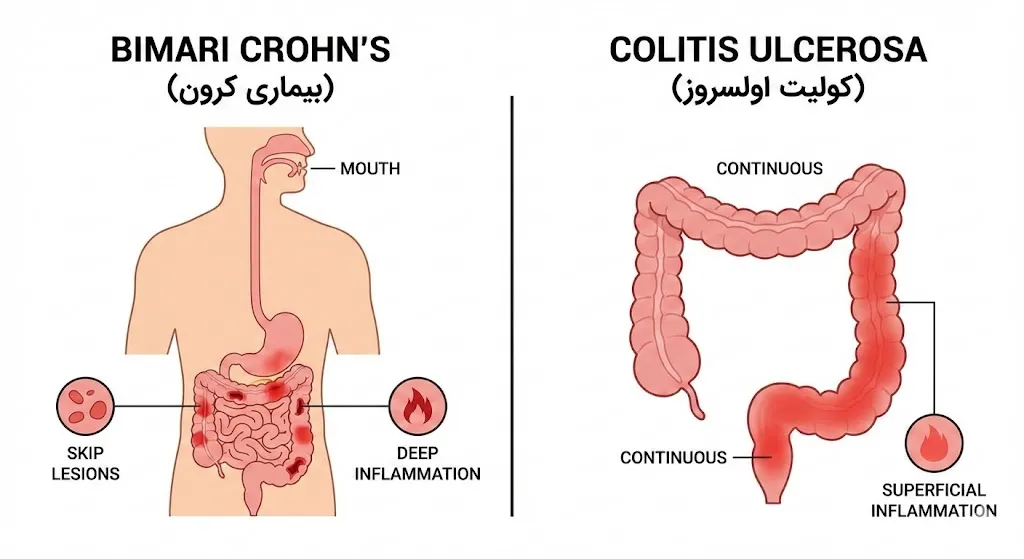
کولیت اولسروز (Ulcerative Colitis) یکی از بیماریهای التهابی مزمن روده است که عمدتاً روده بزرگ (کولون) و راستروده (رکتوم) را درگیر میکند. This disease can significantly affect a person's quality of life, because it is associated with symptoms such as frequent diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue, and sometimes bleeding. Accurate knowledge of the nature of the disease, possible causes, symptoms, and available treatments helps patients and families make more informed decisions for disease management. In this article, an attempt has been made to provide a comprehensive picture of ulcerative colitis in scientific but simple language; in a way that is understandable for both patients and the general audience.
What is ulcerative colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by chronic inflammation and superficial ulcers in the lining of the large intestine. This inflammation usually starts from the rectum area and may continuously spread to the higher parts of the colon. Unlike Crohn's disease, which can affect any part of the digestive system, ulcerative colitis is limited to the large intestine.
The chronic nature of this disease means that the person experiences periods of recovery (quietness of the disease) and periods of symptom recurrence. Also, the severity of the disease can vary from mild to severe.
Types of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is divided into several types based on the location of intestinal involvement:
- Ulcerous proctitis: inflammation is limited to the rectum and usually has milder symptoms.
- Proctosigmoiditis: the rectum and the sigmoid part of the colon are involved.
- Left-sided colitis: inflammation extends from the rectum to the descending part of the colon.
- Pancolitis: The entire colon is involved and usually causes more severe symptoms.
Knowing the type of ulcerative colitis is very important in choosing the treatment method and prognosis of the disease.
Causes of ulcerative colitis
The exact cause of ulcerative colitis is still not fully known, but research shows that a combination of the following factors play a role in the disease:
- Immune system disorder: In ulcerative colitis, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy intestinal cells and causes chronic inflammation. This abnormal immune response is considered one of the most important causes of disease in different people.
- Genetic factors: People who have a family history of inflammatory bowel diseases are more susceptible to colitis. The presence of certain genes can increase a person's sensitivity; However, genetics alone is not considered a definitive factor.
- Environmental factors: Environmental factors such as improper diet, chronic stress, use of certain drugs (such as antibiotics) and intestinal microbial changes may play a role in the occurrence or exacerbation of the disease.
- Lifestyle: Smoking, physical inactivity, and severe psychological stress can influence the course of the disease, although the exact role of each is still being investigated.
Symptoms and symptoms of ulcerative colitis
Severity and type of symptoms are different in different people and depend on the degree of intestinal involvement. Among the most important symptoms of colitis, the following can be mentioned:
- Frequent diarrhea, sometimes accompanied by blood or mucus
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Feeling of urgency to defecate
- Chronic fatigue and decreased energy
- Unwanted weight loss
- Slight fever in severe cases Anemia due to chronic bleeding
In children and adolescents, ulcerative colitis can cause growth and maturation disorders that require special medical attention.
Possible side effects of ulcerative colitis
If not properly controlled, ulcerative colitis can lead to serious complications; Among these complications, the following can be mentioned:
- Severe anemia Dehydration due to frequent diarrhea
- Intestinal perforation in rare but dangerous cases
- Increased risk of colon cancer in long-term conflicts
- Osteoporosis, especially in patients who use corticosteroids for a long time
These are the reasons why regular medical follow-up is very important in this disease.
Methods for diagnosing ulcerative colitis
An accurate diagnosis of ulcerative colitis requires a combination of clinical examinations and specialized tests. Normally, the following methods are used to diagnose this disease in different people:
- History and physical examination
- Blood test to check for inflammation, anemia and infection
- Stool test to check for infections
- Colonoscopy with sampling (biopsy), which is considered the most accurate method of diagnosis
- Imaging like CT scan in certain cases
Treatment of ulcerative colitis
The main goal of treating ulcerative colitis is to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, prevent disease recurrence and improve the patient's quality of life. The treatment of this disease is usually done in stages and based on the severity of the disease. Among the most important methods of treating this disease in different people, the following can be mentioned.
Pharmaceutical treatments
The first step in the treatment of ulcerative colitis is the use of drugs. The most important drugs suitable for the treatment of this disease in affected people are as follows:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (aminosalicylates)
- Corticosteroids to control severe inflammation
- immune system suppressing drugs
- Biological drugs that specifically inhibit inflammatory pathways
In many patients, the treatment of ulcerative colitis with appropriate drug therapy can put the disease into a silent phase.
Surgical treatment
In severe cases or when medical treatment is not effective, surgery to remove part of the colon or the entire colon may be recommended. Although surgery is a basic procedure, in some patients it can completely cure the disease.
The role of nutrition in the management of ulcerative colitis
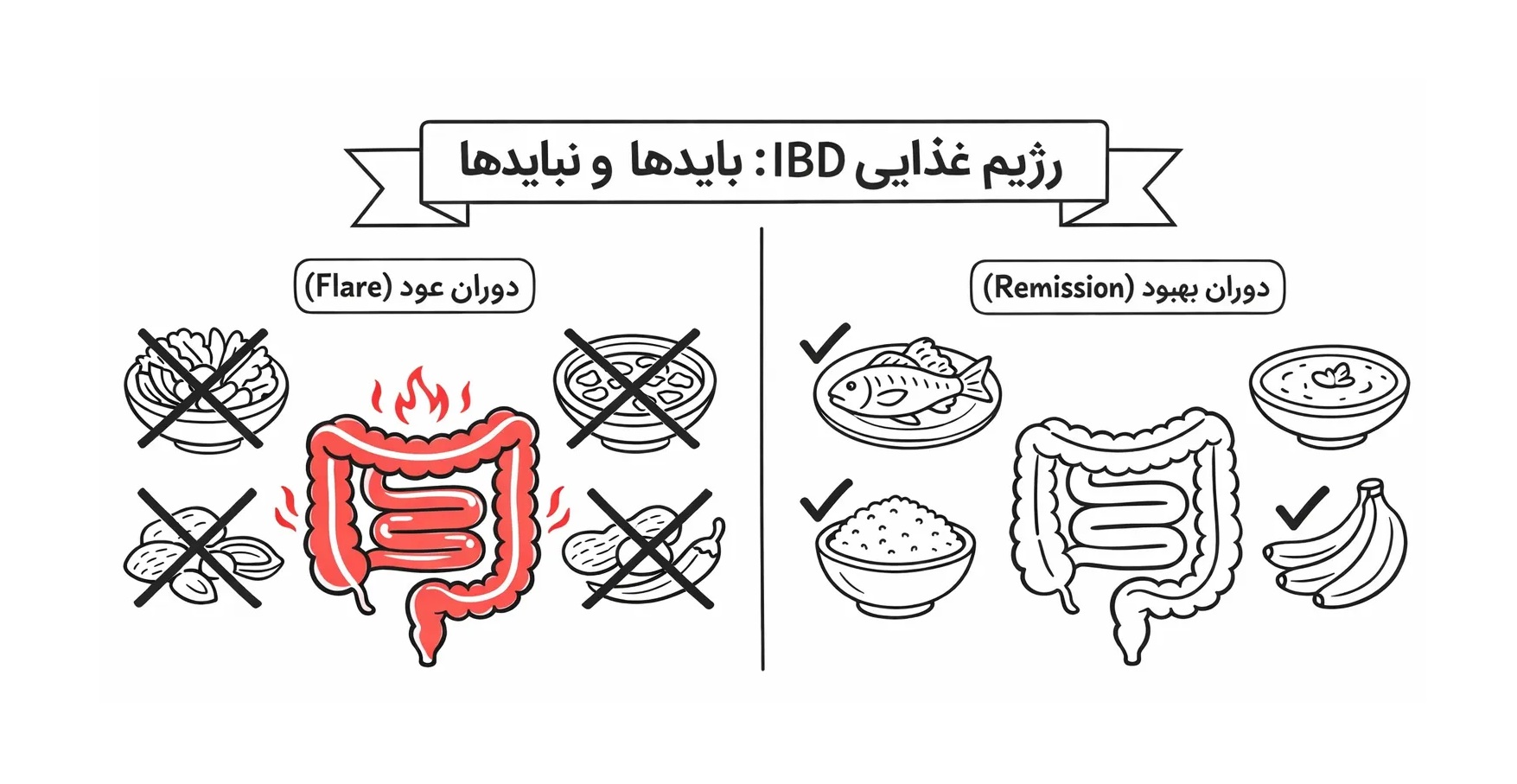
Diet plays an important supportive role in controlling the symptoms of ulcerative colitis, however, nutrition is not recognized as a substitute for drug treatment. General recommendations about nutrition in people with the disease are as follows:
- Consumption of low-fiber foods during active periods of the disease
- Avoid eating fatty, spicy and processed foods
- Drink enough fluids
- Using supplements in case of lack of vitamins and minerals
The important point about colitis disease is that each patient should adjust the diet according to his conditions in consultation with a doctor or nutritionist.
Living with ulcerative colitis
Although ulcerative colitis is considered a chronic disease, many patients can live an active and normal life with proper treatment. Awareness, regular medical follow-up and adherence to treatment play a key role in disease control.
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that requires timely diagnosis and basic treatment. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps patients take an active role in managing their disease. With medical advances, today it is possible to effectively control the disease and improve the quality of life of patients more than in the past.
Dr. Alireza Sima, as a gastroenterologist and liver specialist at Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Clinic, relying on his high power and expertise as well as the use of new and advanced equipment and methods, helps people who suffer from ulcerative colitis to treat their problem and continue their active and normal life.