion or rupture and other methods such as drug therapy or non-surgical treatments have not been effective for them. In this method, the surgeon directly accesses the spine by making an incision on the back and removes the damaged part of the disc or the pressure on the nerve root. This surgery is recommended for patients who have severe and chronic sciatica pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, or who have problems with urine and stool control. Although the recovery time in this method is longer than minimally invasive surgeries, in many cases it can significantly reduce the patient's pain. Closed lumbar disc surgery is a non-invasive procedure that, unlike open surgery, is performed without the need to make a deep incision on the back. In this type of operation, the surgeon uses advanced devices and new technologies. For closed lumbar disc surgery, methods such as epidural injection, discogel and disc laser are used. The fact that this method is less complicated than open surgery has made it more popular among people who need surgery. The main goal of closed lumbar disc surgery is to use smaller incisions and tubular instruments including fluoroscopy, X-ray and microscope, to cause the least possible damage to the muscles and tissues of the spine. Due to the many advantages of closed surgery, this method is preferred over open surgery: Stop smoking: If you use cigarettes, smokeless tobacco products, or any products containing nicotine, you should stop at least a few months before surgery. People who use these products are at increased risk for surgical complications such as wound infection or delayed bone healing. Be sure to inform your doctor so that he can develop a suitable plan for you to quit smoking. Avoid certain medications before surgery: Some medications, such as aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen, may cause bleeding or interfere with anesthetics. Be sure to make a list of your medications, nutritional supplements, and herbal remedies and show them to your doctor. Find someone to help after surgery: After surgery, you may need help with things like washing, dressing, cleaning. So get help from your friends or hire a nurse to do these activities for you for a few weeks after surgery. There are different types of lumbar disc surgery, and doctors choose one of the following methods to perform this surgery, considering the age of the patient, his general condition, and the location of the disc herniation. In this surgical method, after making a small incision on the back, the surgeon makes a hole in the lamina or arch of the lumbar vertebrae in order to reduce the pressure on the nerve root. If necessary, laminectomy surgery is used to separate the lamina. One of the methods of lumbar disc surgery is called microdiscectomy surgery. In this method, after making a small incision on the back, the surgeon removes part of the disc or all of it using surgical tools to prevent pressure on the nerve root. In artificial disc surgery, as one of the available techniques for this type of operation, the surgeon makes an incision on the patient's abdomen and places an artificial disc in place of the damaged disc. In this method, the patient must be under complete anesthesia and after the operation, he may be hospitalized for a few days. This method is not suitable for the treatment of multiple damaged discs and people suffering from osteoporosis or arthritis. Endoscopic surgery is used as a new and minimally invasive method in the treatment of damaged disc, in which the surgeon, after making a small incision on the back, uses an endoscope camera and microscopic instruments to remove the damaged disc from the patient's spine. In discopathy surgery, the doctor makes a small incision in the lower back, uses microscopic tools or lasers and removes part of the damaged disc to reduce pressure on the nerves. The lumbar artificial disc operation is performed only if the disc protrudes in the lower part of the back and requires general anesthesia. This method is not suitable for people with arthritis or osteoporosis. In the surgical method, Tehran lumbar disc surgeon (neurosurgeon) chooses one of the following methods for treatment: Discectomy surgery is performed as a procedure to remove material that is putting pressure on nerve roots or the spine. This surgery is also known as microdiscectomy, percutaneous discectomy, lumbar discectomy, lumbar disc herniation surgery, or decompression surgery. In this procedure, the surgeon removes the prominent part of the intervertebral disc (nucleus pulposus), because this part can put pressure on the nerve root or spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, weakness, balance problems, or movement problems. Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive type of discectomy. In this method, the surgeon removes the prominent part of the nucleus pulposus by making a small incision of 4-2.5 cm length using traditional methods or laser. The surgeon uses a microscope during the operation. Also, in percutaneous discectomy, the surgeon removes part of the disc by making a small incision and using a laser or suction. A discectomy can be performed on different parts of the spine, for example, a lumbar discectomy is performed to remove a protruding part of a lumbar disc. Discectomy is performed with the following goals: laminectomy or
Fusion surgery or drying of the vertebrae of the spine is generally performed to solve the problem of instability of the spine caused by wear or degenerative disc disease, scoliosis (spine deviation) or other problems related to the order and alignment of the spine. is recommended as the "last" solution for the treatment of idiopathic scoliosis (scoliosis with an unknown cause), congenital scoliosis (present from birth), neuromuscular scoliosis (a side effect of other diseases) or degenerative scoliosis (caused by wear and tear). The surgeon fuses and fixes two or more vertebrae using healthy bone - usually a bone graft taken from the patient's own bone or a bone bank is used to connect the vertebrae together, and often devices such as screws, plates, and metal rods are used to stabilize and dry the vertebrae. Fusion surgery is a permanent solution to correct degenerative problems or spinal misalignment. Fusion of the vertebrae stabilizes the spine in a more correct and straight position. Fusion surgery corrects the curvature of the spine by 50-70%. Spinal curvature of 40-50 degrees or more is considered "severe" spinal curvature. Fusion surgery is recommended to correct the deformity and treat related side effects. Fusion surgery is performed with the following goals: The worn and damaged facet joint sometimes enlarges or bony appendages known as bone spurs develop on it, which in turn puts pressure on the nearby nerves. Sometimes it is also necessary to remove a small part of the facet joint so that the surgeon can access the damaged disc. Facetectomy surgery is performed in both cases. It should be noted that the presence of facet joints is necessary for the overall stability of the spine, so depending on how much of the facet joint is removed, it may be necessary to perform another surgery to stabilize the spine. When the pressure caused by a herniated disc is removed from the nerves, leg pain and back pain are relieved, sensory disturbances are reduced, muscles become stronger, and bowel or bladder function returns to normal. In addition, by performing lumbar disc surgery, you prevent possible paralysis. Approximately 10 to 15% of patients after disc surgery may face recurrence of disc herniation in the future. Recurrence of a herniated disc may occur within the first few days after surgery, years later, or at any other time. Diagnosing the recurrence of disc herniation is possible only with the reappearance of clinical symptoms. Leg and hip pain usually subsides immediately after the initial surgery due to reduced pressure on the nerve. Re-herniated disc may cause old pain to suddenly start again. The lumbar disc surgeon informs the patient about all these complications before performing the surgery. Most patients can resume office or light work ten to fourteen days after surgery, but you should wait four to six weeks before starting heavy manual work. After six weeks, there are usually no restrictions on activities. For more certainty, be sure to consult with your back disc surgeon. Lumbar disc surgery is a surgical procedure that is performed to treat herniated or damaged discs in the lumbar region. This action can help relieve pain caused by pressure on the nerve roots. Depending on the severity and location of the disease, the doctor may use different methods such as open surgery, endoscopy, or other minimally invasive methods to perform the operation. Matab Chi is a comprehensive reference for introducing doctors and medical services in Iran, which helps you easily find the best doctor you need. If you are looking for complete information about Dr. Mehran Moradi's profile or plan to contact Get to know the best lumbar disc doctor in Tehran, just use the professional and accurate facilities of Chi's office and make the best choice.
When do we need lumbar disc surgery?
Lower back disc surgery procedures
Open Lumbar Disc Surgeon
Lumbar disc surgery
Is open lumbar disc surgery better or closed?
Measures before lumbar disc surgery
Types of lumbar disc surgery
Laminectomy operation
microdiscectomy operation
Synthetic disk action
Endoscopy operation
Discopathy operation
Lum artificial disc operation
How is lumbar disc surgery performed?
Discectomy
laminectomy
Disc replacement
facetectomy
Advantages of lumbar disc herniation surgery
Possible risks of lumbar disc surgery
Complications of lumbar disc surgery include severe bleeding, damage to the cauda equina (in 1-2% of cases), muscle weakness and in more severe cases paralysis, sensory disorders, sensory disorders in the joints and lack of coordination. These complications rarely occur. Also, hemorrhaging or bleeding from the surgical wound after the operation, back pain and recurrence of hernia are other complications of lumbar disc surgery.How long is the recovery period after lumbar disc herniation surgery?