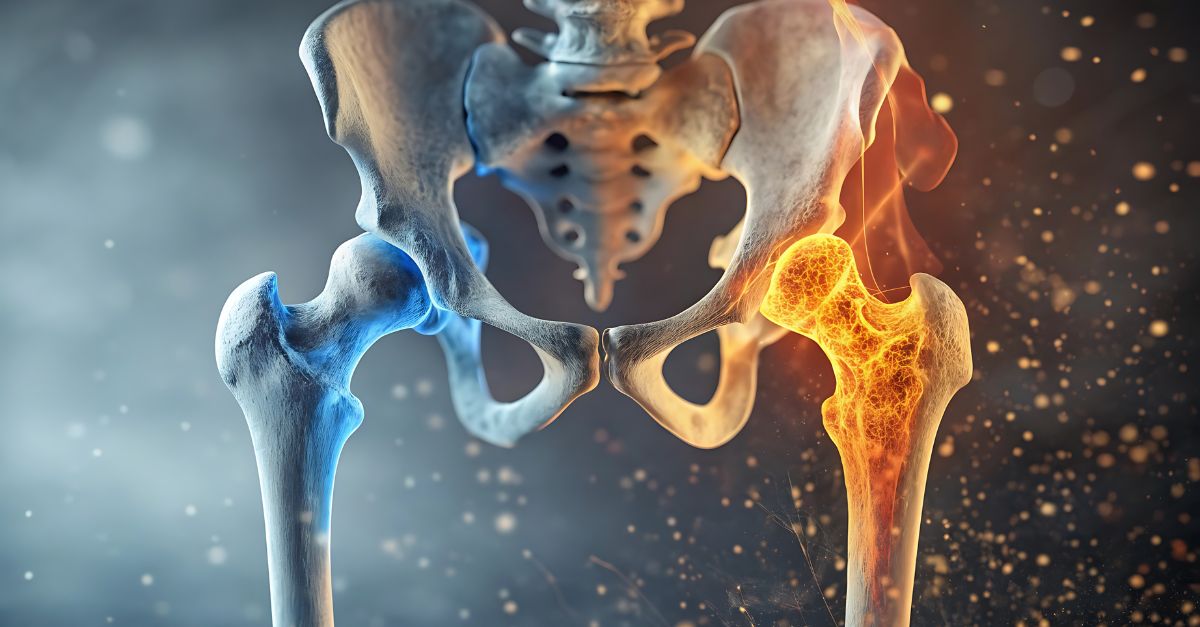
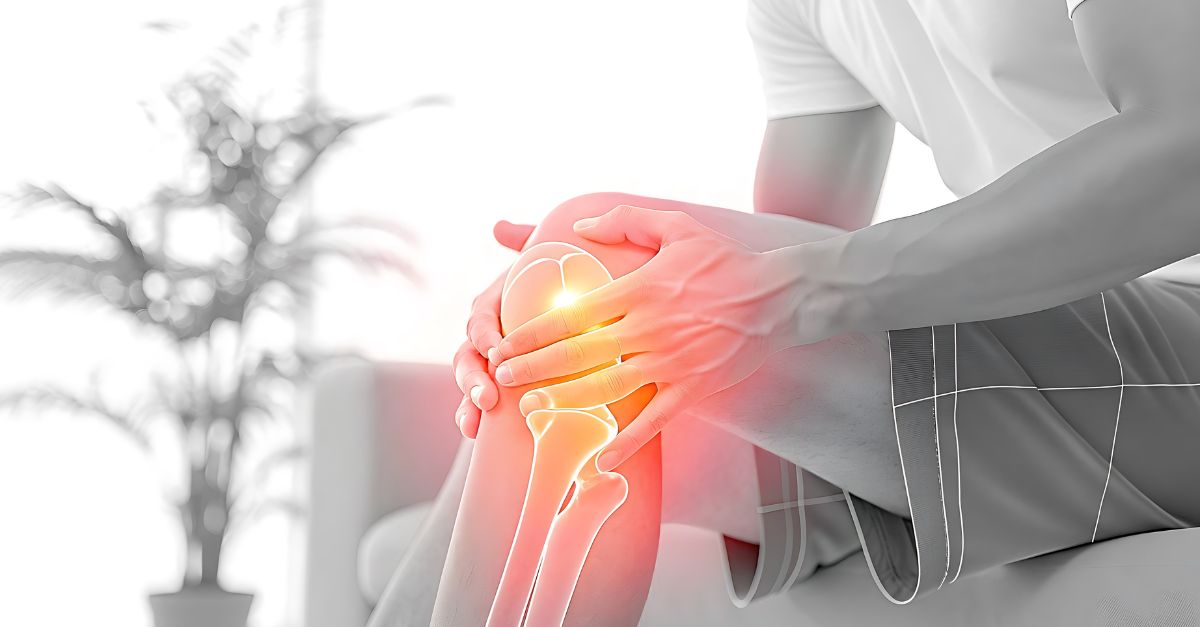
پوکی استخوان (Osteoporosis) یکی از شایعترین بیماریهای استخوانی در جهان است که بهتدریج باعث کاهش تراکم و استحکام استخوانها میشود. این بیماری معمولاً بدون علامت آغاز میشود و تا زمان بروز شکستگی، بسیاری از افراد از وجود آن بیخبرند. Osteoporosis is actually a "silent disease" that, if not diagnosed and treated in time, can lead to dangerous fractures in the spine, hip, and wrist.
What is osteoporosis?
In the human body, bone tissue is always being regenerated; Cells called osteoblasts build new bone and osteoclasts break down old bone. Normally, these two processes are in balance. But in osteoporosis, bone breakdown is more than its production, as a result, the bones become thin, porous and fragile.
In affected individuals, even light blows or simple movements such as bending or lifting light objects can cause bone fractures. Most fractures occur in the hip, spine and wrist areas.
causes of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can occur due to several factors. Some of the most important risk factors are:
- Aging: With age, the production of bone-forming cells decreases and the risk of osteoporosis increases.
- Decreasing sex hormones: In women, the decrease in estrogen levels after menopause is one of the most important causes of osteoporosis. In men, testosterone reduction has a similar effect.
- Deficiency of calcium and vitamin D: These two substances are vital for the formation and maintenance of healthy bones. Their lack causes bone weakening.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and regular exercise reduces bone density.
- Cigarettes and alcohol: Both factors interfere with calcium absorption and reduce the function of bone-forming cells.
- Underlying diseases: Thyroid problems, kidney diseases, or long-term use of corticosteroids can cause osteoporosis.
symptoms of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis has no symptoms in the early stages and is usually diagnosed when a person suffers a fracture. However, some warning signs may include:
- Decrease in height over time (due to the compression of the vertebrae of the spine)
- Bending or hump in the back (kyphosis)
- Chronic back or neck pain
- Bone fractures with slight blows or falls
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
The best way to diagnose osteoporosis is bone density scan (DEXA Scan). This non-invasive test measures bone mineral density in areas such as the pelvis and spine. The results are reported numerically (T-score):
- T-score between +1 and -1 → normal
- T-score between -1 and -2.5 → decrease in bone density (osteopenia)
- T-score less than -2.5 → osteoporosis
To find the cause of the disease, the doctor may also prescribe blood tests to check the level of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin D and hormones.
treatment of osteoporosis
Osteoporosis treatment is done with the aim of strengthening the bones, preventing fractures and slowing down the process of bone loss. Treatment methods include the following:
1. Drug therapy
- Bisphosphonates: such as alendronate and risedronate, which prevent bone destruction by reducing the activity of bone-eating cells.
- Hormonal therapy: In postmenopausal women, estrogen or hormone-like drugs are sometimes used to maintain bone density.
- Newer drugs: such as Denosumab (Denosumab) or Teriparatide (Teriparatide), which stimulate bone formation.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements: are necessary to support drug treatment and increase bone resistance.
2. lifestyle modification
- Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, cycling or yoga to strengthen bones
- Stop smoking and limit alcohol consumption
- Nutrition rich in calcium (milk, yogurt, green vegetables, almonds, sardines)
- exposure to sunlight for natural absorption of vitamin D
3. Prevention of falls
In elderly patients with osteoporosis, prevention of falls is very important. Using the right shoes, installing a fence in the bathroom, having enough light in the house and maintaining balance while walking are important safety tips.
The difference between osteoporosis in men and women
Osteoporosis is much more common in women, especially after menopause, because the decrease in the hormone estrogen accelerates the process of bone loss. However, men may also suffer from this disease in old age or as a result of testosterone deficiency, corticosteroids or chronic diseases. Early diagnosis and preventive care are essential for both sexes.
prevention of osteoporosis
Prevention is always better than cure. To maintain bone health at any age, the following are recommended:
-
Adequate daily intake of calcium (1000 to 1200 mg) and vitamin D (800 international units)
- Regular exercise at least 30 minutes a day
- Avoid smoking, hookah and alcohol Periodic examination of bone density in women over 50 years old and men over 65 years old
- Maintaining a healthy weight and a balanced diet
final summary
Osteoporosis is a silent but preventable disease. Early diagnosis and compliance with nutritional and exercise tips play an important role in preventing bone fractures. If you have a history of osteoporosis in your family, or if you suffer from inactivity, menopause, or long-term use of corticosteroids, be sure to consult an orthopedic or rheumatology doctor to check your bone density to make sure your body's skeleton is healthy. Healthy bones are a solid pillar for an active and pain-free life.