التهاب پروستات یا پروستاتیت شرایطی است که با التهاب غده پروستات، غده ای کوچک به اندازه گردو که درست زیر مثانه در مردان قرار دارد، مشخص می شود. این التهاب می تواند علائم مختلفی ایجاد کند و اغلب بر اساس علت و تظاهرات آن به انواع مختلفی طبقه بندی می شود.
علائم پروستاتیت بسته به نوع و شدت بیماری می تواند متفاوت باشد اما ممکن است شامل موارد زیر باشد:
درد و ناراحتی: درد در ناحیه لگن، اندام تناسلی، کمر یا راست روده در پروستاتیت شایع است. This pain may be dull, aching, or sharp and may worsen with bowel movements or ejaculation.
Urinary symptoms: Prostatitis can cause urinary symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency (sudden and intense urge to urinate), difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, or pain or burning sensation when urinating.
Sexual dysfunction: Some men with prostate problems may experience sexual problems such as erectile dysfunction, painful ejaculation, or decreased libido.
Flu-like symptoms: In acute bacterial prostatitis, symptoms may resemble those of a severe urinary tract infection and may include fever, chills, body aches, and fatigue.
causes of prostate inflammation
Prostatitis can have different causes and this disease is often classified into different types based on its origin:
Acute bacterial prostatitis: This type is caused by a bacterial infection of the prostate gland. Bacteria from the urinary tract or other parts of the body can enter the prostate and lead to inflammation and infection. Common bacteria responsible for acute bacterial prostatitis include Escherichia coli (E. coli) and other pathogens.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis: Unlike acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis is characterized by recurrent urinary tract infections involving the prostate gland. The infection may persist for a long time and lead to chronic inflammation.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: This type is the most common form of prostatitis and accounts for the majority of cases. The exact cause is often unclear, but may include inflammation, nerve dysfunction, pelvic muscle tension, or other factors. This is not usually associated with a bacterial infection, although inflammation may still be present.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis: Some men may have inflammation of the prostate gland without experiencing any significant symptoms. This type is usually diagnosed incidentally during the evaluation of other conditions.prostatitis treatment methods
The treatment of prostatitis depends on its type, severity and main cause.
Antibiotics: Antibiotic treatment is the main treatment for acute bacterial prostatitis and chronic bacterial prostatitis. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment may vary based on the specific bacteria identified and the individual's response to treatment. Completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a specialist is necessary to ensure complete eradication of the infection.Alpha blockers: Alpha blockers are drugs that help relax the prostate and bladder neck muscles, improve urine flow, and reduce symptoms such as urinary urgency and hesitancy. These drugs are often prescribed to men with chronic prostatitis to reduce urinary symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory drugs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation associated with prostatitis. These drugs can help relieve symptoms such as pelvic pain and discomfort.
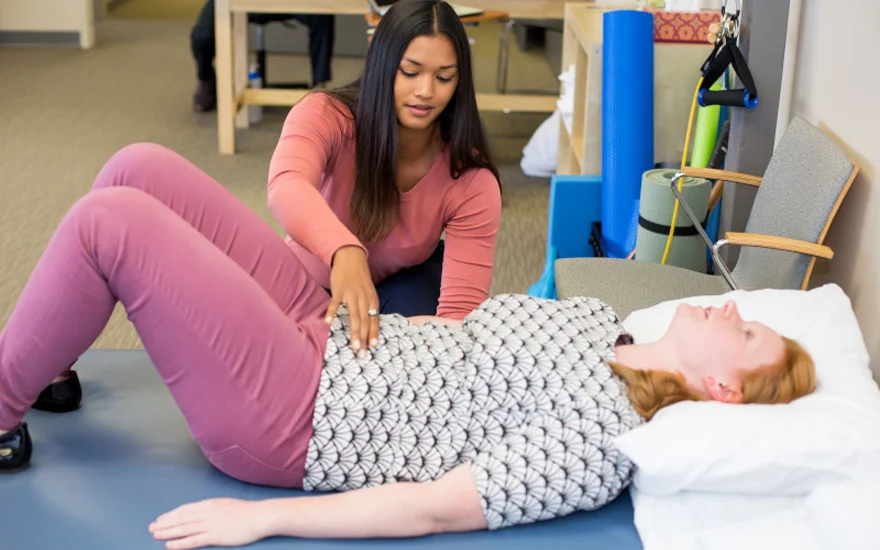
Physiotherapy: For men with prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain, techniques Pelvic floor physiotherapy such as pelvic floor muscle relaxation exercises, Biofeedback and trigger point release therapy may be helpful. The goal of pelvic floor physiotherapy is to reduce muscle tension and improve the function of the pelvic floor, thereby reducing pain and urinary symptoms.
Other treatment methods
Lifestyle modification: Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms and improve overall prostate health. These may include dietary modifications (such as avoiding spicy foods and caffeine), stress reduction techniques (such as relaxation exercises or meditation), and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms (such as prolonged sitting or cycling).Prostate massage: Prostate massage, performed internally or externally by a health care provider, may help relieve prostate symptoms by promoting drainage of prostate secretions and reducing inflammation. However, this method is not suitable for all people and should be done under the supervision of a doctor.
Psychotherapy: For men with prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain, psychotherapy or counseling may be helpful in addressing underlying psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or depression.
Surgical intervention: In rare cases when prostatitis does not respond to conservative treatments or is associated with complications such as abscess formation or urinary obstruction, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options may include transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or prostatectomy.