ضربان قلب و فشار خون
فشار خون بالا یک مشکل بالینی شایع و خطر اصلی برای بیماریهای قلبی عروقی در مواقع سکته است.
افزایش ضربان قلب با افزایش فشار خون و در میان افراد مبتلا به فشار خون بالا افزایش خطر ابتلا به بیماریهای قلبی عروقی مرتبط است. Despite these important relationships, heart rate is generally not considered in the selection of antihypertensive drugs.
Although there is a positive relationship between heart rate and external blood pressure, there is also an inverse relationship between heart rate and central blood pressure. The use of antihypertensive drugs, especially drugs that affect heart rate, may not reduce central blood pressure as much as peripheral blood pressure.
Heart rate and blood pressure relationship
One reason to consider heart rate in the selection of blood pressure drugs is the observation that increased heart rate is a common feature in patients with hypertension, and increased heart rate with high blood pressure. It is relevant.
15% of hypertensive patients had a resting heart rate of 85 beats per minute, and approximately 27% had a heart rate of 80 beats per minute. In addition, persistently elevated heart rate is a strong predictor of high blood pressure that requires medical treatment.
People with high blood pressure have higher heart rates than normal people. In addition to high blood pressure, heart rate is associated with other cardiovascular risk factors.
Results from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study show that higher heart rate and lower heart rate variability are associated with increased risk of diabetes, even when controlled for body mass index and physical activity.
Among patients at high cardiovascular risk, increased initial heart rate is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality, independent of achieved blood pressure.
In summary, increased heart rate with Elevated blood pressure is associated with an increased risk of developing high blood pressure (and diabetes) and all-cause mortality.
However, the relationship between heart rate and blood pressure becomes more complicated when central and peripheral blood pressure are considered. The studies mentioned above measured blood pressure externally.
Recent research has shown the importance of central blood pressure and vascular conduction properties in relation to adverse outcomes.
Routine blood pressure measurement in the office is done externally, usually from the brachial artery.
Unfortunately, this measurement has significant variability. It does not take into account vascular compliance, which leads to differences between central and peripheral pressure measurements of up to 20 mm Hg.
These marked differences have led to increased recognition of central blood pressure as an important clinical marker for increased cardiovascular risk.
Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate
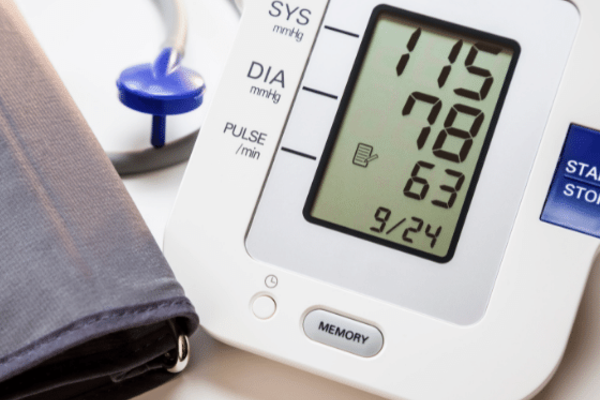
Blood pressure is measured with a sphygmomanometer cuff. and is in milligrams of mercury (mm of mercury).
Heart rate can be measured with an automatic sphygmomanometer cuff, with a pulse oximeter, or manually by counting the pulse. Heart rate is measured in beats per minute (bpm).
Factors affecting heart rate
Heart rate is very sensitive to the nervous system, hormones, and volume status, which includes:
• Effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
• Exercise and fitness Body (resting heart rate is lower in people who are physically fit)
• Thyroid hormone levels
• Dehydration
• Caffeine (can increase heart rate)
Medications such as stimulants, asthma medications, some anti-inflammatory medications Depression and thyroid medications can increase heart rate. Medications including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and digoxin can slow the heart rate.
High blood pressure
Anyone who notices high blood pressure should be evaluated by a cardiologist in Isfahan. High blood pressure increases the risk of stroke, heart attack, and heart failure.
Low blood pressure
Low blood pressure is accompanied by symptoms such as lightheadedness, fatigue, or fainting, along with signs of bleeding or infection.
Best time to measure blood pressure
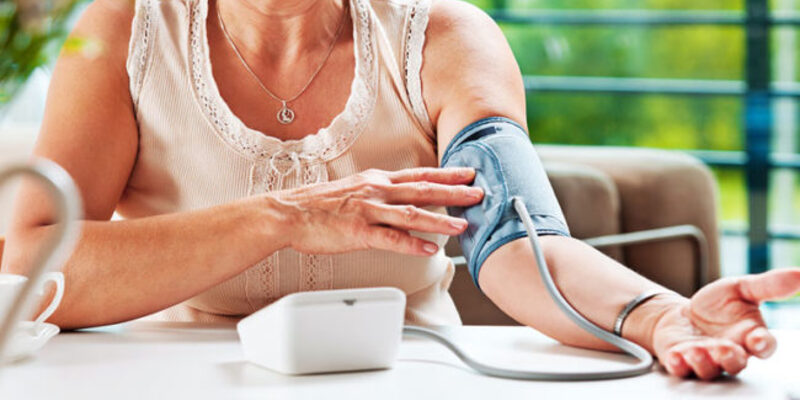
Blood pressure is best measured at rest. First, sit on a chair for five minutes and place your feet on the floor. Make sure your arm is at heart level and resting on the table.
Then Remove the sphygmomanometer, making sure to use an appropriately sized cuff. Do not measure the blood pressure until 30 minutes after exercising, smoking or eating.
High heart rate
When not under the influence of exercise, emotional stress or caffeine, a high heart rate can indicate an underlying problem. A high heart rate can cause symptoms such as:
• fatigue
• heart palpitations (change in heart rate)
• lightheadedness
• dizziness
• chest pain Chest
• Shortness of breath
If you have periods of high heart rate with palpitations, note whether your heart rate is regular or irregular.
Also note whether the changes started suddenly or gradually. This information can be helpful as cardiologist in Isfahan looks for certain patterns of arrhythmia.
If your cardiologist suspects arrhythmia, he may recommend a wearable heart monitor that can detect the arrhythmia.
cardiologist in Isfahan may also order tests such as Prescribe thyroid hormone and electrolyte levels.
Low heart rate
Some people who are naturally fit have a low resting heart rate. The heart rate also usually slows during sleep.
If a low heart rate is observed in a young, healthy person and causes no symptoms, it is probably not a cause for alarm.
However, a low heart rate can indicate an underlying heart problem, such as heart block.
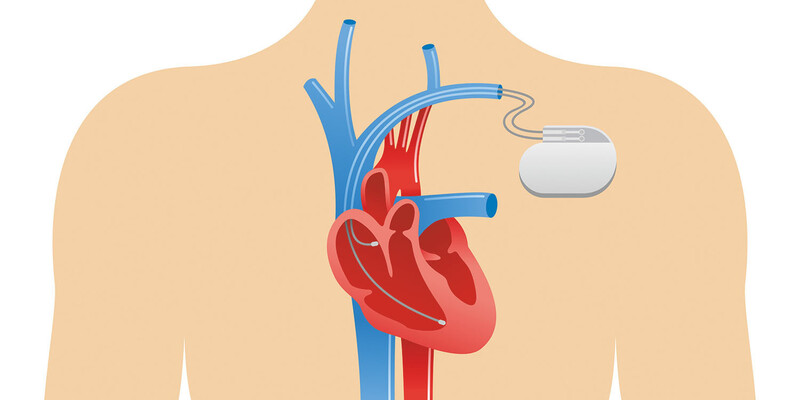
Heart block is a condition in which the electrical system The heart is not working properly. Symptoms can include fatigue, lightheadedness, dizziness, and fainting. Sometimes heart block requires a pacemaker.
What are the harms of smoking for the heart and heart patients?
Smoking increases the risk of heart disease. Tobacco smoke damages the lining of the arteries, which can lead to plaque build-up.
which can cause the arteries to narrow (atherosclerosis) and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Cigarettes can also cause:
• Peripheral artery disease
Artery disease Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition in which the arteries outside your heart and brain become narrowed or blocked.
This can lead to reduced blood flow to your organs, causing pain, numbness, or weakness. PAD can also lead to ulcers or gangrene (dead tissue) in your legs or feet.
• Aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is a bulge or balloon in the aorta, the large artery that carries blood from the heart to your body. An aortic aneurysm can rupture and cause dangerous internal bleeding.
• Sudden cardiac death
Sudden cardiac death is a sudden and unexpected death caused by a change in heart rhythm (cardiac arrest).
• Respiratory diseases
Smoking also increases the risk of other respiratory diseases such as emphysema, bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Smoking is responsible for more than 85% of COPD deaths.
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death. Sudden cardiac death is a sudden and unexpected death caused by a change in heart rhythm (cardiac arrest)
• According to the 2014 report on Smoking and Health, smoking is the leading cause of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Even people who smoke fewer than five cigarettes per day may show early signs of CVD.
The risk of CVD increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and when smoking continues for several years.
Smoking with lower levels or nicotine does not reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Exposure to cigarette smoke causes heart disease in non-smokers.
Final Word
Blood pressure and heart rate are two related vital signs that help ensure adequate blood flow to the brain and organs. They act separately, but one can change in response to the other.
Increased blood pressure and heart rate during exercise and stress are normal. دلایل دیگر برای داشتن فشار خون یا ضربان قلب بیش از حد بالا یا پایین ممکن است نشان دهنده یک مشکل پزشکی باشد.
با استفاده گسترده از فناوری های کمکی مانند مانیتورهای تناسب اندام و ساعت های هوشمند، اطلاعات ضربان قلب همیشه در دسترس شما قرار دارد.
اگر متوجه دورههایی از ضربان قلب شدید که بهطور تصادفی و بدون محرک اتفاق میافتند، ممکن است یک مشکل قلبی تشخیص داده نشده داشته باشید.
در تماس با متخصص قلب و عروق در اصفهان برای چکاپ ارزیابی تردید نکنید.