Table of Contents
- What is the symptom of a blood clot during a period?
- Symptoms and symptoms of a blood clot Meaty
- What is the symptom of meaty blood clot during period?
- Types of bleeding clot during period
- How to diagnose the cause of meaty blood clot
- Methods for treating and removing blood clots during menstruation
- Complications of blood clots during menstruation
- Prevention of blood clots during menstruation
- For blood clots Which doctor should we visit during period?
- Conclusion
Sometimes during periods, instead of thin blood, thicker, jelly-like pieces or even tissue-like lumps are excreted. Most menstrual clots occur when the bleeding is heavy and the body coagulates the blood to prevent bleeding. But if the discharge of blood clot during period is accompanied by very heavy bleeding, unusual pain, bad smell, fever or the possibility of pregnancy, it should be investigated more seriously because it can be a sign of an underlying cause such as hormonal disorders, fibroids, adenomyosis, pelvic infection or even miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. The important point is that the term meat blood clot does not necessarily mean the removal of meat. Some people describe large clot-like lumps as fleshy, but sometimes pieces of the inner lining of the uterus are actually expelled. In this article, we will help you diagnose it by examining the causes, symptoms and treatment methods of a blood clot from your doctor.
What is the symptom of the discharge of blood clot during period?
During menstruation, with the shedding of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) and contraction of the cervix, blood and separated tissues are expelled. Discharge of fleshy blood clot during period can occur on the heaviest days of menstruation and is normal for many people. The body produces anticoagulants to prevent the formation of large clots. But in case of lack of these substances, severe bleeding or blood remaining in the uterus for a long time, the possibility of blood clot formation increases.
These fleshy blood clots are usually part of the normal menstrual cycle, but sometimes due to thickening of the uterine wall, hormonal imbalance, or problems such as fibroids and endometriosis, they become larger and look like pieces of meat. If you are in doubt about the symptoms of a blood clot during your period, pay attention to these patterns: a sudden change in the intensity of bleeding, repeated heavy periods and blood clots over several cycles, bleeding between two periods, or bleeding after menopause. These cases can be a subset of abnormal uterine bleeding and need to be evaluated.
Symptoms and symptoms of flesh blood clot
Menstrual blood clots are usually seen with more bleeding in the first day or two and may be accompanied by a little pain in the lower abdomen.
Messial blood clot, unlike normal clots, is usually accompanied by symptoms that help to diagnose it in time and prevent serious complications. But menstrual blood clots become more worrisome when warning signs are added, such as dizziness, severe weakness, or sharp, one-sided pelvic pain. In such situations, the possibility of anemia or causes such as infection or pregnancy problems should be investigated. If you have the following symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor:
- Heavy period bleeding or long (so that the person has to change their sanitary napkin every 1-2 hours)
- Severe pain and cramps, especially in the lower abdomen and back
- Persistent pelvic pain
- Recurrent large clots with low mood, palpitations, or pallor
- Severe dizziness: Severe bleeding can lead to low blood pressure or anemia, which are accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness and even fainting. Fainting, shortness of breath or severe weakness
- Stomach pain and nausea, caused by strong contractions and pressure on the uterus
- any type of abnormal bleeding in case of possible pregnancy or after menopause
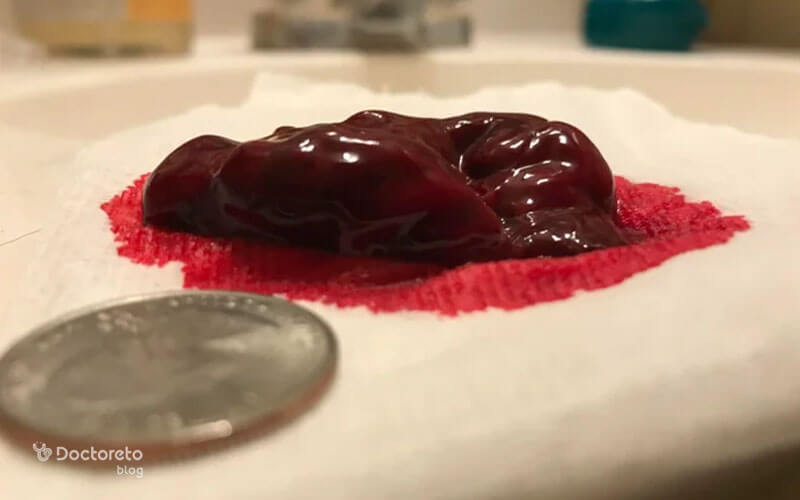
Photo of blood clot during menstruation
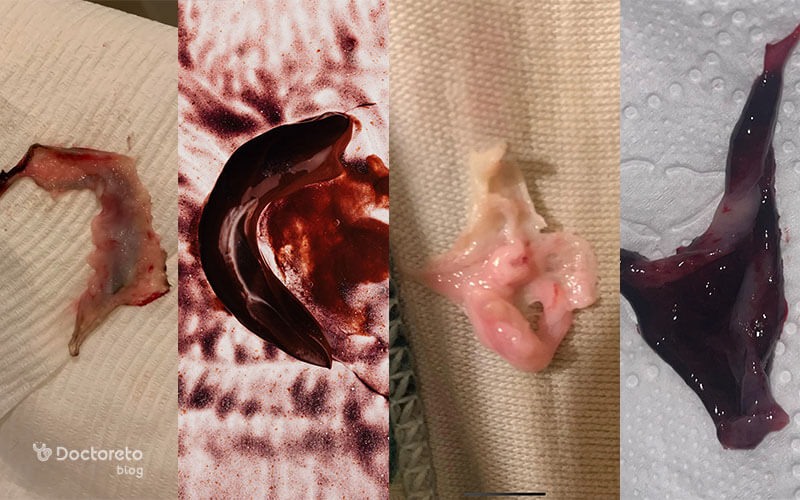
In the photo above, you can see some photos of liver-like blood clots during periods, which are different in terms of shape and color. Some clots are dark and jelly-like and are usually more visible when the bleeding is heavy or the blood stays in the uterus for a long time. Some others have a lighter and textured appearance and are more like a piece of mucus or inner tissue of the uterus that is sometimes excreted with the period. Elongated and dark sheet samples can also be a combination of clotted blood and thick secretions. These images do not help with a definitive diagnosis, but if the clots are large and recurring, or occur with severe pelvic pain, dizziness, extreme weakness, fever, and vaginal odor, you should see a gynecologist.
Comparison of meat blood clot compared to normal menstrual clot
During menstruation, blood clots are usually normal, but fleshy clots can be a sign of underlying problems. Normal clots are often jelly-like, dark red, and on heavier days, they become smaller as bleeding decreases. But what people describe as a period blood clot is sometimes larger, more solid, or tissue-like, and may be accompanied by more pain or a marked change in the bleeding pattern.
Clinically, the doctor pays more attention to the clinical background than the appearance of the mass: age, pregnancy probability, amount of bleeding, pain and signs of infection. For example, in pregnancy, discharge of clots and tissues can be related to abortion, and bleeding and discharge of blood clots during periods should not be confused with pregnancy bleeding. Knowing these differences can help the patient to better understand the condition and the need to see a doctor. In the table below, you can see the difference between a meat blood clot and a normal blood clot.
| Characteristics | Fleshy blood clot | Normal menstrual clot |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance and texture | Dense, thick and similar to liver or meat | Jelly, soft and textureless Characteristic |
| Color | Usually brownish or dark red | Dark or bright red |
| Size | Usually between 1 and 3 cm or more | Usually less than 1 cm |
| Causes of formation | Thickness Abnormal uterine lining, fibroids, hormonal imbalance, etc. | Blood accumulation and clotting before exiting the body |
| Pain level | Severe pain and cramping | Usually no pain or mild pain |
| Bleeding rate | Heavy bleeding and longer than normal menstruation | Severe bleeding Normal menstruation |
| Need to see a doctor | Recommended in case of recurrence or severe symptoms. | No need to visit usually. |
| Ejection time | May occur mostly at the beginning of menstruation. | May occur at any time during the period. |
What is the symptom of blood clot during period?
It is normal to see a blood clot during menstruation, but if the clots are large (for example, larger than about 2.5 cm), or if the bleeding is very heavy and prolonged, it needs to be investigated. These clots often form when the uterine wall becomes thicker than normal and the bleeding is heavier than normal. The cause of period blood clotting is usually related to the increase in bleeding volume. The more severe the bleeding, the more likely it is to form a clot, as the body activates clotting factors to control the bleeding. However, the cause of blood clots during periods can be different from irregular ovulation and hormonal imbalance to structural problems of the uterus such as fibroids and adenomyosis.
If the period blood clots just started, the period is heavy and the blood clots are repeated for several cycles, or accompanied by spotting and pain, the possibility of an underlying cause increases. The most important causes of blood clots during periods are:
- Hormonal imbalance Endometriosis and adenomyosis
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Uterine fibroid and polyp Coagulation disorders
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) Ectopic pregnancy
- Abortion
- hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- Menopause
- Uterine obstruction
- Consumption of certain drugs
1. Hormonal imbalance
The imbalance of estrogen and progesterone hormones can cause thickening of the uterine lining and as a result heavy bleeding and blood clots. Irregular period is one of the most important signs of hormonal imbalance. This imbalance can occur for various reasons, including extreme stress, weight changes, ovarian problems, and the use of hormonal drugs.
2. Endometriosis and adenomyosis
Endometriosis and adenomyosis can cause severe and painful periods and increase bleeding during periods. In adenomyosis, endometrial-like tissue grows inside the uterine muscle, and the result is usually heavy or prolonged bleeding with clots and pelvic pain. If endometriosis or adenomyosis is involved, period pains, pain during sex, and sometimes bleeding between periods are usually seen.
English text:
drseckin
The longer the blood stays inside the uterus, the darker it is in color, and the likelier it is to form clots.
Text translation:
The longer the blood stays in the uterus, the darker its color and the more likely it is to form clots.
3. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
In polycystic ovary syndrome, ovulation may become irregular and this can lead to irregular and sometimes heavy bleeding. Some people in this condition experience a clotted period and may think of it as blood clots from the discharge of the ovarian cyst during the period, while most of the time, the thickening of the uterine lining is due to the ovulation disorder, not the clot from the cyst discharge during the period. If you have symptoms such as acne, hairiness, weight gain, or prolonged irregular periods, a PCOS checkup can help. Also, irregular and long periods in people with ovarian laziness also increase the possibility of the formation of these clots.
4. Uterine fibroids and polyps
Uterine fibroids and polyps are non-cancerous masses in the uterus. From Symptoms of Uterine Polyps An increase in the thickness of the uterine lining and a decrease in the natural contractions of the uterus can lead to an increase in the accumulation of blood in the uterus, increased bleeding, and finally the formation of meat clots. Fibroids are usually benign but can cause prolonged bleeding, pelvic pressure, and anemia. If you have heavy periods and blood clots along with pelvic heaviness, frequent urination or abdominal enlargement, pelvic ultrasound is usually the first step in diagnosis.
5. Coagulation disorders
If the blood does not clot properly or, conversely, the coagulation system is unbalanced, menstrual bleeding can become very heavy and prolonged, resulting in larger clots. Some blood coagulation disorders can cause blood clots by increasing the level of platelets and coagulation factors. These problems may be hereditary or caused by the use of certain drugs and agents.
6. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Ascending infections of the genital tract can cause inflammation of the uterus and tubes and be accompanied by pelvic pain, foul-smelling discharge, fever, or abnormal bleeding. Pelvic inflammatory disease refers to an infection of the female genital tract that can cause inflammation and thickening of the uterine wall. In this case, the bleeding may be irregular and sometimes clotted, and if the treatment is not done on time, complications such as chronic pelvic pain or infertility may arise. This inflammation may cause the accumulation of blood and the formation of a fleshy clot during the period. This condition can be dangerous, especially if severe unilateral pain, dizziness or fainting occurs. If you are likely to be pregnant, any abnormal bleeding or discharge of blood clots during pregnancy should be checked with a pregnancy test and an immediate examination.7. Ectopic pregnancy (blood clot in pregnancy)
In general, the presence of a blood clot in pregnancy usually indicates a serious problem and should be followed up quickly. In an ectopic pregnancy, symptoms can include vaginal bleeding (sometimes dark or watery) and abdominal or pelvic pain (often unilateral), and some people may have no symptoms at first. Discharge of tissue or mass can be seen in pregnancy bleeding (e.g. miscarriage) and the diagnosis should be made with a pregnancy test and immediate evaluation.
English text:
If the embryo ruptures, it can cause internal bleeding and can be life-threatening. href="https://www.webmd.com/women/decidual-cast-what-is-it" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">webmd
8. Abortion
In early pregnancy, miscarriage can cause heavy bleeding with fleshy clots. In this case, the body cleans the uterus by expelling fetal tissues and endometrium. Many people describe this state as the discharge of a piece of meat with menstrual blood. Also, premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall may cause increased bleeding and meat clots.
9. Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland plays an important role in regulating the body's hormones, and a change in its function can lead to hormonal imbalance. Hormonal imbalance in women can increase the thickness of the uterine wall and cause blood clots. Some people with hypothyroidism experience severe periods and blood clots, and menstrual irregularities may also occur in hyperthyroidism. If you are experiencing weight changes, heart palpitations, hair loss, or severe fatigue, checking TSH and thyroid hormones can clarify the cause of period blood clots.
10. Menopause
During perimenopause and after, severe hormonal fluctuations cause irregular menstruation and the formation of meat clots. But bleeding after menopause is not normal and must be checked, because it can be a sign of endometrial problems. If you are menopausal and you see bleeding or clots, do not delay medical follow-up.
11. Obstruction of uterus Uterine obstruction can occur for reasons such as uterine fibroids and polyps, adhesions of the uterus and fallopian tubes, cervical stenosis, ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy, endometriosis or adenomyosis. In this situation, the accumulation of blood in the uterus causes the formation of large and fleshy clots with severe pain and bleeding.
12. Taking some drugs
The use of some drugs such as birth control pills, thyroid and corticosteroids cause the formation of meat clots by changing the balance of hormones. Also, anticoagulants such as warfarin and heparin may increase bleeding and the formation of these clots. Also, some treatments or hormonal drugs can change the pattern of bleeding. If after starting a new drug, blood clots in the period or prolongation of the period and blood clots have occurred, it is better to consult a doctor without stopping the drug arbitrarily.
Types of period bleeding
Bleeding clots during period can be different in terms of color and shape, and these differences sometimes give clues as to how long the blood remained in the uterus or how intense the bleeding was. For example, darker or black blood can be related to blood remaining in the uterus or vagina, while bright red blood is usually a sign of more active bleeding. However, it is not possible to make a definite diagnosis only by color, and accompanying symptoms are more important.
If you want to know which color of period blood is dangerous, look for the general pattern instead of just the color: very large clots, very heavy bleeding, lasting more than a week, severe pain, fever or possible pregnancy. In the following, we will explain the common types separately so that you know when it is more natural and when it needs to be checked.
What is the sign of blood clot like liver in period?
Liver-like clots are usually caused by heavy bleeding and blood accumulation in the uterus, and their darker color is related to blood oxidation. If these clots only occur occasionally and on heavy bleeding days and you have no warning signs, it may not be a serious problem. But if it repeats continuously, is accompanied by weakness and symptoms of anemia, or if you have heavy periods and blood clots, the cause of clot discharge during periods should be investigated.
| Type of flesh blood clot | Description | Accompanied symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Similar to the liver | Heavy bleeding and blood accumulation; darkening due to oxidation | if it repeats constantly or is accompanied by weakness and symptoms of anemia, it needs to be investigated |
| white flesh | mucous and remnants of uterine tissue; Sometimes desicual cast | If it is accompanied by severe pain, unusual bleeding, unpleasant odor or fever |
| Red and white | Fresh blood with mucus or discharge | If it is accompanied by burning, itching, bad smell or pelvic pain, infection or pelvic inflammation is considered |
| Black | blood stays in the uterus or vagina and darkening | Check if accompanied by severe pain, foul odor, abnormal bleeding, or history of obstruction |
| Brown | Older, oxidized blood | Check if accompanied by foul odor, pelvic pain, prolonged spotting, or marked change in pattern |
| Jelly | Clotting in heavy bleeding and Little opportunity for dilution | If there is a need to change pads frequently or dizziness and weakness, it is necessary to check for anemia and the causes of heavy bleeding |
What is the sign of white-meat blood clot in period?
The presence of white clots during periods is usually caused by mucus and remnants of uterine tissue and is usually not dangerous; However, if these clots are accompanied by symptoms such as severe pain, unusual bleeding, foul odor, or fever, it is best to see a doctor. This condition can be due to the complete removal of uterine tissue (decisive cyst), infection or inflammation of the uterus, and in rare cases, the removal of uterine cysts.
Red and white blood clot in period
The combination of red and white clots can indicate fresh blood with mucus or discharge. If accompanied by burning, itching, bad odor or pelvic pain, vaginal infection or pelvic inflammatory disease should be considered. If it occurs only in one cycle and without other symptoms, it may not be alarming, but in case of recurrence or severe bleeding, investigation is necessary.
What is the sign of black blood clot in period?
Often, the black blood clot after the period is period, that is, the blood has remained in the uterus or vagina for some time before exiting and has turned dark. This state can be seen at the beginning or end of the period and is not always dangerous. But if the black blood clot after the period is accompanied by severe pain, bad smell, abnormal bleeding or a history of outflow obstruction, it is necessary to be checked because the outflow of blood may not be done well or there is an underlying cause.
cause of brown blood clot during period
Brown blood is usually older blood that left the uterus later and oxidized along the way. This condition is common in the last days of the period and is often considered normal. But if the cause of the brown blood clot in the period is accompanied by a bad smell, pelvic pain, long spotting or a clear change in the menstrual pattern, it becomes important to investigate the causes such as infection, polyps or hormonal disorders.
jelly blood clot in period
Jelly clot is usually the same clotted blood that occurs with a larger bleeding volume. If the bleeding is too heavy, the blood doesn't have enough time to mix with the menstrual fluids and it looks more like jelly. If this condition is accompanied by the need to change pads frequently, dizziness or weakness, you should be checked for anemia and causes of severe bleeding such as fibroids or adenomyosis.
Ways to diagnose the cause of fleshy blood clot
Diagnosing the cause of uterine fibroids during menstruation requires careful evaluation by a doctor, because this condition may be caused by various factors such as hormonal changes, uterine fibroids or other problems in the reproductive system. The doctor may recommend the following clinical examinations and tests to identify the exact cause. Timely and correct diagnosis plays a key role in choosing the appropriate treatment method, controlling symptoms, and preventing possible complications such as anemia or severe pain. Also, this process can help improve the quality of life and maintain a person's general health.
- Checking the person's symptoms and medical history by a doctor
- Pelvic examination: to check the uterus and other reproductive organs for the presence of fibroids or polyps Ultrasound of uterus and pelvis
- Blood test: evaluation of hemoglobin, iron and hormone levels and identification of coagulation disorders
- Uterine biopsy: Sampling of the inner lining of the uterus to check cell changes
- Hysteroscopy: direct observation of the inside of the uterus using a hysteroscope
Methods of treatment and removal of blood clot during period
Choosing the right method to treat meat clots in menstruation depends on several factors such as underlying causes, severity of symptoms, general health status of the person and age. The doctor can determine the best treatment solution by fully evaluating the patient's condition. The following methods, which include drug treatments, lifestyle changes, and in certain cases, surgery, can help relieve symptoms and treat fleshy clots. Each of these methods should be performed according to the specific conditions of each person and under the supervision of a doctor in order to obtain the desired effectiveness and prevent possible complications.
Various medications such as the following may be prescribed to reduce pain, regulate hormones, and control bleeding. To avoid medication complications, provide your doctor with a list of your medications.- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (NSAIDs): drugs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and mefenamic acid help reduce pain and cramping and reduce the intensity of bleeding
- Hormonal drugs: combined birth control pills and IUD help to reduce bleeding and prevent the formation of fleshy clots by regulating hormones and reducing the thickness of the endometrium.
- Iron supplements: in case of anemia caused by severe bleeding, iron supplements are prescribed
In cases where meat clots are associated with severe and continuous pain and bleeding and other methods are not effective, surgery is recommended. Usually, endometrial ablation, hysteroscopy, or hysterectomy methods are used to treat meatal blood clots. By treating the main causes of meatal blood clots, these methods help reduce symptoms and improve a person's quality of life.
| Treatment method of fleshy blood clot | Examples | Aim or effect |
|---|---|---|
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs | Ibuprofen; naproxen; Mefenamic acid | reducing pain and cramping and reducing the intensity of bleeding |
| hormonal treatments | combined birth control pills; IUD | regulating hormones and reducing endometrial thickness and bleeding |
| anticoagulants in special cases | warfarin; Heparin | When coagulation disorders are the cause according to the doctor's opinion |
| Iron supplement | Iron supplements | Prevention or treatment of anemia caused by heavy bleeding |
| Surgical interventions in resistant cases | Endometrial ablation; hysteroscopy; Hysterectomy | Reduce bleeding by treating the underlying causes when other methods are not effective |
| Assistive measures for pain | 15-20 minute hot water bag | Reduce pain and uterine cramps |
Methods of home treatment of meat blood clot
Home remedies can play an effective role in reducing the symptoms of meatal blood clot and improving the quality of life. These procedures are usually associated with pain relief, inflammation reduction, and hormone regulation. However, home treatment alone is not enough to resolve the underlying causes, and in case of severe or persistent symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Using a hot water bag: To reduce pain and cramping, place a hot water bag on the stomach at intervals of 15 to 20 minutes Herbal teas and medicines: Ginger, cinnamon, chamomile, five fingers, fennel, saffron, and thyme can help regulate menstruation, reduce pain, balance hormones, and reduce blood clots. Of course, these methods have not been scientifically confirmed
- Adequate diet: eating foods rich in iron (such as spinach, lentils, red meat and liver) and vitamin C helps prevent anemia
- Reduce sugar and caffeine consumption: this helps to balance hormones and reduce symptoms
- Light and mild exercise: Exercises such as walking and yoga help reduce uterine pain and cramps and improve blood flow
- Increasing water consumption and staying hydrated: drinking enough water improves blood flow and removes clots more easily
Complications of blood clots during menstruation
Failure to treat a blood clot can lead to serious complications that affect not only the physical health but also the mental health of a person. These clots may aggravate the existing symptoms and cause more problems for the person. In case of lack of attention and treatment, these complications can reduce the quality of life and in some cases, cause fertility problems and mental disorders. For this reason, it is very important to be aware of possible side effects and take timely treatment. The most important complications of these clots are:
- Anemia and its complications: A meat clot is usually associated with severe bleeding, which can lead to anemia if not treated. This condition is associated with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, headache, dizziness and palpitations
- Increasing pain and uterine cramps: the amount of pain can increase to such an extent that it affects a person's daily life
- Abnormal changes in the wall of the uterus: the continuation of meat clots may cause the thickening of the uterine lining and the formation of fibroids and polyps
- Increasing fertility problems: hormonal imbalance and uterine masses reduce the chance of pregnancy and may lead to infertility
- Progress to acute uterine diseases: lack of treatment can aggravate problems such as fibroids, polyps or endometriosis
- Chronic anxiety: constant pain and bleeding can cause severe anxiety and worry and even cause depression
- Complications of untreated infection such as PID and fertility problems
prevention of blood clot during menstruation
Preventing blood clots during menstruation can help reduce discomfort and maintain body health. Of course, not all cases can be prevented, because some causes, such as fibroids or adenomyosis, are related to the structure of the uterus. But by managing severe bleeding and early identification of the underlying causes, it is possible to prevent the recurrence of severe periods and blood clots and anemia. Regular follow-up plays an important role in prevention if cycles have become irregular or bleeding has recently changed. These solutions are possible by adjusting the lifestyle and following a few simple points such as the following:
- Stress management and hormonal balance: Stress can cause hormonal changes and increase the possibility of developing meat clots. Activities such as yoga and meditation help reduce stress and balance hormones
- Regular physical activity: light activities such as walking and aerobic exercises reduce the possibility of large clots by improving blood flow
- Balanced diet: consuming iron and fiber is useful for maintaining hormonal balance and preventing anemia
- Avoidance of smoking and alcohol: this helps to maintain hormonal balance and the health of the vascular system
- Timely treatment of genital infections and compliance with safe sex
- Checking thyroid and coagulation disorders in case of family history or related symptoms
- Avoid self-medication with hormonal and anticoagulant drugs without a doctor's opinion
Which doctor should we see for blood clot during period?
For more information about blood clots during periods, you can make an appointment with the best gynecologist in Iran. In the following, you can see a list of the most prominent women's doctors in different cities of Iran.
Conclusion
Blood clots during periods can be normal in many people, especially in heavy bleeding, but fleshy or large clots become important when the period pattern has changed or there are warning signs. If you are asking yourself what are the signs of a heavy period, the answer depends on the intensity of bleeding, pain, bad smell, fever, possibility of pregnancy and recurrence in several cycles. Instead of worrying or self-medicating, the best thing to do is to get a professional checkup if the discharge of a blood clot is new, severe, or recurring. Correct diagnosis prevents anemia and severe bleeding complications, and if there are causes such as fibroids, adenomyosis, infection or pregnancy problems, it enables timely treatment.
Your doctor takes care of your health!