Gallbladder laparoscopy - gastroenterologist in Mashhad Dr. Mehdi Afzal Aghaei

What is gallbladder laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy gallbladder removal is a minimally invasive surgery that uses small incisions and specialized tools to remove the patient's gallbladder. Gallbladder is a small organ that is located just below the liver and on the upper right side of the abdomen.
The gallbladder stores bile, actually bile is a liquid that is produced in the liver. The gallbladder releases bile into the small intestine to help break down and absorb dietary fat.
Natural digestion is possible without a gall bladder. If the gallbladder becomes seriously diseased or inflamed, removing it is a treatment option. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal is the most common type of surgery. It is officially known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
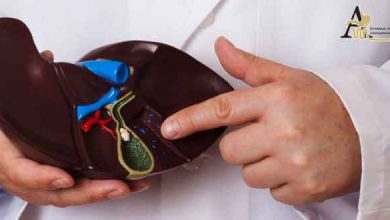
Gall bladder and its function
Gallbladder is not absolutely necessary for human survival. The gallbladder is a part of the human biliary system that plays a role in storing and transporting bile. Bile is a yellowish-brown liquid produced by the liver and used to break down and digest fatty foods in the small intestine. The gallbladder is located under the fourth lobe of the liver and is connected to it on the upper right side of the abdomen.A narrow tube called the cystic duct connects the gallbladder to the main duct of the liver. Bile, which is made in the liver and plays an important role in food digestion, enters the first part of the small intestine from the main bile duct or bile duct.
The gallbladder is a storage tank for bile. Bile is continuously made in the liver. After eating, the gallbladder contracts and empties the bile into the intestine. This contraction occurs as a result of hormonal stimulation by the hormone cystokinin. The main composition of bile is cholesterol, bilirubin and bile salts. There are conditions and conditions that can affect the gallbladder.
Gall bladder laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is the most common type of gallbladder removal surgery. This procedure is formally known as laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy) removes the gallbladder and gallstones through several small incisions (slits) in the abdomen. Gallbladder surgery is usually performed in two ways, open and laparoscopic. In the open procedure, the gallbladder and stones are removed by making a skin incision, usually under the ribs on the right side. In laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, several small holes of about 1 to 1.5 cm are made in the skin of the abdomen and the surgery is performed in this way. Gallbladder surgery is very common, especially in women. By performing this surgery, in addition to eliminating pain, the occurrence of the mentioned complications and gallbladder cancer are prevented. You need general anesthesia for this surgery, which usually lasts 2 hours or less.
Why is gallbladder laparoscopy performed?
The main reason for removing the gallbladder is the presence of gallstones and the resulting complications. Gallstones inside the gallbladder are formed from materials in the bile. They can be as small as a grain of sand or a golf ball. If you have the following symptoms, you may need this type of surgery:
- Biliary dyskinesia occurs when the gallbladder does not drain well due to a defect.
- When gallstones pass through the common bile duct, they potentially cause a blockage that prevents the gallbladder and the rest of the biliary tree from draining.
- Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas and related to gallstones. Gallbladder surgery with laparoscopy is recommended for the function of this organ due to the small size of the surgical site. Smaller incisions reduce the risk of infection, bleeding, and recovery time.
Risks of laparoscopic gallbladder surgery
Removal of the gallbladder by laparoscopy is considered safe. The rate of complications is between 0.5 and 6%. Any surgery carries risks of major complications, but this is usually rare for laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
The doctor performs a complete physical examination and reviews the medical history before the operation. This minimizes the risks.
Dangers of gall bladder erosion by laparoscopy are:
- Allergic or adverse reaction to anesthesia or other drugs
- Bleeding
- Blood clotting
- Damage to blood vessels
- Heart problems such as fast pulse
- infection
- Damage to bile ducts, liver or small intestine Pancreatitis
Preparation for laparoscopic gallbladder surgery
Before surgery, various tests are performed to ensure adequate health and readiness for surgery. These tests are:
- blood test
- Gallbladder imaging tests
- Full physical examination
- Medical history review
- Over-the-counter medications or dietary supplements: You may need to stop taking certain medications before surgery. Also, inform your doctor if you are pregnant or think you are pregnant.
The doctor will give you complete instructions on how to prepare for surgery, which may include the following:
- Ask someone to stay with you immediately after surgery.
- Do not eat or drink anything for 4 hours or more than 4 hours before the surgery.
- Planning to stay in the hospital in case of complications.
- Take a shower with a special antibacterial soap the day before or the day of the operation.
Study proposal: colon cancer screening test
How to remove the gallbladder with laparoscopy?
First, before the operation, you wear hospital clothes. Then you will be given an IV so that the doctor can give you medicines and fluids through your veins. You will be put under general anesthesia, which means you will be pain-free before and during the procedure.
A tube is placed down the throat that is connected to a ventilator to help with breathing. For this procedure, the surgeon makes four small incisions in the abdomen. They use these incisions to guide a tube with a small, bright camera inside the abdomen. Then, while watching a monitor that shows what the camera is capturing, they guide other tools through the cuts. The abdomen is inflated with gas so that the surgeon has room to work. They remove the gallbladder through incisions. After the surgeon removes the gallbladder, he uses special X-rays to check for problems with the bile duct. This technique is called intraoperative cholangiography.
This indicates any abnormalities in the remaining bile duct structures, such as gallstones, that the surgeon may need to remove. When the surgeon is satisfied with the results, he sutures and tapes the incisions.
After the operation, you will be taken to a room to recover from anesthesia. Vital signs are always closely monitored. Most people can go home later the same day.
What happens after the gallbladder is removed?
Symptoms related to diet after gallbladder removal surgery are mild and rare, but may include diarrhea. The doctor will tell you how much time you need to prepare for normal daily activities. It usually takes about a week to recover and resume normal activities.
The advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopy
The most important question for patients in the field of laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is the advantages and disadvantages of using this method. Of course, one should not expect that laparoscopy will be without complications and will not cause problems for the person, but compared to open surgery, it will bring much less complications.
For example, adhesion is one of the problems that arise in a person after open surgery, but in laparoscopy, because the abdomen is not open, it is not exposed to the ambient air and body tissues do not come into contact with each other. With the materials used during the operation, less adhesion is created. One of the advantages of laparoscopy is that the surgical scar (wound) is small. For example, if the surgery to close the fallopian tubes is performed with open surgery, a surgical incision of at least seven to eight centimeters must be made, but in this method, it can be done with two holes of half a centimeter to a maximum of one centimeter. Considering that in the laparoscopic method, the scar is smaller than open surgery, it is expected that complications and problems after the operation will be less.
This work is both cosmetically beneficial for the patient and helps him to return to daily life and return to normal activities much faster after surgery. The possibility of infection is also much less in this method. Also, in the open surgery method, the inside of the abdomen is not illuminated like in the laparoscopic method, and because the body parts are placed on top of each other, many tissues may not be seen well, but this causes problems. It does not exist in laparoscopy.
Of course, it should be said that blowing gas inside the abdomen, which is done laparoscopically, is dangerous for some people, so people with heart and respiratory diseases should not use this method. Since this method may be uncomfortable for some people, especially those with certain diseases, you should be careful about this. People with heart disease or obstructive lung disease should not use this method. Therefore, laparoscopy does not cause any problems for people who do not have any special problems and are in perfect health and at the right age. Laparoscopy surgery is not suitable for people over 60 years old. Of course, people who decide to use this method should consult with a doctor who specializes in this field. The doctor who performs laparoscopy must have completed special courses and have sufficient skills in this field, because this operation, contrary to being comfortable and useful for the patient, is relatively difficult for the surgeon.
*Gastroenterologist in Mashhad* Facebook Twitter Pinterest WhatsApp Telegram Viber Share via emailcontent team
-
Similar posts
Gallstones and its treatment methods
2019-07-21Write your opinion Cancel reply





















