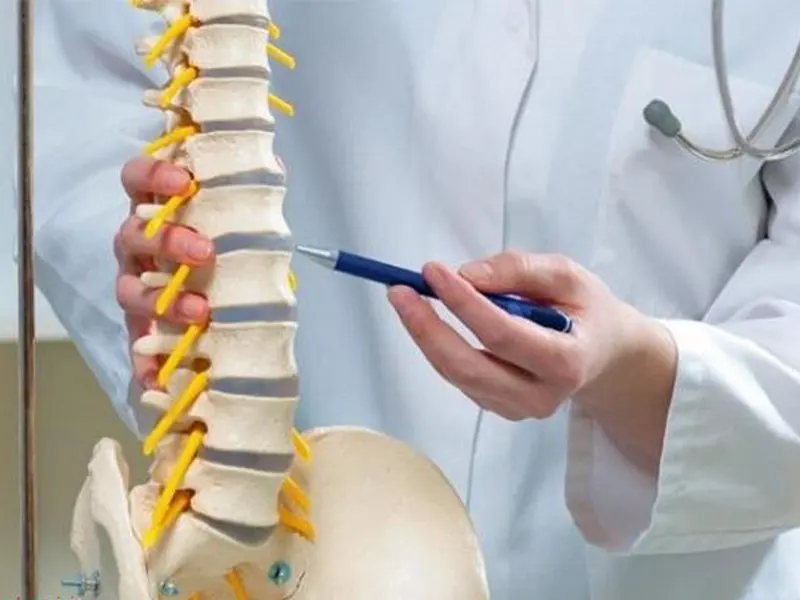
شکستگی مهره کمر یکی از آسیبهای جدی ستون فقرات است که میتواند بدون هشدار قبلی، زندگی روزمره فرد را کاملاً تحت تأثیر قرار دهد. Sudden pain, limitation of movement and even the possibility of spinal cord injury are only part of the consequences of this fracture. But do all fractures require surgery? What signs should be taken seriously? In this article, we will examine the causes, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment of lumbar vertebra fracture so that you can make the best decision for treatment with more knowledge.
Are fractures of the lumbar vertebrae always dangerous?
No, a lumbar fracture is not always dangerous, but neglecting it can lead to serious and even irreversible complications. Some fractures, such as mild stress fractures from osteoporosis, may heal without surgery and with rest, braces, and medication alone. But if the fracture causes instability of the spine or pressure on the spinal cord, it can lead to severe pain, impaired movement or even paralysis.
Types of Lumbar Fractures
In the following, you will learn about the types of lumbar vertebrae fractures. Each of these fractures have differences depending on the severity of the injury, the location of the fracture and the general condition of the patient:
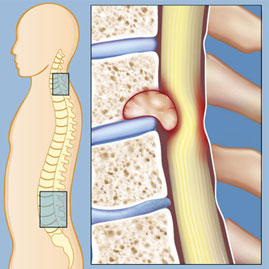
Compression fracture
This type of fracture occurs when the front part of the vertebra is under a lot of pressure and collapses. It is seen in elderly people or those with osteoporosis. The appearance of the vertebra in this case is crushed or reduced in height in the front part, and is often accompanied by sudden pain, height reduction, and spinal deformity.
crack or wedge fracture
In this case, the front part of the vertebra is more damaged than the back, and the shape of the vertebra changes to wedge or triangular. This type of fracture occurs gradually and may be seen more in people who carry heavy loads or have structural weakness in the bones. Changing the shape of the vertebra can lead to a hump in the back in the long run.
Explosive Fracture
In this type of injury, the vertebra is completely crushed and the broken pieces may move around or into the spinal canal. It is caused by a strong impact such as an accident or falling from a height. Due to the scattering of bone fragments in this fracture, the risk of damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves is high and may be associated with symptoms such as numbness or movement disorders.
Moved fracture
In this type of fracture, the vertebrae are not only fractured, but also out of their normal position. Dislocation of the vertebra with a fracture occurs as a result of a strong impact such as a high-speed accident or a fall from a height. This fracture is one of the most dangerous types of vertebral injuries and is associated with serious damage to the spinal cord and nerves.
Stress Fracture
These fractures are caused gradually and as a result of repeated pressures on the spine. People who do heavy physical activities or professional sports are more prone to this type of injury. A stress fracture may start with mild pain at first and gradually increase in severity, without the person noticing a serious injury.
What are the symptoms and signs of lumbar vertebra fracture?
Symptoms of a lumbar fracture may vary depending on the severity of the injury, the exact location of the fracture, the age of the patient, and the general health status. In some cases, the symptoms are obvious and immediate, but sometimes they may remain mild or hidden for a long time. In the following, we discuss the most important and common symptoms:

Sudden and severe pain in the lower back
The most common symptom of lumbar vertebra fracture is severe and sudden pain in the injured area. This pain may be present at rest or worsen when moving, standing, sitting or bending. The pain is felt centrally at the fracture site and increases with pressure or touching the area.
Decreasing height or humpback
In compression fractures, especially in the elderly or patients with osteoporosis, the gradual decrease in height and the formation of a hump in the back (senile hump) can be one of the initial symptoms. This state is caused by the depression of the front vertebrae and the change in the shape of the spine.
Limited movement and stiffness in the back
People with a lumbar fracture may not be able to bend, turn, or even walk easily. Limited range of motion in the spine and dryness of the muscles around the affected area are common symptoms caused by pain and inflammation.
Numbness, tingling or weakness in the legs
In more severe cases where the fracture causes pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots, the patient may experience numbness, tingling (tingling) or muscle weakness in the legs. These symptoms indicate the involvement of the nervous system and the urgent need for medical examination.
Incontinence of urine or stool
If the fracture has seriously damaged the spinal cord, bladder or bowel control may be impaired. This condition is a warning sign of spinal cord injury and requires immediate evaluation by a doctor.
Pain radiating to the buttocks or legs
In some patients, especially in fractures that put pressure on nerves, pain may radiate from the lower back to the hips, thighs, or legs. This type of pain may be confused with sciatica pain, but its origin is a fracture of the vertebra.
Chronic or persistent pain if not treated on time
If not treated properly, a fractured vertebra can lead to long-term pain, impaired standing, and chronic spine problems. Sometimes these pains get worse over time and severely reduce the quality of a person's life.
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially after a fall, accident or lifting heavy objects, it is necessary to see a doctor. تشخیص به موقع میتواند از عوارض جدی جلوگیری کند.
چه عواملی در بروز شکستگی ستون فقرات نقش دارند؟
عوامل متعددی در بروز شکستگی ستون فقرات (مهرههای کمر یا گردن و پشتی) نقش دارند که برخی از آنها به وضعیت جسمی و سبک زندگی فرد مربوط میشوند و برخی دیگر ناشی از حوادث یا بیماریهای زمینهای هستند. In the following, we examine the most important of these factors:
osteoporosis (osteoporosis)
The most important cause of spinal compression fractures, especially in the elderly, is osteoporosis. In this disease, the bone density decreases and the bones become fragile and prone to breaking even with minor pressures or falls.
Severe blows (direct trauma)
Car accidents, falling from a height, hitting the back during sports or occupational accidents can cause vertebrae fractures. Impact intensity and impact angle play a big role in the type and amount of damage.
Lifting heavy objects incorrectly
Lifting heavy objects without using proper technique can put a lot of pressure on the lumbar vertebrae. In cases where the back muscles are weak, this pressure may lead to cracks or fractures.
Metabolic or inflammatory bone diseases
Some diseases such as bone cancer, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis or Paget's disease can destroy the bone structure and make it vulnerable to fracture.
Old age
With increasing age, the strength of bones decreases. People over 50 years old, especially women after menopause, are more at risk of spine fracture.
severe obesity or overweight
Excessive weight, especially in the abdominal area, puts constant pressure on the spine, which may cause wear and tear of the vertebrae over time, especially if it is accompanied by weak back muscles.
Sedentary lifestyle and muscle weakness
Lack of regular physical activity, weak back and core muscles, and incorrect sitting postures can gradually weaken the structure of the spine and increase the likelihood of fractures.
Long-term use of corticosteroids
Corticosteroids, if used for a long time, reduce bone density and increase the risk of vertebral compression fractures.
Congenital defects or structural deviations of the spine
Some people are born with congenital problems such as scoliosis or severe kyphosis, which can make the vertebrae more vulnerable to pressure and impact.
Methods for identification of lumbar vertebra fracture
Diagnostic procedures for lumbar vertebra fractures include a series of clinical examinations and detailed imaging that help the doctor identify the type, severity, and exact location of the injury. In the following, we review the most important diagnostic methods of this type of damage:
Neurological examinations
To more accurately assess the type and severity of the injury, the doctor first performs neurological tests. These examinations help to diagnose disorders of the brain and spinal nerves. At this stage, the power of moving the limbs, the ability to walk, and the patient's nervous reactions are thoroughly examined to determine whether the spinal cord or nerve fibers are damaged or not.
Diagnostic Imaging
According to the conditions of the accident and the patient's symptoms, the doctor uses different imaging methods to identify the exact extent and location of the fractured vertebrae. These images play an important role in choosing the treatment method. In the following, we mention the most important imaging methods:
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
In this method, strong magnetic fields are used to produce accurate images of the spinal cord, nerves and soft tissues around the vertebrae. MRI is especially effective for examining nerve damage caused by fractures and provides high-quality images of the damaged areas.
CT Scan
A CT scan creates layer-by-layer images of the spine using X-rays. These images are very useful for checking the condition of vertebrae, spinal canal space and surrounding structures. In certain cases, the doctor may use a myelogram along with a CT scan. In this method, a contrast agent is injected into the space around the spinal cord to provide a better view of the condition of the spinal cord and the location of the fractured vertebrae.X-ray imaging
X-ray is one of the most common primary methods to examine the structure of the spine bones. With this method, it is possible to observe the presence of fractures, displacement of the vertebra, or changes in the shape of the bones. Although X-ray is not as accurate as MRI or CT Scan, it is very useful for initial evaluation.
bone densitometry
In patients who are suspected of osteoporosis, it is recommended to perform a bone density test. This test measures bone density and determines whether or not a decrease in bone strength is the main cause of vertebral fractures. Early detection of osteoporosis helps prevent future fractures.

Treatment methods for lumbar vertebra fracture
Methods for treating lumbar vertebra fractures vary depending on the severity of the injury, the type of fracture, the patient's age, general health status, and the degree of spinal cord involvement. In some cases, the treatment is done conservatively, and in other cases, surgical intervention is needed. In the following, we review the most important treatment methods for this injury:
Rest and activity restriction
In cases where the fracture is mild and stable (such as compression fractures without damage to the spinal cord), rest, reducing physical activities and avoiding lifting heavy objects is the first treatment. This rest gives the body a chance to start the healing process naturally.
Using brace or medical belt
To stabilize the spine and prevent the movement of the damaged vertebrae, the doctor may recommend the use of a special waist brace or a medical belt. By reducing the pressure on the vertebrae, these devices help to heal the fracture and prevent the condition from worsening.
Drug therapy
Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to reduce pain and control inflammation around the injury site. In patients with osteoporosis, bone-strengthening drugs may also be prescribed to prevent future fractures.
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation
After reducing the acute pain and stabilizing the condition of the vertebrae, physiotherapy sessions are started with the aim of strengthening the back muscles, improving flexibility and returning to normal function. Rehabilitation plays a very important role in preventing dry joints and restoring movement power.
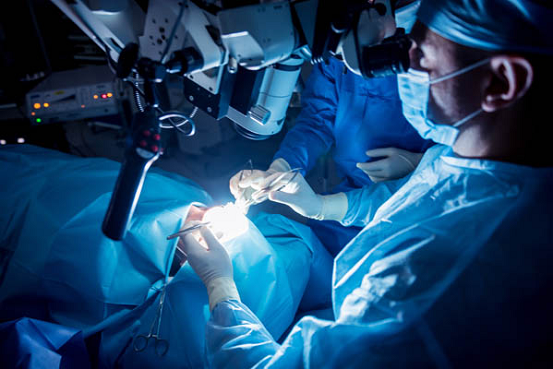
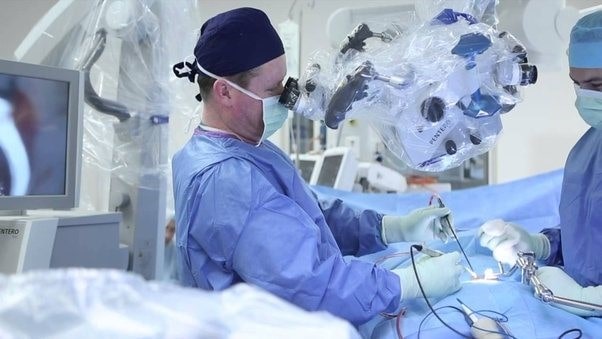
Vertebroplasty surgery
kyphoplasty surgery
Kyphoplasty surgery is a minimally invasive and effective way to treat lumbar vertebrae fractures, especially compression fractures that often occur in patients with osteoporosis. This technique is very similar to vertebroplasty, but the main difference is the use of a small balloon that is first inserted into the broken vertebra and then inflated to open the interior space of the vertebra and partially restore its normal shape. After creating this space, bone cement is injected into the vertebra. In addition to stabilizing the broken vertebra and reducing pain, the goal of kyphoplasty is to restore the height of the vertebra and correct the deformity of the spine. This method reduces the pressure on the spinal cord and nerves and preserves the shape of the spine as much as possible. Kyphoplasty surgery is performed under local anesthesia or light anesthesia, and due to being less invasive, it has a shorter recovery period than open surgeries. Surgery is necessary in severe, unstable fractures or in cases where the broken pieces have put pressure on the spinal cord. In this method, the vertebrae are stabilized, the pressure is removed from the spinal cord and the normal structure of the spine is restored. Surgery may involve the use of screws, rods, or metal cages. The act of reducing pressure is to relieve the pressure on the spinal nerves or nerve roots. This operation involves removing part of the bone or surrounding tissues that causes spinal canal stenosis or pressure on the nerve. have been Although this surgery is mostly used for problems such as disc protrusion or spinal canal stenosis, in some special cases, fractured vertebrae may also cause pressure on the nerves. In such situations, decompression surgery is performed as part of the treatment process, along with vertebral stabilization methods such as vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty, or fusion. The most common pressure reduction methods include removing part of the lamina (laminectomy) or removing the damaged disc (discectomy), which helps reduce pressure and improve neurological symptoms. The cost of treating a lumbar fracture varies greatly depending on the type and severity of the injury. Simple fractures treated with non-surgical methods such as rest, medication and physical therapy are less expensive. But in more complicated cases that require surgery, minimally invasive procedures such as vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty, and hospitalization in well-equipped hospitals, the costs increase significantly. In addition to the type of treatment, the duration of hospitalization, post-operative care and the use of advanced equipment are also influential in determining the cost. Also, patient insurance coverage plays an important role in reducing treatment costs, and costs are lower in government centers than in private hospitals. For this reason, in order to get a more accurate estimate of the cost, it is better to first consult with the attending physician and medical centers to determine the best treatment plan and the related cost based on individual conditions and the type of fracture. According to the age of the patient and his level of health, the doctor comes to the conclusion that how long the patient needs to rest at home, but the patient can resume his physical activities within 2 to 6 months. Spine fusion surgery is also associated with complications and disadvantages because this method removes the normal function and movement of two vertebrae, and thus the level of movement of the patient's body will be limited. Also, a lot of pressure will be applied to the vertebra that is near the fusion site, which will increase the risk of fracture in that vertebra. Even after completing the recovery period, the patient should refrain from doing certain movements and lifting heavy objects in order to prevent excessive pressure on the spine. The complications and risks of surgery include nerve damage, infection, bleeding, and stiffness of the soft tissues of the body.Spine surgery
Decompression surgery
Fusion surgery (spinal fusion)
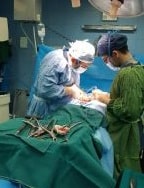
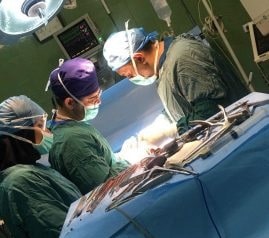
A few examples of vertebra fracture surgery by Dr. Moradi
Surgery of a patient with a severe fracture of the lumbar vertebrae in one session and through the back and without opening the abdomen and inserting an artificial vertebra
The cost of treating a lumbar fracture
fracture with dislocation of the lumbar vertebra
Duration of rest after surgery of lumbar fracture
Frequently Asked Questions About Lumbar Fracture
What are the side effects and risks of surgery? Is surgery a safe procedure?