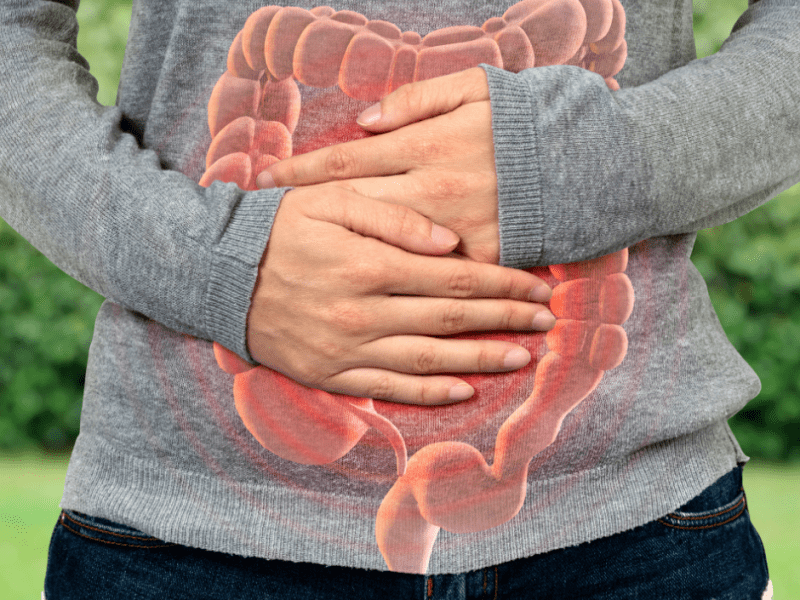
چسبندگی روده نوارهایی از بافت اسکار هستند که بین حلقههای روده یا بین روده و سایر اندام های شکمی ایجاد می شوند. آنها می توانند علائم مختلفی از جمله درد شکم، نفخ، یبوست و حالت تهوع ایجاد کنند. در برخی موارد، چسبندگی همچنین می تواند منجر به انسداد روده شود که یک وضعیت پزشکی جدی است.
چسبندگی می تواند پس از هر نوع جراحی شکم ایجاد شود، اما این چسبندگی ها پس از جراحی هایی که روده ها را درگیر می کنند، شایع تر هستند. خطر ایجاد چسبندگی در افرادی که چندین عمل جراحی شکم داشته اند نیز بیشتر است.
علت دقیق چسبندگی ها به طور کامل شناخته نشده است، اما تصور می شود که این چسبندگی زمانی رخ می دهد که روند طبیعی بهبودی بدن به اشتباه پیش می رود. پس از جراحی، بدن بافت اسکار تولید می کند تا بافت آسیب دیده را ترمیم کند. در برخی موارد، این بافت اسکار می تواند بین حلقه های روده یا بین روده و سایر اندام های شکمی چسبندگی ایجاد کند.
چسبندگی روده می تواند از نظر اندازه و شدت متفاوت باشد. برخی از چسبندگی ها کوچک و نازک هستند، در حالی که برخی دیگر بزرگ و ضخیم هستند. The bigger and thicker the adhesions, the more likely the symptoms will be.
Symptoms of adhesion can be different depending on the location and intensity of adhesion. Some of the most common symptoms are:
- abdominal pain
- flatulence
- constipation
- nausea
- vomit
- diarrhea
- Difficulty in passing gas
- abdominal expansion
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Shiver
In some cases, adhesions can also lead to intestinal obstruction. This is a serious medical condition that occurs when adhesions prevent food and waste from passing through the intestines. Symptoms of intestinal obstruction include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- nausea
- vomit
- diarrhea
- constipation
- abdominal expansion
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Shiver
If you experience any of the symptoms of adhesions, it is important to see your doctor. Your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the adhesions. Surgery is the only effective treatment for adhesions.
Intestinal adhesion treatment
Treatment for intestinal adhesions depends on the severity of the disease and the symptoms you are experiencing. In some cases, adhesions may not require treatment if they do not cause symptoms. However, if you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, or nausea, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the adhesions.
Surgery is the only effective treatment for intestinal adhesions. The type of surgery that is performed depends on the location and severity of adhesions. In some cases, laparoscopic surgery may be performed. This type of surgery is performed using small incisions and a camera. In other cases, open surgery may be necessary. This type of surgery involves making a larger incision in the abdomen.
After surgery, you will need to stay in the hospital for a few days. You will be given pain medication to help manage the pain. You will also be given instructions on how to take care of yourself at home.
Most people recover from surgery without any problems. However, there is a risk of complications such as infection, bleeding and blood clots. If any complications occur, it is important to see your doctor immediately.
Methods of prevention
There are several things you can do to reduce the risk of adhesions after surgery:
- Follow your doctor's instructions carefully after surgery.
- Get up and move as soon as possible after surgery.
- Avoid vigorous activity for several weeks after surgery.
- Have a healthy diet that contains plenty of fiber.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Use stool softeners or laxatives to prevent constipation.
- If you have concerns about adhesions, talk to your doctor.
endometrial connection and intestinal adhesion
There is a connection between intestinal adhesions and endometriosis. In fact, women with endometriosis are more prone to developing intestinal adhesions than women without endometriosis.The exact reason for this connection is not fully understood, but it is thought that inflammation from endometriosis can damage the abdominal tissue and lead to adhesions.
If you have endometriosis, it is important to be aware of the risk of intestinal adhesions. Talk to your doctor about ways to reduce your risk and manage your symptoms.