therapeutic use of chewing gum in children with special needs
Introduction
Gum, at first glance, is a simple and everyday food; But in the therapeutic environment, it can become an effective tool for the rehabilitation of children with special needs. از تقویت عضلات گفتاری تا تنظیم حسی و کاهش رفتارهای خودتحریکی، آدامس اگر با برنامهریزی و نظارت استفاده شود، ظرفیتهای درمانی قابل توجهی دارد.
فواید درمانی آدامس برای کودکان با نیازهای ویژه
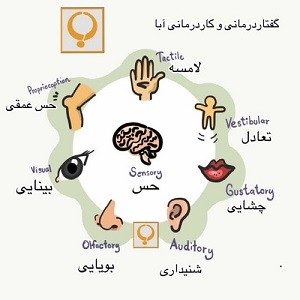
۱-تنظیم حسی
• جویدن آدامس باعث تحریک حس دهانی میشود و به کودکان کمک میکنه تا اضطراب، بیقراری یا تحریکپذیری خودشان رو بهتر مدیریت کنند.
• در کودکان با اختلال پردازش حسی، آدامس میتونه به تنظیم ورودیهای حسی کمک کرده و آرامش بیشتری ایجاد کند.
۲-تقویت گفتار و عضلات دهان
• عضلات فک، زبان و لبها در حین جویدن فعال میشوند و این فعالیت میتواند به بهبود تلفظ، وضوح گفتار و حتی بلع کمک کند.
• آدامس همچنین آگاهی دهانی کودک رو افزایش میدهد، یعنی کودک بهتر متوجه موقعیت زبان و لبها در تولید صداها خواهد شد.
۳-بهبود تمرکز و رفتار
• جویدن آدامس میتونه به افزایش تمرکز در کودکان با ADHD یا اختلالات یادگیری کمک کند.
• این فعالیت میتواندجایگزین رفتارهای خودتحریکی مثل مکیدن انگشت یا گاز گرفتن اشیاء باشد.
۴-سلامت دهان و دندان
• آدامسهای بدون قند، بهویژه با زایلیتول، در کاهش باکتریهای مضر دهان و افزایش ترشح بزاق مؤثرند.
• این ویژگیها به کاهش خطر پوسیدگی دندان و بهبود بهداشت دهان کمک میکنند.
کاربردهای آدامس در جلسات گفتاردرمانی و کاردرمانی
- استفاده قبل از تمرینهای گفتاری برای گرمکردن عضلات دهان
- تمرین تلفظ صداهای خاص مثل /س/، /ش/، /ز/، /چ/ پس از چند دقیقه جویدن
- تمرینهای هماهنگی تنفس و گفتار با آدامس در دهان
- بازیهای درمانی مثل “آدامسبان” برای آموزش کنترل، تمرکز و آگاهی دهانی
- استفاده در موقعیتهای پرتنش مثل ورود به کلاس یا درمانگاه برای کاهش اضطراب
انتخاب نوع آدامس: نرم یا سفت؟
راهنمای انتخاب نوع آدامس برای استفاده درمانی
آدامس نرم
- مناسب برای: کودکان کمسن یا دارای ضعف عضلات دهان
- کاربرد درمانی: تمرینهای سبک، آشنایی اولیه با جویدن
- مزایا: جویدن راحتتر، تحریک حسی ملایم، کاهش احتمال خستگی فک
آدامس سفت
- مناسب برای: کودکان بزرگتر یا با قدرت عضلانی بیشتر
- کاربرد درمانی: تقویت عضلات دهان، تمرینهای پیشرفته گفتاری
- مزایا: تحریک حسی قویتر، افزایش تمرکز، تقویت بهتر عضلات گفتاری
نکته: همیشه از آدامسهای بدون قند و ترجیحاً با زایلیتول استفاده شود.
زایلیتول (Xylitol) یک نوع شیرینکننده طبیعیست که معمولاً از منابع گیاهی مثل ذرت یا درخت توس گرفته میشود.این ماده در دستهی الکلهای قندی قرار میگیرد، اما برخلاف قند معمولی، تأثیرات منفی کمتری روی بدن دارد.
ویژگیهای زایلیتول
- طعم شیرین مشابه قند دارد اما با کالری کمتر.
- شاخص گلیسمی پایین دارد، یعنی قند خون رو بهسرعت بالا نمیبرد.
- برای دندانها مفید هست، چون باکتریهای مضر دهان نمیتوانند از آن تغذیه کنند.
🦷 فواید زایلیتول برای سلامت دهان
- کاهش خطر پوسیدگی دندان: با جلوگیری از رشد باکتریهایی مثل Streptococcus mutans که عامل اصلی پوسیدگی میباشد.
- افزایش ترشح بزاق: که به پاکسازی دهان و خنثی کردن اسیدها کمک میکند.
- مناسب برای کودکان: بهویژه در آدامسهای درمانی یا مراقبتی، چون هم شیرین هست و هم به سلامت دهان کمک میکند.)
⚠️ نکات احتیاطی
- زایلیتول برای انسانها بیخطره، اما برای سگها سمی هست؛ So it should not be accessible to pets.
- High consumption of this substance may cause bloating or heartache in some people, because it is not absorbed in the intestine and is fermented.
Gum consumption timing and reasons for restrictions
⏱️ suggested time
- Duration: 5 to 10 minutes per session
- Number of times: 1 to 3 times a day, depending on the treatment needs and the child's ability
Why should chewing gum be limited?
- Prevention of jaw muscle fatigue
- Prevention of behavioral dependence or excessive consumption
- Reducing the possibility of swallowing air and digestive problems
- Maintaining the therapeutic purpose and preventing gum from becoming an everyday food
- Prevention of loss of appetite in children
Teaching safe gum chewing and swallowing prevention
Practical solutions
- Video and story training about "not eating gum"
- Practice with play dough or modeling before real gum
- Full control the first time, with a short time (2 to 3 minutes)
- Concentration games like "Gumbuster" to strengthen control
- Choose a smaller soft gum to start with
- Review and encourage the child after each successful practice
1. Visual and verbal training
- Talk to the child that the gum is not edible, but should only be chewed.
- Use a picture or story: say, for example, "Gum is like a little exercise ball for the mouth, we just have to exercise with it, not eat it!"
2. Practice with artificial gum or modeling
- Before giving real gum, you can use play dough or a jelly model so that the child just practices chewing.
- This exercise makes the child understand the concept of "not eating" better.
3. Short time and full supervision
- In the first times, just give gum for a minute and be with the child yourself.
- Frequently ask the child: "Where is the gum? Is it still in the mouth?" to behave more consciously.
4. The game "gum slayer"
- Make a game where the child plays the role of gum keeper and must not let the gum escape. (that is, it should not be swallowed).
- This game makes the child pay attention with more excitement and concentration.
5. Choosing the right type of gum
- Use smaller, softer gums that are easier to chew and less likely to be swallowed.
- Use mild flavors so that the child is not tempted to swallow the gum.
6. Repetition and consolidation
- In the first few days, gum should be given only in the presence of adults.
- After each practice, review with the child how he managed not to eat the gum and encourage him.
Safety considerations for families in case of a problem
1- If the child swallowed the gum:
- If there are no signs of choking, the gum usually passes through the digestive tract.
- In case of concern, consult a doctor.
2- If the child suffocates:
- Bend the child forward and give gentle blows to the back.
- If that doesn't work, use the Heimlich maneuver or call 911.
The Heimlich Maneuver (Heimlich Maneuver) is an emergency method to save a person who is choking and has an object blocking his airway.
✅ Heimlich performance steps for children over 1 year old and adults:
- Stand behind the person and wrap your hands around his waist.
- Put one hand into a fist and place it a little above the navel.
- Place the palm of the other hand on the fist.
- With quick and firm pressure, pull the hands inwards and upwards.
- Repeat this movement until the foreign object is removed or breathing returns.)
3-If an allergic reaction is observed
- Discontinue use and monitor symptoms (itching, swelling, nausea).
- In case of severe symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
4- If the child has jaw pain or restlessness:
- Stop using gum and review the type or duration of use.
- The therapist should be consulted to modify the plan.
Summary and implementation recommendations
Gum, if used with a therapeutic purpose and specialized supervision, can become an effective tool in the rehabilitation of children with special needs, from strengthening speech to regulating sensory and behavior, this simple tool has great capacities in treatment. Families can benefit from this opportunity properly by observing safety tips, proper training and cooperation with the therapist.
Resources:
-Chewing Gum: Cognitive Performance, Mood, Well-Being, and Associated Physiology
Andrew P Allen (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=%22Allen%20AP%22%5BAuthor%5D) 1,*, Andrew P Smith (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=%22Smith%20AP%22%5BAuthor%5D)
-The Neural Correlates of Chewing Gum—A Neuroimaging Review of Its Effects on Brain Activity (https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/15/6/657)
-Nonspeech oral movements and oral motor disorders: A narrative review (https://pubs.asha.org/doi/abs/10.1044/2015_AJSLP-14-0179)
– (https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/13/5/768) Oromotor nonverbal performance and speech motor control: Theory and review of empirical evidence (https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/13/5/768)
-Can chewing exercises improve mastication and articulation? A comparison of two different treatments (https://search.proquest.com/openview/751c0371c1799d15c0e830b3b18c14b4/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=2026366)