ام اس به زبان ساده
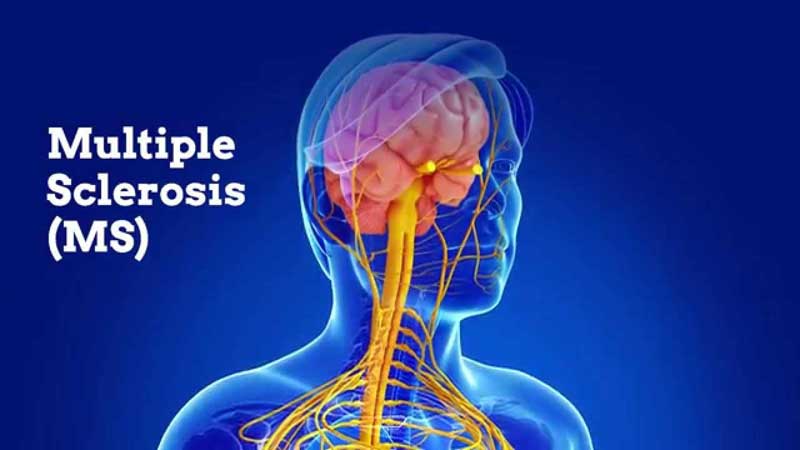
مولتیپل اسکلروزیس (MS) چیست؟
مولتیپل اسکلروزیس (MS) یک بیماری بالقوه ناتوان کننده مغز و نخاع (سیستم عصبی مرکزی) است.
در ام اس، سیستم ایمنی به غلاف محافظ (میلین) که رشته های عصبی را می پوشاند حمله می کند و باعث ایجاد مشکلات ارتباطی بین مغز و بقیه قسمت های بدن می شود. در نهایت، این بیماری می تواند باعث آسیب دائمی یا زوال اعصاب شود.
طیف علائم و نشانههای ام اس بسیار گسترده و متفاوت است و به میزان آسیب عصبی و همچنین اعصاب تحت تأثیر بیماری بستگی دارد. برخی از افراد مبتلا به ام اس شدید ممکن است توانایی راه رفتن مستقل را از دست بدهند، در حالی که برخی دیگر ممکن است دورههای طولانی بهبودی را بدون علائم جدید تجربه کنند و زندگی عادی شان را سپری کنند.
هیچ درمان کاملی برای ام اس وجود ندارد. However, treatments and medications can help speed recovery after attacks, modify disease courses, and manage symptoms.
Symptoms of SMS in plain language
Symptoms and symptoms of multiple sclerosis may vary greatly from person to person and during the course of the disease depending on the location of the damaged nerve fibers.
Symptoms of this disease often affect movement, such as:
• Numbness or weakness in one or more organs that usually occurs on one side of the body at the same time or in the trunk and legs.
• A feeling of electric shock that occurs with specific neck movements, especially bending the neck forward (Lhermitte's sign).
• Shaking, uncoordinated movements or unsteady walking
Vision problems are also common, including:
• Complete or partial loss of vision, usually in one eye, often with pain during eye movement.
• Double vision and long-term diplopia
• Blurred vision
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis may include the following:
• Uncertain speech
• Fatigue
• Dizziness
• Tingling or pain in parts of the body
• Sexual, bowel and bladder problems
When should you see a doctor?
If you see any of the above symptoms without a specific reason, see a doctor.
Illness period
Most people with MS have periods of relapse and recovery. They experience periods of new symptoms or relapses that develop over days or weeks and usually resolve partially or completely. These relapses lead to slow periods of recovery that can last months or even years.
A slight increase in body temperature can temporarily worsen the signs and symptoms of MS, but these cases are not considered true relapses of the disease.
At least 50% of relapsing-remitting MS sufferers, eventually, within 10 to 20 years after the onset of the disease, suffer from a steady progression of symptoms, with or without a recovery period. This is known as secondary progressive MS. Worsening symptoms usually include movement and walking problems. The rate of disease progression in people with secondary progressive MS is very different.
Some people with MS experience a gradual onset and steady progression of signs and symptoms without any relapses, known as primary progressive MS.
What is the cause of MSS in simple language?
The cause of multiple sclerosis is unknown. MS is considered an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks the body's own tissues. In the case of MS, this disorder in the functioning of the immune system causes the loss of the fatty substance that covers and protects the nerve fibers of the brain and spinal cord (myelin).Myelin can be compared to the insulating coating on electrical wires. When the protective myelin is damaged and a nerve fiber is exposed, messages traveling along that nerve fiber may be slowed or blocked.
It is not known why MS develops in some people and not in others. It seems that a combination of genetic and environmental factors are responsible for this.
Disease risk factors
The following factors may increase the risk of developing multiple sclerosis:
Age: MS can occur at any age, but its onset usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40. However, younger and older people can also be affected by this disease
Gender: Women are more than two to three times more prone to relapsing-remitting MS than men.
Family history: If one of your parents or siblings has MS, you are more at risk of developing this disease.
Certain infections: Various viruses have been linked to MS, including Epstein-Barr, the virus that causes infectious mononucleosis.
Race: White people, especially those of Northern European descent, have the highest risk of developing MS. Asian, African, or Native American people have the lowest risk.
Climate: MS is more common in countries with temperate climates, including Canada, the northern United States, New Zealand, southeastern Australia, and Europe.
Vitamin D: having low levels of vitamin D and low exposure to sunlight are associated with a higher risk of developing MS.
Some autoimmune diseases: If you have other autoimmune disorders such as thyroid disease, psoriasis, type 1 diabetes or inflammatory bowel disease, you are slightly more at risk of developing MS.
Smoking: Smokers who experience an initial attack of symptoms that may be a sign of MS are more likely than non-smokers to have a second attack, which confirms relapsing and remitting MS.
Symptoms of MS in plain language
Also, people with multiple sclerosis may have the following problems: • Muscle stiffness or spasm • Paralysis, usually in the legs• Bladder, bowel, or sexual function problems • Mental changes, such as forgetfulness or mood swings • Depression • Epilepsy and convulsions