Advice on hair transplantation
Consultation
Introduction
Consultation is preferred for success in hair restoration surgery. Establishing a good interaction between the patient and the doctor begins with the patient's visit to the office. This initial consultation dimension may begin with online research on the practice's website, an initial phone call, or reading a brochure or similar.
During the consultation, if the patient is a suitable candidate, a decision for hair transplantation will be made. In addition, the consultation is an opportunity for the patient to know what to expect from the hair transplant operation and to review all the details of the operation, including any pre-operation or post-operation care. If done well, well-directed counseling alone can increase patient satisfaction with the procedure. Counseling may be done with a designated expert counselor.
Choosing a hair transplant candidate
Choosing a hair transplant candidate is the main determinant of success in surgery. If the patient is medically and psychologically fit and healthy, the process of selecting a candidate for hair transplant is done. Evaluating criteria such as age, degree of hair loss, adequate hair bank, hair quality, and hair color are helpful in choosing the right candidate. The ideal candidate must have an adequate hair bank to achieve coverage of desired hair transplant areas, control of advancing hair loss, and most importantly, reasonable expectations.
age
People aged 25 and above are preferred for hair transplant. Excessive and unspecified use of medication to slow down ongoing and progressive hair loss is not effective. From this point of view, the final rate and severity of hair loss at ages younger than 25 years is much less predictable than 25 years and older.
Compared to older candidates, these younger patients are more likely to desire their original hairline rather than an older hairline, which is not a reasonable expectation.
Real expectations in hair transplantation
Real expectations of the density that can be created determine how satisfied the patient is with the final result of the cosmetic procedure. Hair restoration surgery is no longer the old "hair grafts". A significant conversion of 10 to 25 larger hair follicle units to smaller units occurs, most commonly one to three hair follicle units. (Image 1.1). The goal is to improve the appearance of patients without it being clear that surgery has been done. The expected result of a hair transplant is a natural and undetectable improvement in hair density that should not at all look like a graft-filled appearance. Additionally, even with smaller follicular grafts, the hair transplant can look unnatural if the hairline is too smooth and uneven.
The final result of the hair transplant should follow the "irregular appearance and unevenness" of the natural hair growth line (image 1.2).
A very important point here is the primary concern of patients about their own appearance. They may tend to have an advanced hairline, thickening of the frontal skin, or thickening and densification of the vertex or parting of the head (Figure 1.3). The most important beauty improvement is achieved by filling and strengthening the hair, which is done by adjusting and framing the face and by strengthening the hair growth line in the front of the head and increasing the density that can be created in the skin of the front of the head.
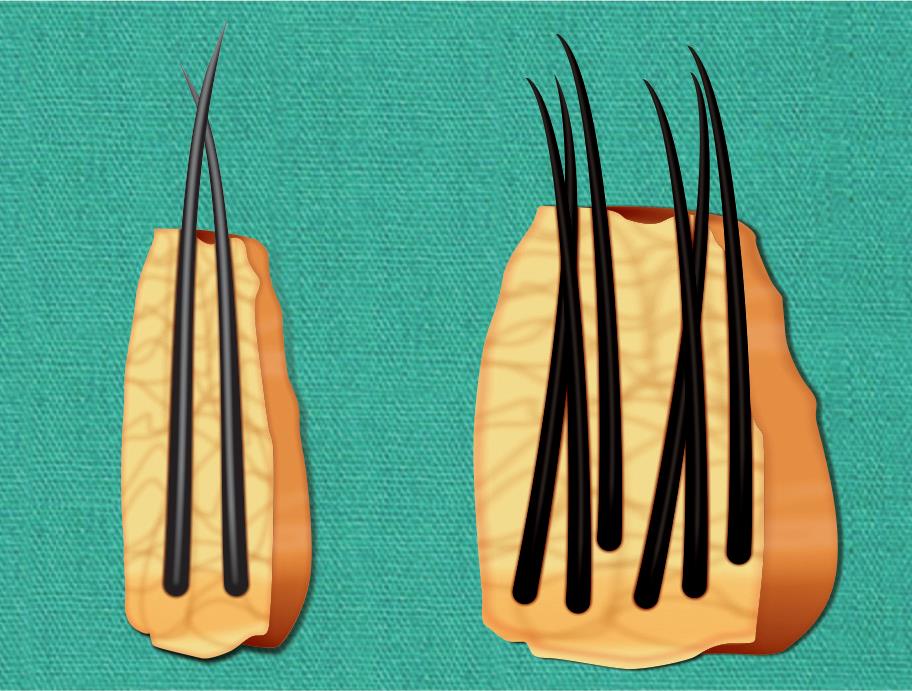
Image 1.1: In the modern hair transplant method, compared to larger grafts full of follicles in the old methods, a smaller follicular unit is divided and transformed into a triple follicular unit.
In addition, hair transplants should be designed to prevent progressive hair loss. In this way, you can ensure the result of the work and the natural appearance in the near and distant future. Therefore, if the patient has a limited hair bank and significant baldness, he should be advised that the most important aesthetic result is obtained by focusing on the areas that mainly affect the framing of the face. Explaining this concept is very important for men with androgenetic alopecia who tend to have a lower and thicker hairline or a thicker skin covering of the vertex or part of the head. If the grafts are placed too anterior or forward and the hairline recedes, what is left is a row of unnaturally grafted hairs in front of the receding hairline. When counseling men who wish to transplant hair from the vertex or part of the head, this point should be explained that even if a complete coverage of the vertex skin is created with the hair transplant, it may not be so noticeable and noticeable to the patient.
In addition, since the twist and angle of sleep of the hair follicles in the skin of the vertex grow in different directions, more grafts are needed to adequately cover this area. And if the progressive hair loss is not controlled, the patient may experience an abnormal ring of baldness around the transplanted grafts. Considering the long-term cosmetic results, the transplantation of follicular units in the anterior two-thirds of the scalp is the safest area.
The important point here is the perceptible density that can be created and is considered as a function that includes not only the density of the transplanted grafts but also the hair waviness and hair quality.
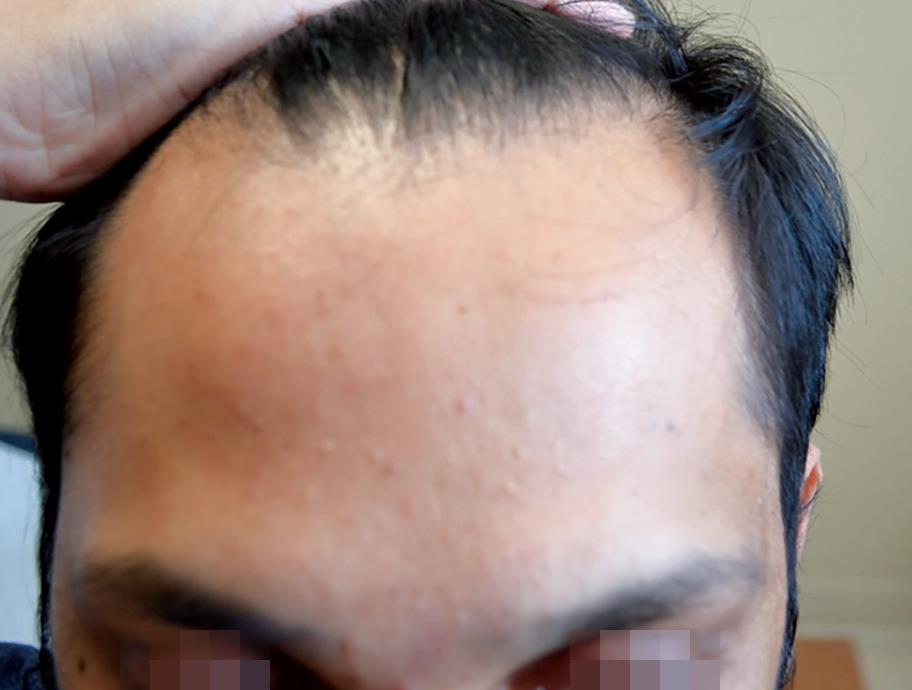
Picture 2.1: The patient has a normal hair growth line.
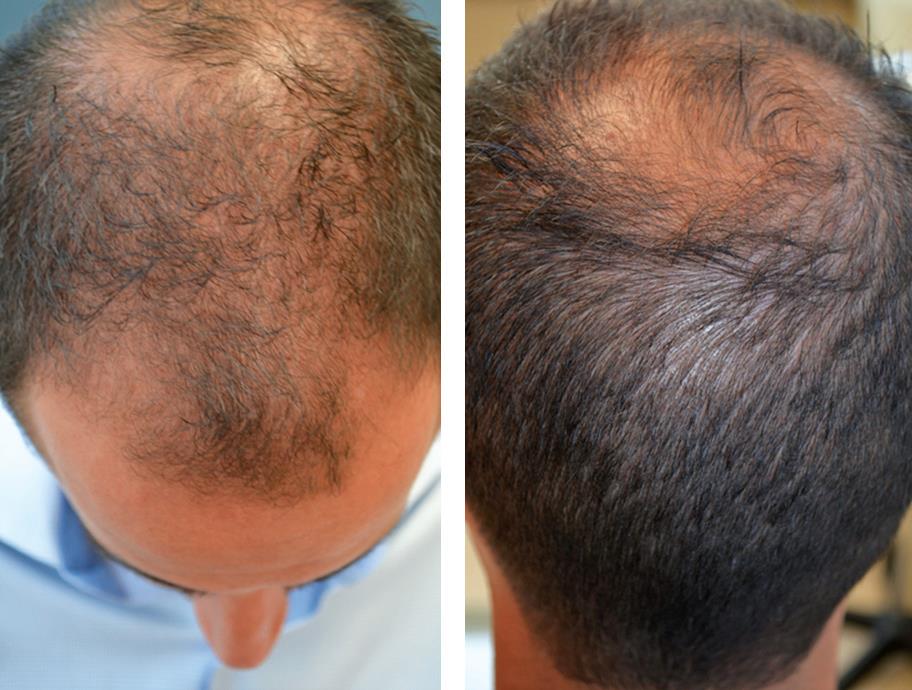
Figure 3.1: Public consultation. A 28-year-old man has a receding hairline on the forehead and receding hairline on the front and vertex.
A patient with thin and sparse hair should not expect the same improvement in beauty as a person with thick and curly hair. Even with the same number of transplanted grafts and growth, thick and curly hair can be 50% to 100% denser than thin, straight hair. In addition, the net density is equal to the number of transplanted hairs, minus the hair loss in the hair transplant recipient area. It is more difficult to produce a noticeable and significant net increase in patients with rapid and progressive hair loss than in patients with a slower rate of hair loss or those whose hair loss is medically controlled.
More surgeries may be necessary to achieve the desired result, which may be due to advancing hair loss or any technical limitations in the initial surgery that prevent complete and desired coverage.
Depending on the size of the transplant recipient area, the amount of hair loss in progress and the provision of the individual's hair bank, it is possible to achieve the desired aesthetic goal in two surgeries.
Accurate medical records
Hair transplantation is an option for treating alopecia, however, it may not be the optimal treatment for the patient. As with any hair loss assessment, we first need to get a proper diagnosis. Hair restoration surgery in all types of alopecia, except for androgenetic alopecia, requires special considerations and the results may be different in general; Therefore, it is important to be able to reliably distinguish androgenetic alopecia from alopecia-like scars. This requires taking a detailed patient history (Table 1.1), performing a thorough scalp examination, and possibly further investigations, such as taking a biopsy. People with androgenetic alopecia should report hair loss if the loss is gradual, progressive, asymptomatic, and unrelated to a specific disease or stressor or aggressive hair styling. Any previous hair transplant surgery should also be discussed with the doctor (Table 2.1).
The patient's health status and surgical history should also be specified. A comprehensive medical record must be prepared from the patient in a documented form.
| Table 1.1: History of previous hair transplantation |
| Suggested questions to obtain a detailed medical history from the patient during the consultation |
| How much hair loss is there now? |
| Is hair loss sudden or gradual? |
| Is the hair loss regional and limited or scattered? |
| Is hair loss associated with increased shedding and emptying of the head? |
| Is there itching, burning, sensitivity to touch or discharge? |
| How does hair loss bother you? |
| What are your expectations from hair transplant? |
| What medications are you currently taking? Do you use anticoagulants? do you |
| What medicines do you use to treat hair loss? |
| Have you ever had surgery, including hair transplant surgery? |
| Do you currently smoke? If yes, how many packages per day? |
| Do you have keloids or hypertrophic scars and is the disease progressing? has done |
| Whether in the past or in the present of aggressive and damaging hairstyles or hairstyles do you use |
For any condition that may affect surgery, it may be advisable to discuss it with a specialist or primary care physician. Although hair transplantation is low-risk and associated with minimal complications, it is recommended that any patient over the age of 55 obtain medical clearance from their primary care physician. Their current list should also be checked carefully. The use of anticoagulants can have relative side effects in surgery.
Nevertheless, hair transplants are still performed for patients with coagulation disorders, which can be technically more difficult. Lack of hemostasis or interruption of proper blood flow in the body may make hair graft implantation more difficult and is associated with increased secretion, decreased vision, and shedding of the transplanted graft. The patient can consult with his primary care physician about stopping the medication before surgery; However, elective surgery may not be recommended with the potential risk of cardiovascular events. Even if the patient is taking anticoagulants for prevention, his primary care physician must approve discontinuation of the medications.
Scalp examination (Table 3.1)
A thorough scalp examination should help diagnose the type of alopecia, as well as determine if the patient is a good candidate.
| Table 2.1: Questions for Extraction of patient records |
| Get previous history of hair transplant |
| Which hair removal method was performed from the hair bank area: skin strip removal or FUE? |
| Identify the patient's hair transplant area. How many grafts are placed in this area? |
| Are the grafts left healthy enough? |
| Have there been any complications? (i.e. Oscar broadcast) |
| Were there any aspects of the previous surgery that the patient was unhappy with? |
(FUE: Follicular Unit Extraction).
| Table 3.1: scalp examination |
| Determining the scale of hair loss: in the Hamilton-Norwood (Norwood-Hamilton) or Ludwig (Ludwig) category |
| Note the presence of any inflammation |
| Note any evidence of hair loss associated with scarring |
| Examination of the former scar in the hair bank area |
| Evaluation of hair bank area density |
| Evaluation of hair quality |
| Attention to hair color |
| Assessment of scalp laxity |
In addition, it is possible to determine the area of hair follicle harvesting at that time. It is also possible to approximately determine the number of grafts needed to repair the desired area.
Harvest area assessment
Clinically, androgenetic alopecia is a type of asymptomatic hair loss with a pattern of short, scanty and thin hair in the affected areas. The thickness of the hair decreases, the ends of the hair pigments become thin and short and pale. In alopecia with male pattern hair loss, there is more progressive hair loss on the forehead (front of the head) and gradual thinning of the front of the head and the skin of the vertex (part of the head). If this disease is not treated, smoothness and baldness of the scalp will progress in the affected areas and spread all over the head. The most common classification system used to assess male pattern hair loss is the Hamilton-Norwood scale (Figure 4.1). In contrast, in female-pattern alopecia, the hairline (on the front of the scalp) is preserved with progressive thinning and miniaturization (shortening) of the follicle throughout the scalp (Figures 5.1 A and B). This hair loss condition has been likened to a "Christmas tree" pattern with a wide center section and the "thin and thin" nature of the hair. Female pattern hair loss may rarely progress to progressive baldness. Alopecia with a female pattern can be classified using the Ludwig scale.
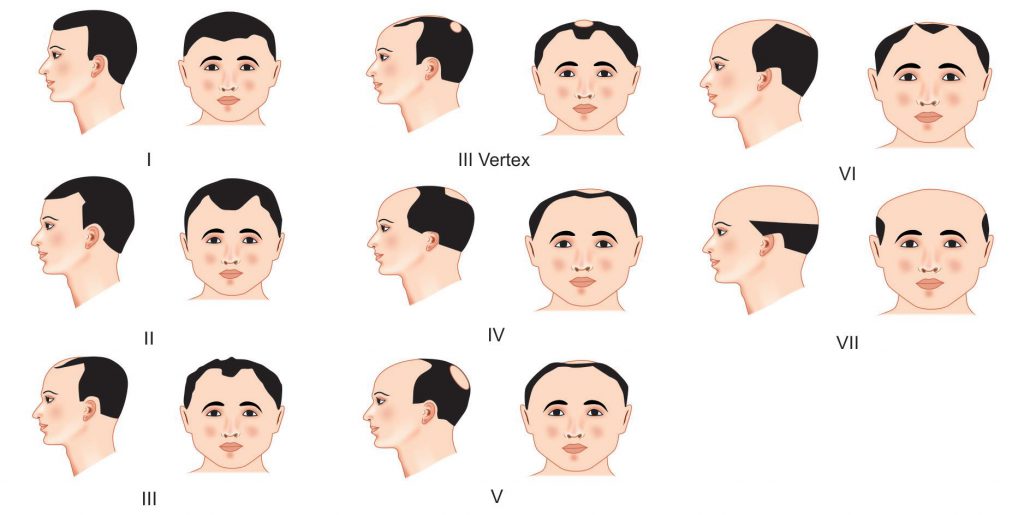
Figure 4.1: Hamilton-Norwood classification scale for male pattern hair loss.
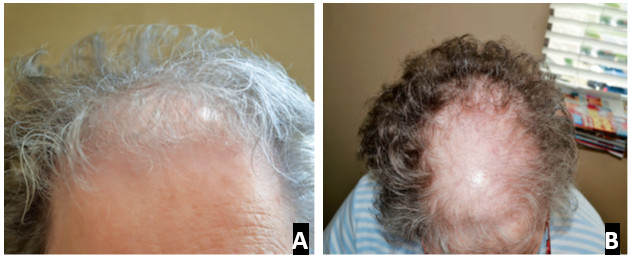
Figure 5.1 A and B: A woman with female pattern hair loss and Ludwig scale type III, showing preservation of the frontal hairline (A) along with shortening of the follicles and increased central emptying of the frontal scalp (B).
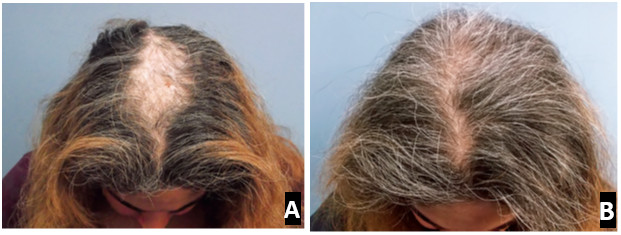
Figure 5.1 A and B: A 29-year-old woman came for hair transplant consultation. (A) In the initial visit, he appears to have hair loss with a female pattern and Ludwig scale type III. A biopsy also confirmed female pattern hair loss (FPHL). (B) However, within 5 months of taking minoxidil, her hair returned to its previous state. Therefore, he had shown telogen effluvium similar to female pattern hair loss.
In the case of women, there should be enough space to create incisions and the grafts should be placed without transversely cutting the existing hair follicles. Additionally, further investigation such as laboratory and histological examination may confirm any unusual presentation.
It should be noted that alopecia with a pattern is different from telogen effluvium or inflammatory alopecia such as lichen planopillaris (lichen planus) or cicatricial alopecia (central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia) and it should be carefully diagnosed (images 6.1 A and B).
Assessment of hair bank area
The area of the hair bank is the area designated and designed for the purpose of harvesting transplanted grafts. In order to successfully perform a hair transplant, it is essential to have enough hair from the hair bank. There are many factors that determine whether the area of the hair bank is suitable for graft extraction. The surgeon must be able to provide enough grafts to provide the desired coverage in the transplant recipient area. In addition, it should be noted that extracting the graft in an area where continuous and progressive shedding may eventually occur is avoided, as the survival and integrity of these grafts can be limited. Additionally, if the skin strip is removed and progressive hair loss occurs in the hair bank area, a linear scar (hair removal scar) may become visible.
Mo Bank Area "Safe Zone"
The hair bank area theory shows that grafts harvested from areas that are not affected by hair loss should maintain the same genetic density when implanted in the involved recipient area and therefore continue to grow indefinitely. Therefore, grafts should be extracted from an area of the hair bank that is as safe as possible from future hair loss.
Most people with androgenetic alopecia have a horseshoe-like area along the back of their scalp that is less likely to eventually be affected by shedding and is considered the "safe zone" and is the area where most grafts are extracted for hair transplantation (Figure 7.1).
"Safe zone" is defined as a horseshoe-shaped band with a width of 5 to 6 cm, which is stretched across the back of the head and extends to the skin of the temporal area. To create the upper border of this area, it can be more accurately estimated by drawing a horizontal line between the upper dimensions of the cochlear part of the earlobe. The indentations of the back of the head or the back of the neck define the lower border. Extending this strip below this line appears to increase the risk of extensive scarring. The lateral borders of the safe zone should not extend beyond the temporal part above the cochlear part of the earlobe. Because the low ridge progression and hair thinning may eventually lead to a linear scar, it is recommended to remove about 2 cm from the upper and lower borders.
A healthy area without progressive hair loss in women with sporadic androgenetic alopecia should be carefully and correctly identified. In "patterned" alopecia in women, the width of the central section in the front of the scalp should be wider compared to the back of the scalp. In diffuse alopecia, the back of the head may appear thin and sparse, and the scalp may be visible. This condition is a relative obstacle to graft harvesting in the usual "safe zone" in these individuals, because in diffuse alopecia the grafts already begin to shrink and may not remain healthy indefinitely. It is possible to estimate the amount and degree of hair loss in people with androgenetic alopecia. For example, a 60-year-old man with slow progression to Norwood type III alopecia is unlikely to progress to severe Norwood type VI.
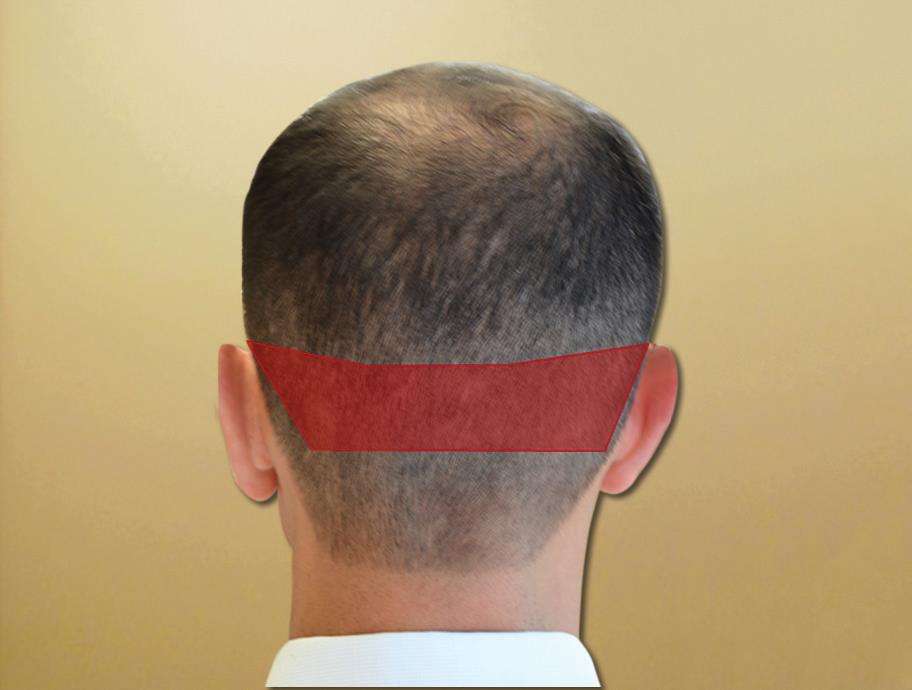

Figure 7.1: Hair bank area
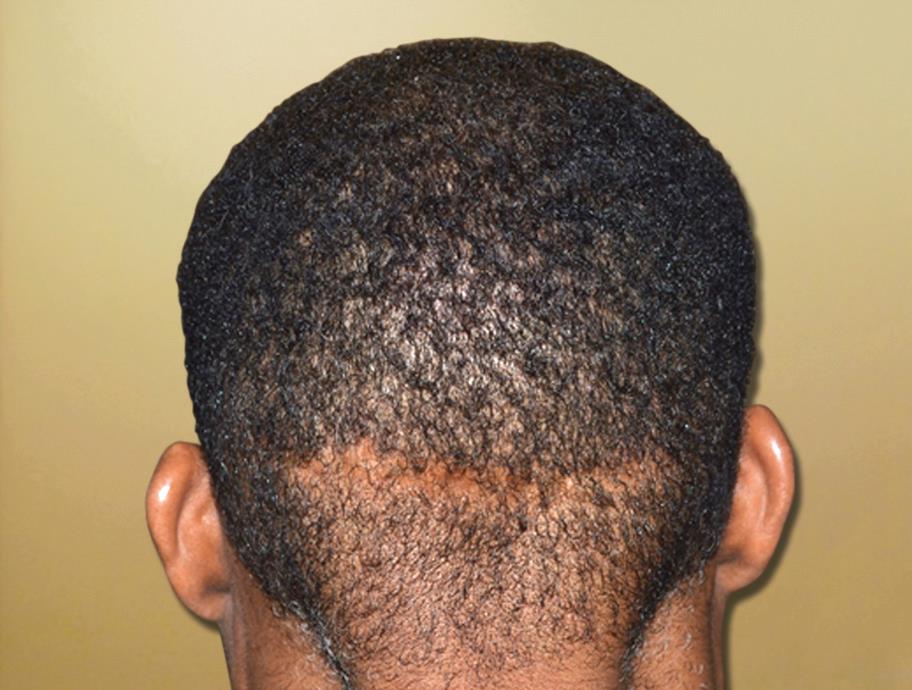
Figure 8.1: A clear and extensive scar on the back of the head of an African-American man with a very short haircut
Similarly, it can be assumed that a 22-year-old male with Norwood type III alopecia is at high risk of progression to Norwood type VI alopecia. These people are not good candidates for skin strip removal because a linear scar (scar from the removal of hair follicles) will be visible in them. In addition, it may be limited that the transplanted grafts remain healthy.Review previous hair bank area
Many patients have experienced previous hair transplant surgery. If tape removal has already been done, the previous scars should be checked. Any complications include wound dehiscence, infection, extensive scarring, or keloid formation (Figure 8.1). It should be considered and investigated.
Furthermore, the hair bank area should be assessed for adequate supply for implantation and around the previous wound for skin laxity. The next surgery may be done in the area where there is a previous scar. Follicles implanted around fibrosis and scarring are unlikely to remain healthy. If follicular unit extraction (FUE) has already been performed, the hair bank area should be examined for the possible presence of atrophic scars with hypopigmented macular scarring. It is also possible that there was too much harvesting with the FUE method, and a scar-like appearance was created in the area of the hair bank.
density of hair bank area
Hair density is defined by the number of follicular units per square centimeter versus hair per square centimeter. There are several methods and tools for estimating hair bank area density. An easy method is to count the number of follicular units in a 0.25 cm2 area and multiply by four, which confirms that the density is not uniform throughout the area of the hair bank. The ideal hair transplant candidate has a hair bank area density of at least 70 to 90 follicular units per square centimeter. A density of less than 40 follicular units per square centimeter is considered a weak hair bank supply.
hair quality
The quality and thickness of the hair is also an important feature to evaluate. The quality of the hair affects the perception of the density of the final result of beauty. Any hair follicle larger than 70 microns is considered a thick hair. Thick and curly hair provides more coverage than straight and thin hair. A person with thin, straight hair may need twice as many grafts for the same density (Figure 9.1 A and B). In contrast, people with thick, curly hair with limited hair bank areas seem to be lucky because they do not need a large number of hair grafts to provide adequate coverage in their transplant recipient area. This concept can be useful for example in cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) patients. To create increased density in individuals with thin and frizzy hair, a larger number of 3-4 larger follicular unit grafts can be transplanted into the recipient area. In addition, women with curly hair should not use chemical straighteners after hair transplant, because it significantly reduces the desired density.
Scalp flexibility or laxity
Flexibility of the scalp is also one of the determining factors for providing the hair bank area in the tape removal method. The main risk factor for extensive hypertrophic scars is wound stretching.
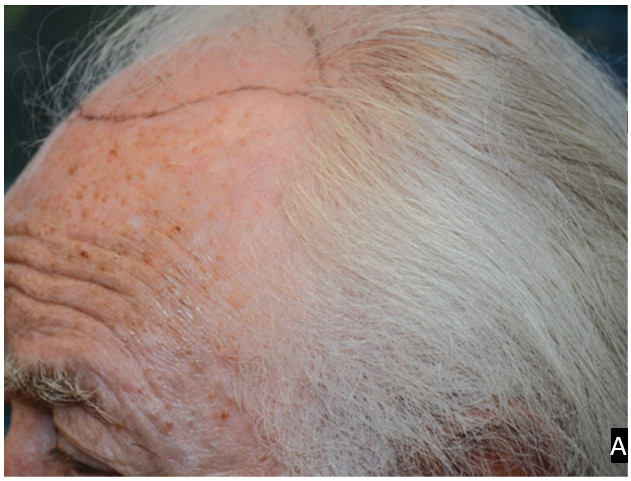
Figure 9.1 A and B: (A) shows gray, thin, smooth hair on fair skin. (B) shows black, curly, thick hair on darker skin.
If there is more laxity and stretching of the scalp, a wider and safer strip and more grafts may be extracted.
Keeping the maximum width of the skin strip less than 1 cm reduces the risk of spreading the wound or scar. However, if the scalp is tight or a strip of skin wider than 1 cm is desirable, then a scalp laxity assessment is warranted.
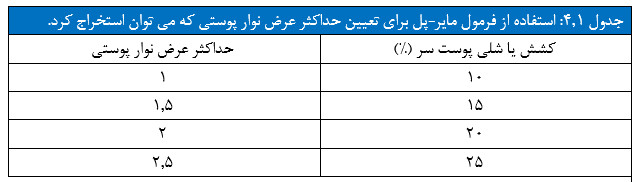
The Mayer-Paul formula is a useful measure of scalp elasticity and is used to determine the width of the hair bank area. The surgeon places his thumb and index finger 5 cm apart and squeezes the scalp together. The percentage change of the original distance to the compressed distance is measured (D) (Table 4.1).
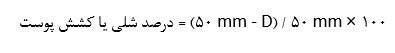
Hair color
The hair color of the hair bank or donor area may affect the cut of the grafts and the final result of the cosmetic procedure. Considering the cut, it is difficult to identify the entire subcutaneous route of gray hair, especially if it is curly, and this leads to an increase in the implementation steps of the preparation of grafts and implantation. This problem may be solved by coloring the follicles with the help of Violet de Jansin (purple gentian).
Even with adequate density predicted in the transplant recipient area, on individuals with very dark hair and very light scalp, the result may be too little or too little density. Dark hair can highlight a light scalp, making the effect of the transplant more visible. In addition, any complications in the transplant recipient area such as indentation, smooth hairline or tissue changes can be significant. Therefore, patients with very fair skin tones are advised to dye their hair lighter. On the other hand, people with darker skin should keep their hair color darker. Ideally, the closer the hair color is to the color of the scalp, the less the problem of identifying the transplanted hair in the recipient area.
Important concepts for the hair bank area
- An ideal hair transplant candidate has a donor hair bank to cover the transplant recipient area.
- The wound of the previous hair bank, if any, should be checked.
- The density of the hair bank area and the quality or thickness of the hair determine the final density expected in the implantation.
- If the skin strip is cut and removed, the scalp tension should be evaluated.
Details required for patient review: Preoperative instructions and items should be reviewed with the patient (Table 5.1). If the patient chooses the follicular unit extraction method, they should be consulted about hair cutting and harvesting before the operation. Typically, a large strip of 5-6 cm should be cut from the hair bank area to harvest the hair. However, depending on the original length, it may take several weeks for the hair to grow back.
Table 5.1: Preoperative items Check the patient's satisfaction Take photos before the operation Aspirin should be stopped if used Stop using minoxidil one week before surgery Hair should be cut if needed Table 7.1: Post-operative cases The dressing should be removed the day after the operation Wash the recipient area gently with shampoo Oral prednisone at a dose of 40 mg, up to 3 days as needed to reduce skin edema Vicodin up to 7 days Antibiotics after surgery as needed If the skin tape is removed, the stitches or threads will be removed within 7 days Hair grafts may fall out 2 to 3 weeks after surgery Use of minoxidil or stimulation with low power laser light for possible improvement Growth and reduction of the risk of telogen effluvium after surgery to the required extent Start taking medications to control persistent and progressive hair loss For the full effect of the cosmetic surgery, you have to wait 9 to 18 months after the surgery For this reason, patients may accept to have their entire head shaved or only shave a small part of the back of their head and cover the hair bank area with the surrounding hair. Alternatively, they may want to keep their hair a few inches longer to cover the shaved area.
Details of surgery should also be discussed with the patient. The patient should know that hair transplantation is an outpatient operation under local anesthesia and is performed by surgeons and a team of technicians. This discussion should include the type of method used to harvest from the hair bank area, how to prepare the grafts and place them in the incisions, and the approximate duration of the transplant procedure. All possible risks and complications should also be explained (Table 6.1).
The survival and health of the grafts depends on the technical aspects of the surgery as well as the post-operative care. Transplanted grafts should be protected from trauma or impact, and adherent scabs should not be manipulated or removed. Therefore, thorough reviews of postoperative care and expectations are important (Table 7.1).
In short, preoperative counseling and evaluation are the determining factors in hair transplant success. The final result should be natural and depending on the supply of the individual's hair bank area, the quality and thickness of the hair and the control of progressive hair loss are determined (Table 8.1).
Table 6.1: Possible risks and complications Caused by hair transplant Folliculitis who is opening of the wound infection Neuropathic pain caused by skin tape removal Ischemic necrosis in the hair transplant recipient area - in the condition of high density of hair and in smokers The possibility of danger increases Abnormal appearance Poor probability of hair graft staying healthy Table 8.1: Key concepts Hair transplant should be natural Grafts remain alive and healthy according to the hair bank area theory There are two harvesting methods: skin strip harvesting vs. FUE method Removing the skin strip creates a visible, linear scar In the FUE method, a large area Shaved carries the risk of spreading, faded, and freckled scars Supply of hair bank area is limited Expected density is functional, including density of implanted grafts and quality Hair thickness Net result of cosmetic surgery, number of implanted grafts minus progressive hair loss (FUE: Follicular Unit Extraction).
Finally, if the patient decides to have the procedure, a package with instructions Complete before and after surgery, prescriptions for post-operative medications and a complete consent form to be sent to him will be Patients are encouraged to call if they have any concerns before the procedure.