Everything about MS MS - Dr. Hamidreza Torabi Neurologist
All about MS

All about MS
masoud77771401-12-11 16:57:03 +00:00MS diagnosis
There is no specific test for amas and it is based on the rejection of other diseases with similar signs and symptoms.
Blood test to help rule out other diseases with symptoms similar to asthma. Tests for specific biomarkers associated with asthma are being developed and may help diagnose the disease.
Spinal tap (lumbar puncture) in which a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid is removed from your spinal canal for laboratory examination. This sample can show abnormality of antibodies related to AMAS. Spinal palpation can also rule out infections and other diseases with similar symptoms. A new antibody test (for light chains without kappa) could be faster and more cost-effective than previous CSF tests.
MRI, which can determine the areas of amas lesions in the brain, cervical spinal cord and chest. You may have an intravenous injection of contrast material.
Evoked potential tests, which record the electrical signals produced by your nervous system in response to a stimulus, may also be done. Visual or electrical stimulation may be used. In these tests, you watch a visual stimulus pattern while short electrical impulses are applied to the nerves in your leg or hand. Electrodes measure the speed of information movement in your nerve path.In most people with recurrent-recovery amas, direct diagnosis is made based on the pattern of symptoms consistent with the disease and is confirmed by a brain imaging scan such as MRI.
Emas can be more difficult to diagnose in people with unusual symptoms or progressive disease. In these cases, further tests may be required.
Treatment of MS disease
Treatment is generally focused on accelerating recovery from attacks, reducing new radiographic and clinical recurrences, reducing disease progression, and managing symptoms. In some people, the symptoms are so mild that they do not need treatment.
Treatment of Amos attacks
Corticosteroids such as oral prednisone and intravenous methylprednisone are prescribed to reduce nerve inflammation.
Plasma change (plasmapheresis). If there is no response to steroids, this method is used.
Treatment to moderate progress
There are a variety of disease-modifying therapies (DMT) for relapsing-remitting ascites. Some of these DMTs can be useful in secondary progressive asthma, and there is one for primary progressive asthma.
Often immune responses related to asthma occur in the early stages of the disease. Serious treatment with these drugs as soon as possible reduces the rate of relapse, the formation of new lesions and the risk of brain atrophy and the accumulation of disability.
Many of these methods have important side effects. Choosing the right treatment is done by considering various factors such as the duration and severity of the disease, the effectiveness of the previous treatments, other health problems, cost and pregnancy status.
Treatment options for recurrent-healing amas include injectable, oral and infusion drugs.
Injectable treatments include
Interferon-beta medications: These medications used to be the most commonly prescribed medication for asthma. They act by interfering with the diseases that attack the body and reduce inflammation and increase nerve growth. They are injected under the skin or into the muscles and can reduce the frequency and severity of relapses.
Side effects of interferon include flu-like symptoms and injection site reactions. It is also necessary to take a blood test to check liver enzymes because liver damage is also a possible side effect. Antibody neutralization may also occur and reduce the effectiveness of the drug.Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone, Glatopa): This drug may block the immune system's attack on myelin and must be injected under the skin. Side effects include skin irritation in the injection area.
Monoclonal antibodies: Ofatumumab (Xympta, Arzera) targets cells that destroy the nervous system. These cells are called B cells. The method of use is subcutaneous injection and can reduce brain damage, swelling and worsening of symptoms. Side effects include infections, local reaction to injection and headache.
Oral treatments include
Triflunomide (Obagio): This oral medication is taken once a day and reduces the rate of relapse. Triflunomide can cause liver damage, hair loss and other side effects. This drug is associated with birth defects when used by parents. So use contraceptives while taking it and for two years after. This drug requires regular blood tests for monitoring.
Dimethyl fumarate (Tacfidra): This drug is taken twice a day and can reduce relapses. Its side effects are flushing, diarrhea, nausea and a decrease in the number of white blood cells. This drug also needs regular blood tests for monitoring.
Diroxymel fumarate (Vomeriti): This capsule is taken twice a day and is similar to dimethyl fumarate, but has fewer digestive side effects. This drug has been approved for the treatment of recurrent asthma.
Menomethyl fumarate (Bafiratam): Its tablet is taken twice a day and is similar to dimethyl fumarate. The speed of action of this drug is slow and there is hope that the side effects will be less. Possible side effects include hot flashes, liver damage, abdominal pain and infections.
Fingolimod (Jilnia): It is taken once a day and if you have not had chicken pox, you need to get vaccinated. Your heart rate and blood pressure should be closely monitored for 6 hours after the first dose. Other complications include rare infections, headache and blurred vision.
Siponimod (Myzent): This drug is approved for secondary progressive emesis and is associated with clot formation in organs. It is also contraindicated in pregnancy.
Ozanimod (Zeposia): Its pill is taken once a day. It starts with a low dose and starts accumulating in the first week. Complications include dizziness, headache, respiratory infections and cold symptoms, and it is contraindicated in case of liver and heart problems.
Ponzimod (Panuri): It is used once a day and its dose increases over time. With the use of this drug, the attack of lymphocytes on the nerves of the brain and spinal cord is reduced and, of course, it increases the possibility of infection.
Cladribine (Mavenclad): This drug is the second line of treatment for recurrent-healing amas and is also approved for secondary progressive amas and has two treatment courses, first for 5 days of the month and once a day and then once a day in the second month. This drug can increase the possibility of contracting infectious diseases by affecting the immune system. So it is necessary to be checked in this direction. Also, hair loss and rash are among its side effects.
Infusion therapies include
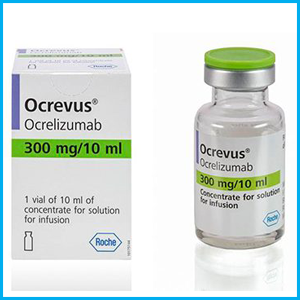
Natalizumab (Tysberry) and Acrelizumab (Acrovus) are used if other drugs are not effective.
Alemtuzumab (Compat, Lemtrada) is also a chemotherapy drug that limits the immune system.
Recent advances or emerging treatments
Burton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTK) is an emerging treatment being studied in relapsing-remitting and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. It works mostly by modulating the immune cells of the central nervous system.Stem cell transplant destroys the immune system of a person with asthma and then replaces it with transplanted healthy stem cells. Researchers are still investigating whether this method reduces inflammation and helps rebuild the immune system or not.
Treatment of signs and symptoms of asthma
Muscle relaxants: Baclofen, tizanidine and cyclobenzaprine are used to improve spasms. Onabotulinum toxin A is another treatment for people with spasms.
Fatigue: Amantadine, Modafinil and Methylphenidate (Ritalin) were used for this purpose. But recent studies have not shown any effect and even create the opposite events.
Other medications: Medications for depression (bupropion, fluoxetine, and sertraline), pain, impotence, insomnia, or urinary control problems (oxybutynin and tolterodine) may also be prescribed.
Physical therapy: Physical or occupational therapist can teach you stretching and strength exercises and show you how to use various tools such as walkers to do daily tasks.
Lifestyle
Having enough sleep and rest, eating healthy food with high fiber, doing stretching and yoga, managing stress and keeping the body cool can help improve symptoms.
Studies show that low amounts of vitamin D can increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids, so it is better to consult a doctor about this.
Living with any chronic illness can be difficult. To manage stress in this situation, keep the following suggestions in mind;
Maintain normal daily activities as much as possible, stay in touch with friends and family, engage in your favorite recreational activities that you are able to do, and talk to your doctor or counselor about your feelings. MS disease
Resources
https://www.webmd.com/multiple-sclerosis/ms-treatment