One of the most important and sweetest events in every couple's life is the experience of becoming parents. Today, unlike in the past, there are many different tests that can inform couples from the very beginning of pregnancy about the existence of genetic diseases that may arise for their child before birth. To know more about the information of your fetus, join sonography of Dr. Seif.
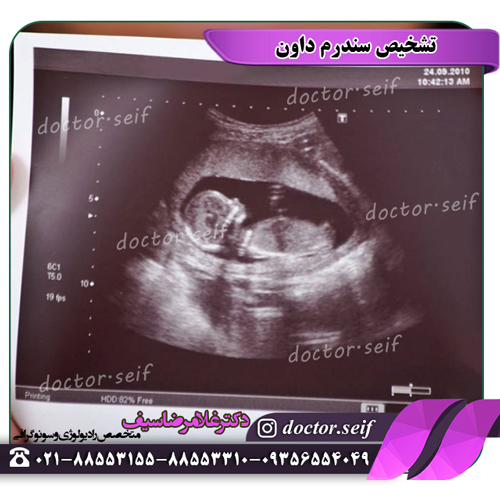
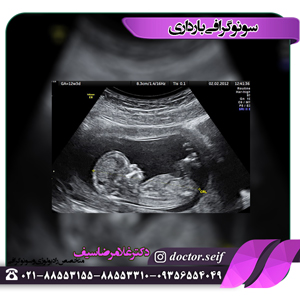
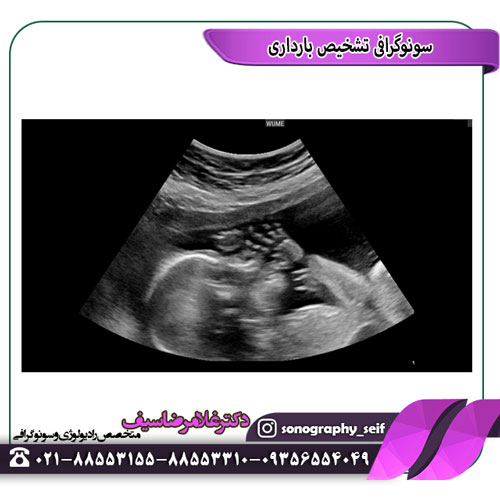
screening in the first three months of pregnancy refers to the examination of any genetic disease in the fetus, when it is between the 11th and 13th week. In fact, this screening is the first screening that investigates chromosomal disorders that lead to mental retardation in the fetus. The screening consists of an ultrasound and a blood test, which is performed in everyone, which is known as NT ultrasound.
List of contents
 NT ultrasound (Nuchal Translucency)
NT ultrasound (Nuchal Translucency)
In this ultrasound, according to a series of special standards, the fetus is photographed and the thickness of the back of the neck is measured. In addition, they look at the nasal bone of the fetus. If the thickness is three centimeters or more or if it is not seen at all, a series of diseases including Down syndrome or trisomy 21 are raised. Not seeing the fetal nasal bone and the thickness of the back of the fetal neck is not a definite sign of this disease and needs to be investigated.
Blood test
There are two types of blood tests; A normal blood test is performed in which the possibility of three common genetic diseases is investigated, which are:
• Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome
• Trisomy 18 or Edward's syndrome
• Trisomy 13 or Patho syndrome
which measures the probability of the above-mentioned diseases in the fetus, if the probability is high, additional necessary investigations are also performed according to the frameworks, such as amniocentesis.
There is another type of screening that is recommended by experts in some women due to the presence of more abnormalities. The name of this screening is Cell Free DNA.
Cell Free DNA Screening
According to the blood taken from the mother, the fetal cells flowing in the mother's blood are separated and the chromosomes are counted. In addition to the three diseases of chromosomal 21, chromosomal 18 and chromosomal 13, they examine the sex chromosomes X and Y. The error probability of this type of screening, which is also expensive, is very low and has a high probability of accuracy, but it is not recommended for all women. This is a suitable screening for people who have a history of chromosomal problems, or their previous fetuses had problems, or they or their spouses have chromosomal problems. But for those who have too much stress and worry, this screening is possible and there is no problem.
The results of the first trimester screening test are divided into three categories:
• dangerous (positive screen/positive screening/high risk)
• Moderate risk
• low risk (negative screen / negative screening / low risk)
Dangerous (positive screen/positive screening/high risk): If the person's risk number is 1.50 or higher (the denominator becomes smaller), he is placed in the dangerous category and a diagnostic test such as sampling of paired villi should be done as soon as possible; CVS or amniocentesis is performed to definitively diagnose the problem.
Average risk: If the result of the screening is between 1.50 and 1.200, the person is placed in this category, you can wait up to 15-16 weeks (second trimester screening) until the blood test of the four markers is done. The screening results of the first and second trimesters will be the criteria for the specialist doctor's action.
Low risk (negative screen/negative screening/low risk): If the final result shows a risk of less than 1.200, there is no need for second trimester screening.
Regardless of the result of the first trimester screening test which is positive or negative, a test called alpha-fetoprotein AFP (An alpha-fetoprotein) is performed to screen for defects in the neural tube of the fetus. There is an ultrasound called anomalous ultrasound, which is recommended between 16 and 18 weeks of pregnancy to screen for any structural abnormalities.
Should you be fasting for screening?
There is no need to fast for the first trimester screening test and it is possible to perform this test at any time of the day or night.
Conclusion
Screening in the first three months of pregnancy does not check all genetic diseases. And only three common genetic diseases, which include trisomy 21 or Down syndrome, trisomy 18 or Edward's syndrome, trisomy 13 or Patou's syndrome, are checked in the screening of the first three months of pregnancy. If the experts find any genetic disorder in the fetus during the first three months screening, there is no other way but abortion, of course, the abortion must be done until the legal abortion of the fetus. To perform the screening of the first three months of pregnancy, you can go to Best See ultrasound in Yusuf Abad.