بی اختیاری ادرار در بیماران پارکینسون یک علامت غیر حرکتی شایع در بیماران مبتلا است که به طور قابل توجهی بر کیفیت زندگی تأثیر می گذارد و مدیریت آن می تواند چالش برانگیز باشد.بی اختیاری ادرار در بیماران پارکینسونی یک موضوع پیچیده است که تحت تأثیر عوامل عصبی و فیزیکی قرار می گیرد. ترکیبی از راهبردهای رفتاری، فیزیوتراپی کف لگن ، داروها، و احتمالاً مداخلات جراحی می توانند به مدیریت آن کمک کنند.
انواع مشکلات ادراری در بیماران پارکینسون
- بی اختیاری فوری: این شایع ترین نوع در بیماران PD است. It is characterized by a sudden and strong urge to urinate, which is accompanied by involuntary loss of urine.
- Nocturnal enuresis: Frequency of urination is common at night, which leads to sleep disturbance.
- Hesitancy and straining: Some patients may have difficulty starting to urinate or experience poor urinary flow.
- Incomplete emptying: feeling that the bladder is not completely empty after urination.
Causes of urinary incontinence in Parkinson's patients
Urinary incontinence in Parkinson's patients can be attributed to several factors related to this disease:
- Autonomic dysfunction: PD affects the autonomic nervous system that controls bladder function.
- Detrusor overactivity: The bladder muscle (detrusor) may contract involuntarily, leading to urge incontinence.
- Drug Side Effects: Some medications for PD can affect bladder control.
- Movement disorder: difficulty with mobility and dexterity can make it more difficult to get to the bathroom on time.
- Cognitive impairment: Cognitive decline in PD can contribute to difficulty recognizing the need to urinate or making timely decisions.
management strategies
Modification of behavior and lifestyle
Timely voiding: Encourage regular bathroom visits to avoid overfilling the bladder.
Fluid management: reduce fluid intake before bed and avoid bladder stimulants such as caffeine and alcohol.
Bladder training: gradually increase the interval between urination to improve bladder capacity and control.
Pelvic floor exercises: strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help control the flow of urine.
Pharmaceutical treatment
Anticholinergic drugs: These drugs can help reduce overactive bladder, but may have cognitive side effects, which is a concern in PD.
Beta 3 agonists (eg, mirabegron): These drugs can help relax the bladder muscle with fewer cognitive side effects compared to anticholinergics.
Botulinum toxin injection: In severe cases, Botox injection into the bladder muscle can reduce overactivity.
Surgical interventions and other interventions
Sacral neuromodulation: implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the nerves that control the bladder.
Catheterization: In cases of significant urinary retention, intermittent or permanent catheters may be necessary.
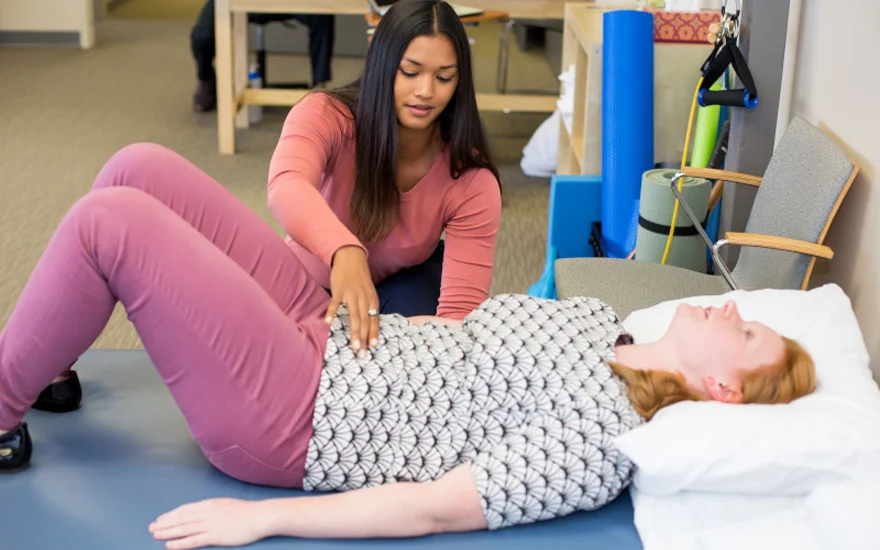
Pelvic floor physiotherapy
Benefits of pelvic floor physiotherapy for Parkinson's patients
- Pelvic Muscle Strengthening: PFP focuses on strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, which can improve bladder and urethral support and help prevent urine leakage.
- Improve muscle coordination: Through targeted exercises, patients can improve coordination of their pelvic floor muscles, which is critical for maintaining continence.
- Behavioral training: Physical therapists can provide training in bladder control techniques, such as strategies for timely urination and suppression of urges.
- Relieve constipation: Constipation, which is common in PD, can worsen urinary incontinence. PFP can help manage constipation and thereby reduce its negative impact on bladder function.
Pelvic floor physiotherapy components
- Pelvic floor exercises: Exercises such as Kegels involve repeated contraction and relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles. These exercises are designed according to the person's abilities and are adjusted gradually.
- Biofeedback: This technique uses electronic monitoring to help patients gain awareness and control of their pelvic floor muscles. Visual or auditory feedback guides the effectiveness of muscle contractions.
- Electrical stimulation: In some cases, mild electrical pulses are used to stimulate the pelvic floor muscles and increase their strength and function.
- Bladder training: Techniques are taught to increase voiding time and improve bladder capacity, helping patients regain control of their bladder function.
- Lifestyle and behavior modification: recommendations are provided regarding fluid intake, diet, and other lifestyle factors that can affect bladder function.