What you should know about the prostate!
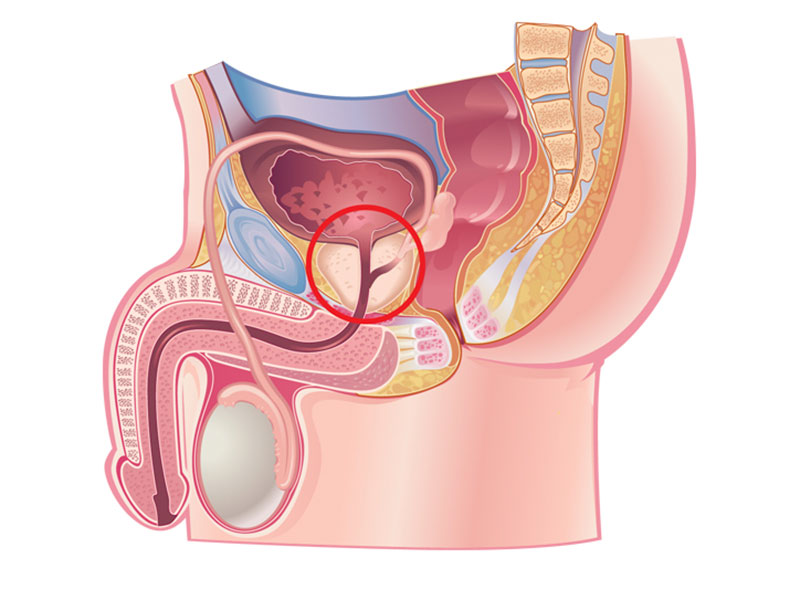
What is the prostate? class="ez-toc-section-end">Prostate (in English: Prostate) is an important gland in the male reproductive system. If healthy and in men younger than 50, it is usually the size of a walnut and weighs about 0.75 ounces.
This gland is located in the abdomen, in front of the rectum and between the penis and the bladder. It consists of connective tissue and glandular tissue. The prostate gland adds fluid to the semen, and its muscles help the semen pass through your urethra.
Ejaculation is a grayish-white fluid that comes out of your penis during orgasm. This fluid contains enzymes, zinc, and citric acid that help nourish sperm cells and lubricate your urethra. The urethra is the tube through which ejaculation and urine leave your body.
Your prostate muscles also help push semen into and out of your urethra during orgasm.
This gland is involved in male fertility and fluid It makes and secretes the prostate, which is part of the semen.
Do women have prostate?
No, women do not have a prostate. Women have Skene glands. However, some people call skin glands as female prostate gland.
Skin glands are located on both sides of the urethra. Medical researchers believe that these glands may secrete a fluid that aids urination (urination) and cleanliness. They may also have a sexual function, possibly providing female ejaculate.
- Location: Your prostate is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Your urethra passes through the center of your prostate.
- Figure: This gland of yours has five lobes: an anterior lobe (in front) and a posterior lobe (in back), two lateral lobes (on the sides), and a medial lobe (in the middle). Connective tissues and glandular tissues form its structure. Fascia covers your prostate. Fascia is a sheet of elastic connective tissue.
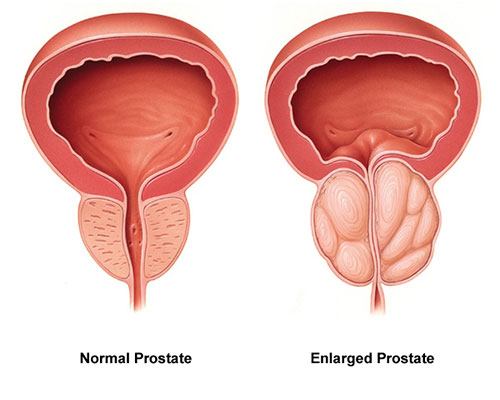
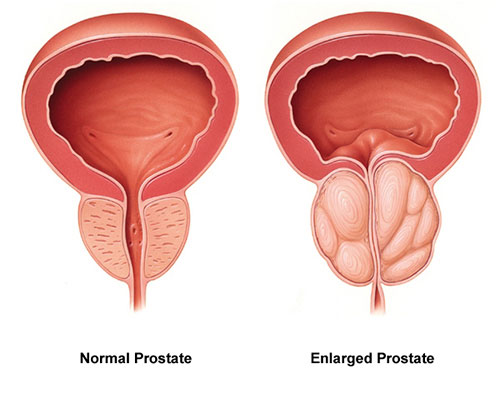
- Size: Your prostate is about the size of a walnut. This gland usually becomes larger after the age of 40 (benign prostatic hyperplasia) and can grow from the size of a walnut to the size of a lemon. This disease is not cancerous and does not increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Weight: It weighs about 30 grams.
What is prostatic fluid?
During ejaculation, sperm move from the testes and through a series of tubes. This causes the muscles of this gland in the urethra to contract, blocking the urethra from any urine passing through it. Then the semen can enter the urethra and the prostate fluid is released and mixed with the semen from the testicles.
This fluid contains an enzyme called prostate-specific antigen (PSA). PSA helps to thin the semen. It also contains enzymes, citric acid and zinc. This specific antigen is one of the parts of semen that helps protect sperm. In particular, semen is chemically basic. It helps sperm to live longer in the vagina and contains fluids that are chemically acidic.
Types of prostate diseases
There are several diseases that can affect this gland, including:
- Greatness Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a condition that occurs when the prostate becomes enlarged. This process happens with age. The reason this is important is that enlargement can start to irritate the bladder or partially block the urethra. This may make it more difficult to pass urine.
- Inflammation Prostate or prostatitis: Four different conditions of prostatitis cause inflammation in your gland:
Warning signs class="ez-toc-section-end">
Common warning signs include:
- existence Blood in the urine
- Examination Digital rectal. Your healthcare provider will insert a gloved, lubricated finger into your bowel and feel your prostate gland. Bumps or hard areas may indicate cancer.
- Prostate specific antigen blood test. Your prostate makes a protein called protein-specific antigen (PSA). Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer. PSA levels may also be elevated if you have BPH or prostatitis.
- Biopsy. Your healthcare provider will use a needle to take a sample of tissue from this gland. A health care provider examines the sample under a microscope in a laboratory.
Treatment depends on the type of your disease.
Prostate cancer
- Active surveillance. You get screenings, scans, and biopsies every one to three years to monitor for cancer growth.
- Brachytherapy. Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy. Your healthcare provider will place radioactive seeds into your prostate. The seeds help to maintain the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Focal therapy. Focal therapy focuses on treating only the cancerous area of your gland. Focal treatment options include high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), cryotherapy, laser ablation, and photodynamic therapy (PDT).
- can remove the obstructive prostate tissue that blocks the flow of urine.
- Hydrotherapy. A health care provider inserts an instrument through your urethra and into your prostate. This steam tool emits steam that kills the cells of this gland and shrinks your prostate.
Help keep your gland healthy by doing the following:
- Regular prostate screening. Most people should start screening at age 50. If you have a family history of prostate cancer, it's a good idea to start screening at an early age.
- Regular exercise. People who are more physically active are less likely to get BPH.
- Eating a healthy diet. Eating the recommended amount of fruits, vegetables, and healthy protein may help keep this gland healthy.
- Quit tobacco products. Tobacco products may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the prostate?
The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system that is located under the bladder and produces part of the seminal fluid.
What is the role of the prostate gland in the body?
The prostate secretes a liquid that helps in the nutrition and movement of sperms and plays a vital role in male fertility.
What is the normal size of the prostate?
In adult men, the normal size is about the size of a walnut and about 20 to 25 grams.
What changes occur in the prostate with age?
As we age, it usually increases in size, which can lead to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
What diseases may affect the prostate?
The most common diseases related to the prostate are: benign prostate enlargement, inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) and prostate cancer.
What are the warning signs of prostate problems?
Symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting to urinate, decreased urine flow pressure, pelvic pain, or blood in the urine can be signs of prostate problems.
When should you visit a doctor to check your prostate health?
If you see any unusual urinary symptoms or after the age of 50 (or earlier if you have a family history), it is necessary to see a doctor.