What is typhoid, enteric fever or typhoid fever?
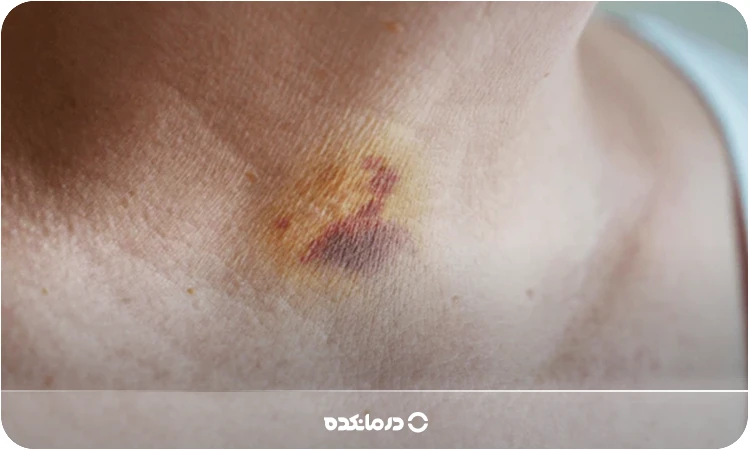
Typhoid, also known as blood spots or skin hemorrhages, refers to purple spots that can be detected on the skin. Spots may appear on organs or mucous membranes, including the lining of the mouth.
Typhoid occurs when blood vessels rupture and cause bleeding under the skin. This can cause purple spots on the skin that range in size from a single spot to larger areas. Typhoid spots are often benign, but may indicate more serious medical problems such as blood clotting disorders.
Sometimes, low levels of platelets can cause bruising and bleeding. Platelets are cells that help your blood clot.. Low platelet levels may be hereditary or genetic, but may also indicate:
- Bone marrow transplant
- Cancer
- Chemotherapy
- stem cell transplant
- HIV infections
- hormone replacement
- Estrogen therapy
- Using some medicines
As soon as you notice the development of spots or changes in the skin, you should consult a dermatologist.
What causes typhoid?
There are two types of typhoid: non-thrombocytopenic and thrombocytopenic.
Non-thrombocytopenia means that your blood platelet levels are low.
Thrombocytopenia means that your platelet count is lower than normal.
The following can cause non-thrombocytopenic typhoid:
- Problems that cause blood clotting disorder.
- Some congenital disorders that manifest at birth or before, such as dilated capillaries (dry skin and connective tissue) or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Certain medications, including steroids and medications that affect platelet function
- Weak blood vessels
- Swelling of blood vessels
- Scurvy or vitamin C deficiency
The following can cause thrombocytopenic typhoid:
- Drugs that prevent the formation of platelets or interfere with normal blood clotting.
- Drugs that cause the body to react immune to platelets.
- Blood transfusion history Immune system disorders such as idiopathic typhoid thrombocytopenia
- Presence of infection in the bloodstream
- Infection caused by HIV or hepatitis C or some viral infections (Epstein-Barr, measles, cytomegalovirus)
- Stone Mountain spotted fever (caused by tick bites)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus[sibwp_form id=1]
How is typhoid diagnosed?
The doctor will examine your skin to diagnose typhoid... He may ask about your and your family history, such as when these spots appeared.... In addition to blood and platelet tests, the doctor may take tissue from your skin.
The purpose of these tests is to determine whether your typhoid is caused by some serious disease such as a platelet or blood disorder. Platelet levels can identify the cause of typhoid and help your doctor determine the treatment method.
Typhoid can affect both children and adults.... Children may develop typhoid after a viral infection and recover without any medical intervention.... Many children with thrombocytopenic typhus can recover within months of the onset of the illness.... However, in adults, the causes of typhoid are usually chronic and require treatment to help manage symptoms and keep platelets within a safe range. They have
..How is typhoid treated?
The type of treatment prescribed by the doctor depends on the cause of typhoid. Adults with thrombocytopenic typhoid may be treated without any intervention.
You only need treatment if typhoid symptoms do not go away on their own.. Treatment includes drug therapy and sometimes removal of the spleen. You may be asked to avoid medications that destroy your platelet function, such as aspirin, blood thinners, and ibuprofen.
Corticosteroids
Your doctor may start treatment with corticosteroids, drugs that help increase platelets by activating the immune system. It usually takes two to six weeks for the platelet count to reach an acceptable level. If this happens, your doctor will stop the medication.
It is important to ask your doctor about the risks of long-term use of corticosteroids... Long-term use of these drugs can cause serious side effects such as weight gain, cataracts, and loss of bone density.
intravenous immunoglobulin
If your type of typhoid is such that it causes heavy bleeding, your doctor may prescribe intravenous drugs called intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)... Also, if you need to increase the platelet count quickly before the operation, intravenous immunoglobulin is prescribed... This method is useful to increase the platelet count, but this method can cause short-term treatment.. Nausea and fever.
Learn more: High fever in adults
Other drug treatments
Recent drugs used to treat low platelets in people with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) include romiplostim (Nplate) and eltrombopag Promacta. These drugs cause the bone marrow to produce more platelets and reduce the risk of bruising and bleeding. Some potential side effects include:
- Headache
- dizziness
- Nausea
- Muscle or joint pain
- High risk of blood clots Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Pregnancy
Biologic therapy such as Rituximad Rituxan can help reduce the immune system response. This is often used to treat patients with severe thrombocytopenic typhoid for whom corticosteroid therapy is ineffective.. Side effects may include the following:
- Low blood pressure
- Burning throat
- Itching
- Fever
Spleen Removal
If drug therapy is not effective in treating thrombocytopenic typhoid, the doctor may suggest splenectomy....Splenectomy is the fastest way to increase the platelet count...because the spleen is the main organ to remove platelets.
If the doctor's diagnosis is this option, you will be referred to a plastic surgeon.
However, removing the spleen does not work for everyone....the procedure comes with risks...such as an increased risk of infection for the rest of your life.
In emergency cases of typhoid that causes severe bleeding, hospitals will prescribe platelet transfusions, corticosteroids, and immunoglobulin. After treatment begins, your doctor will count your platelets to determine whether the treatment has been effective. Your doctor may change your treatment based on its effectiveness.
What is the outlook for typhoid?
The outlook for typhoid depends on the condition that caused typhoid... Once your doctor has diagnosed typhoid, he will suggest treatment options and tell you about the long-term outlook of the disease.
In rare cases, thrombocytopenic typhoid, left untreated, may cause a person to bleed profusely in some part of the body. Profuse bleeding in the brain can cause cerebral hemorrhage.
People who start treatment quickly or whose illness is not severe often make a full recovery....However, typhoid can be chronic in severe cases or when treatment is delayed....If you have typhoid, you should see a doctor right away.
Living with typhoid
Sometimes typhoid spots don't go away completely....Some medications and activities can make the spots appear better....To reduce the risk of new spots or worsening of the spots, you should avoid medications that lower platelets.
Coping with chronic illnesses can be difficult....it can be helpful to talk to people who have such disorders.... Join online groups to talk to other people with typhoid.
Was this article useful for you?
![Which fruit increases blood pressure [high and low]? 18 effective fruits](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_08/ef00bb701cbb99e90a24ba8d73265ba4c08936335e859a33b69553f5c5e737a2.webp)

![For whom is rhinoplasty dangerous? [10 groups+cause+solution]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/3e06a993c87e243daaf67dc69ac3e484d377b2708c93656820e0084ea4f080d6.webp)
![What fruits have vitamin B12? [13 fruits + consumption tips]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/dfaeceb7cb9a203805aeba8715bf7cdea6f5cb2b5b9314e1898807545e874bb1.webp)
![Is nasal massage necessary after surgery? [Training + 5 effective benefits]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/1f2686c8d522130d256828a51d7d46594dbde31ec2253325e6a8a38f04094789.webp)
![The best drops to reduce eye pressure [14 powerful drugs + method of administration]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/0177c50098eb80d878d1c883d09ae31ad2f489b17e1288f52018e3f8ef213e5f.webp)
![What is hair filler? [9 benefits, how to inject + durability of hair filler]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/c21c5e1ff48e9af8214111dfe0b867586f298e3d74a95fadda02b0b04df12598.webp)
![The strongest antibiotic for tonsil infection [7 drugs + method of administration]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/7b5adf6bb8cf556824d96570b6adba58f824b3a7f248993cfaafb73c0b5b8610.webp)
![Garlic pills for weight loss [4 effective benefits and side effects + how to use]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/c49f08b482d5860218c8635e48194a50f2ed48b51ef15925aa2d73d8393ff3ab.webp)
![What foods increase eye pressure? [8 harmful foods and drinks]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/52929c4d1b9ed7916d3fc5a8e45060479fb186f332dd217e68905f71f89a33f0.webp)
![What foods lower eye pressure? [18 useful foods]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/f180eb15f8e64fc9b386f9d5dc7936a5e416af36032be3bdcdf9054925a21d43.webp)
![itchy scalp; 18 causes [medical treatment + 11 home remedies]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/a1e116ec1c6243fd5c4e6fb951da5cb33bbd92a09c44e29b845852a86f550681.webp)
![What is intestinal colitis and what are its symptoms? [3 causes + definitive treatment]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/d3384e9221c036ff3eb447c69ffabb109dd6c0c35f5e5f0af775c4545cfd7ea5.webp)
![The best pills for irritable bowel syndrome [10 powerful drugs]](/storage/posts/covers/2026_01_06/70f02d6808fab88d67b0c6734a623e5e71982d323dbd2fb8158c29669849b813.webp)