Prostate surgery is one of the important treatment methods in the field of urology, which is performed to solve problems caused by benign prostate enlargement, prostate cancer or other disorders of this gland.
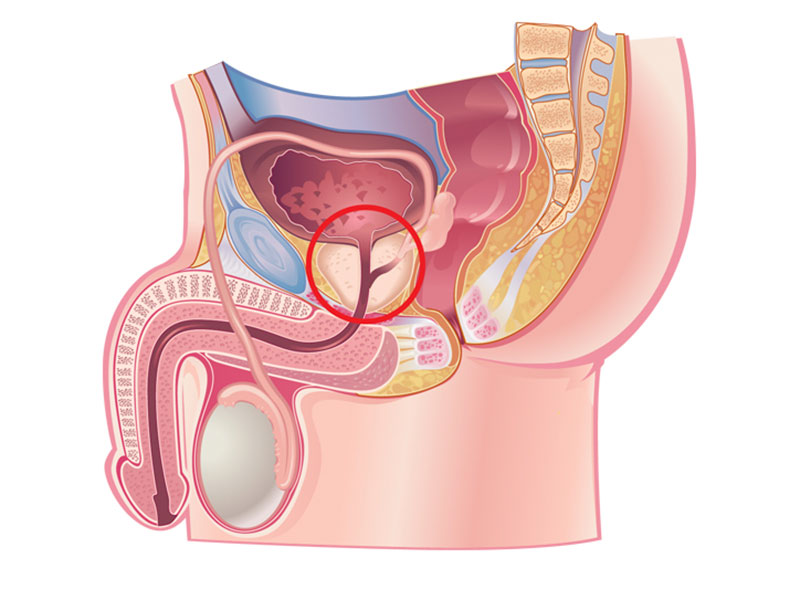
The prostate is a small but vital gland in the male reproductive system, which may change in size or function with age or the occurrence of certain diseases and cause symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, or pain.
When drug treatments or minimally invasive methods are not effective, surgery can be the best option to improve symptoms, prevent complications and increase the patient's quality of life. Depending on the cause and severity of the disease, this surgery is performed in different ways, such as complete or partial removal of the prostate (prostatectomy), transcutaneous prostate resection (TURP) or laser surgery.
What is the prostate and why it may require surgery?
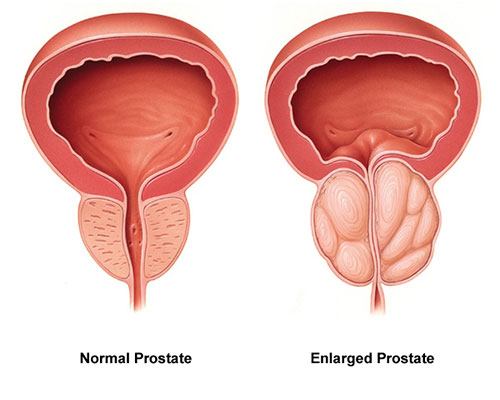
The prostate is a small walnut-sized gland located under the bladder and in front of the rectum and is considered part of the male reproductive system. Its main function is to produce part of the seminal fluid that helps to move and nourish the sperms. With age or due to some diseases, the prostate may experience enlargement or abnormal changes. These changes can cause pressure on the urethra and cause symptoms such as difficulty starting to urinate, weak flow, frequent urination or complete retention of urine.
The need for prostate surgery is usually raised when drug treatments and non-surgical methods are not effective, prostate enlargement causes serious urinary problems or damage to the kidneys, prostate cancer is diagnosed, or frequent infections and severe bleeding occur due to the prostate. In this situation, surgery can restore the normal flow of urine by removing or shrinking the prostate and improve the functioning of the urinary system.

Prostate surgery is performed when the problem of this gland cannot be solved with medicine or minimally invasive methods, or the patient's condition requires immediate intervention. The most important reasons for surgery are:
- : If cancer is diagnosed, complete removal of the prostate and surrounding tissues is done by surgery to prevent the spread of cancer cells. This method can increase the chances of definitive treatment and disease control.
- Severe or frequent urinary retention: When the patient is unable to empty the bladder completely, pressure and discomfort develop and the risk of kidney damage increases. By removing the blockage, surgery restores the normal flow of urine.
- Kidney damage or risk of damage: Prolonged urinary obstruction can put a lot of pressure on the bladder and kidneys, causing them to decrease in function. Prostate surgery prevents permanent kidney damage by reducing pressure and opening the duct.
- Heavy bleeding from the prostate: An enlarged prostate or tumor may cause heavy bleeding or clots in the urine. In cases where drugs are not effective, surgery is necessary to control bleeding and improve urinary function.
- Recurrent urinary tract infections: Chronic obstruction or retention of urine in the bladder can lead to recurrent infections. By removing the blockage, surgery improves the flow of urine and reduces the risk of infection.

Types of prostate surgery
Prostate surgery method is different depending on the type of disease, prostate size, general condition of the patient and available equipment. The most common methods are:
1. Radical prostatectomy (Radical Prostatectomy)
Cut Transcutaneous transurethral prostate (TURP) is the most commonly used surgery for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and is performed without the need for a skin incision. In TURP, the surgeon inserts a special device through the urethra and trims away the extra parts of the prostate that are causing the blockage. This procedure opens the urethra and quickly improves symptoms. TURP usually requires a few days of hospitalization and the recovery period is shorter than open surgery.
3. Laser evaporation of the prostate (Laser Prostate Surgery)
In this procedure, laser energy is used to vaporize or cut excess prostate tissue and is often used to treat BPH or control bleeding from prostate vessels. Due to the high precision of the laser, this procedure has very little bleeding and is suitable for patients who take blood thinners or have heart problems. Also, patients are usually discharged from the hospital earlier and symptoms improve quickly.
4. Simple prostatectomy (Simple Prostatectomy)
are suitable options for elderly patients or people who cannot tolerate heavy surgery. These procedures are often performed under local anesthesia, have a short recovery period, and have a lower risk of serious complications. However, there may be a need to repeat the treatment in subsequent years.

Benefits of prostate surgery
Prostate surgery can effectively remove symptoms caused by prostate enlargement or disease and improve the patient's quality of life. This procedure usually resolves urinary problems such as frequency, dribbling of urine, pressure during urination, and retention of urine. In patients with prostate cancer, surgery enables the complete removal of cancerous tissue and reduces the risk of the disease spreading to other parts of the body. Also, this intervention can prevent possible damage to the kidney and bladder, restore the flow of urine to a normal state, and reduce frequent urinary tract infections.
Possible
Despite the many benefits, prostate surgery may be associated with some complications. The most common of them is urinary incontinence, which is usually temporary but can be long-term in some patients. Also, due to the proximity of nerves related to sexual function, there is a possibility of erectile dysfunction or decreased sexual desire. Infection of the surgical site, bleeding, blood clots, and in some cases narrowing of the duct are other possible complications. Careful selection of the surgical method, skill of the surgeon and compliance with post-operative care can minimize these complications.
- Enough rest in the early days and avoid heavy activities
- Drink plenty of water and fluids to wash the canal and prevent clots or infection
- Caring for the urinary catheter and maintaining its hygiene until removal
- Light and high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and pressure on the surgical site
- Avoid long driving, sexual activity and prolonged sitting for several weeks
- Light walking daily to improve blood circulation and prevent blood clots
- Regular visits to the doctor to follow up the healing process and check the bladder function
- Immediately report warning signs such as fever, heavy bleeding, unusual pain or inability to urinate
- Urinary incontinence: the most common complication after surgery; It is usually temporary, but in some patients it remains long-term.
- Erectile dysfunction and decreased sexual desire: due to the proximity of the nerves that control sexual function.
- Surgery site infection: including incision site or urinary tract.
- Bleeding and blood clots: May require medical attention or additional treatment.
- Urethral stricture: causing problems in the normal flow of urine.
- Serious warnings that require immediate medical attention:
Fever and chills Heavy bleeding Abnormal pain Complete inability to urinate
These tips will help the patient to follow the post-operative care with full knowledge, and in case of problems, the necessary treatment measures will be carried out quickly.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. When is prostate surgery necessary?
When medical or minimally invasive treatments are not effective for prostate enlargement, cancer, or urinary complications, the doctor recommends surgery.
2. What are the types of prostate surgery?
They include radical prostatectomy, transcutaneous prostate resection (TURP), laser surgery, simple prostatectomy, and minimally invasive procedures such as TUMT or Rezūm Therapy.
3. How long is the recovery period after surgery?
Depending on the type of surgery, recovery usually takes between 2 and 6 weeks, minimally invasive methods have a shorter period.
4. What care is required after prostate surgery?
Adequate rest, fluid intake, catheter hygiene, light diet and avoiding heavy activities are recommended.
5. What are the common complications after prostate surgery?
Urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, bleeding, surgical site infection, and urethral stricture are the most common complications.
6. Does prostate surgery improve the quality of life?
Yes, most patients do not experience urinary symptoms and problems caused by prostate enlargement or disease after surgery, and their quality of life improves.