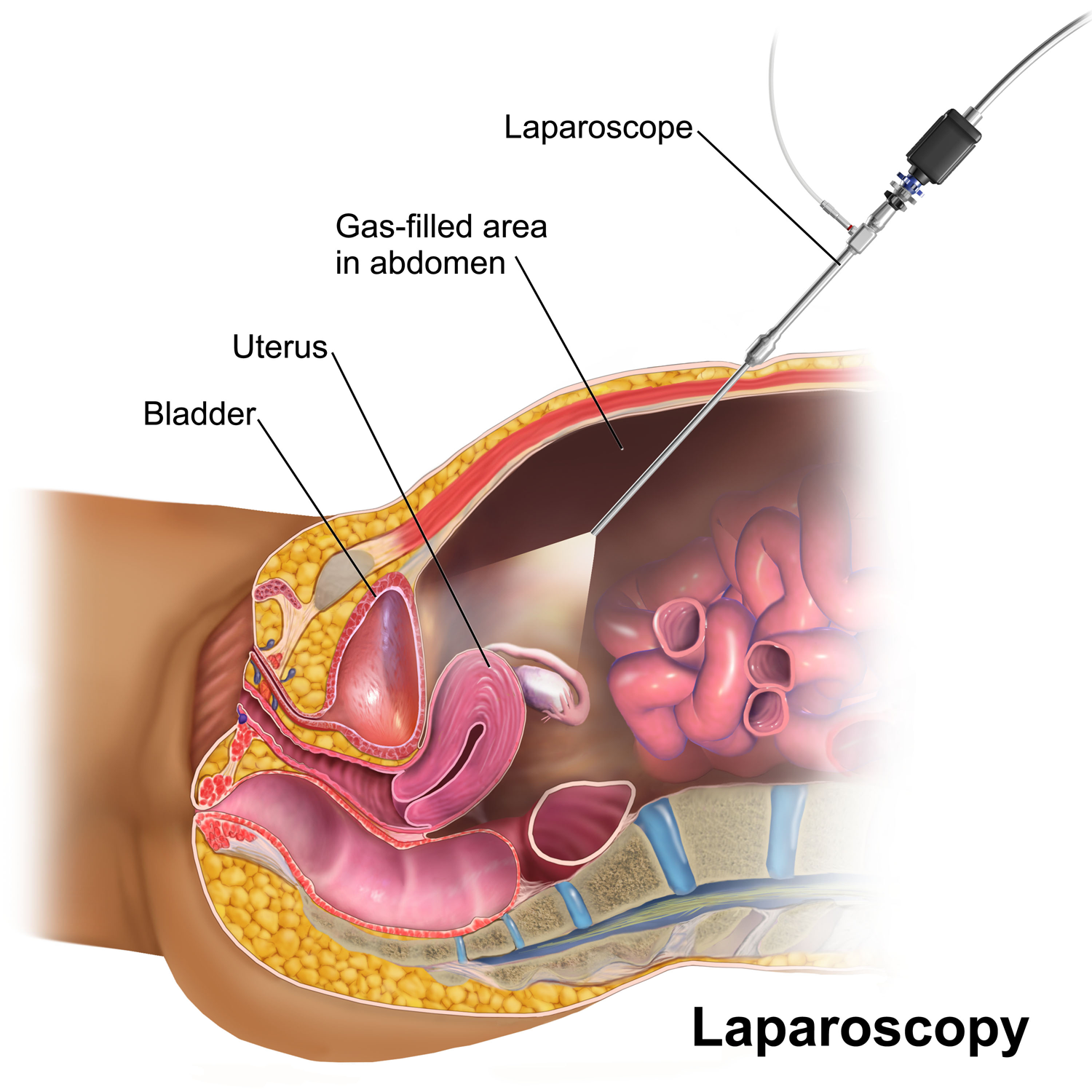
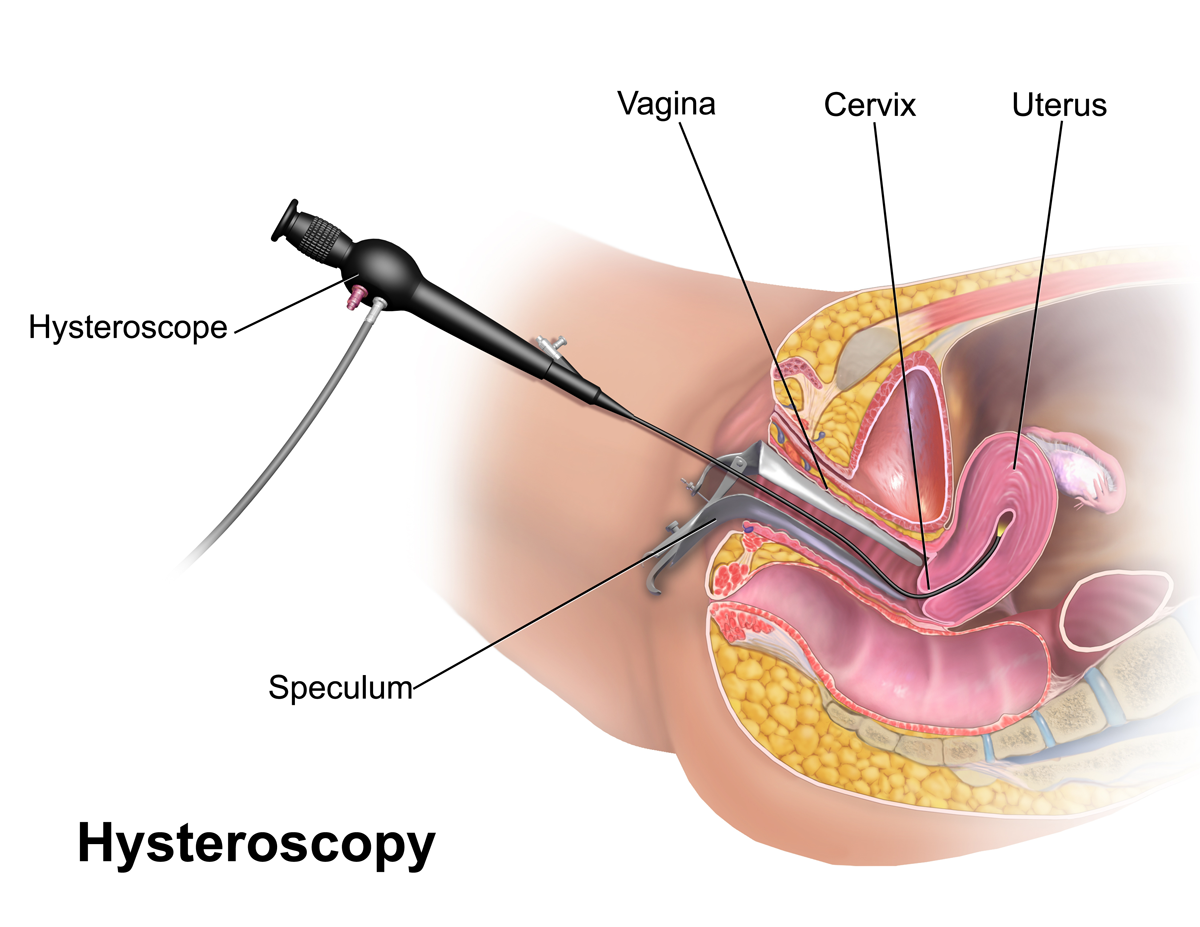
Pregnancy care
Pregnancy care includes visits that are made regularly and at regular intervals for pregnant women. The aim of these cares is to reduce maternal and infant mortality and reduce pregnancy complications. Studies have shown that if care is not used during pregnancy, the rate of premature birth doubles. The rate of stillbirth when using prenatal care is 2.7%, while it is about 14.1% in women who do not use prenatal care.
Also, in cases of using pregnancy care, the rate of infant death due to placental abruption, fetal growth restriction and post-term pregnancy is reduced. The first step in prenatal care is pregnancy diagnosis. Women usually come with symptoms of pregnancy and possibly with a positive result of the administrative test. Blood test (BHCG) is also used to fully confirm pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
1. Amenorrhea or cessation of menstrual cycle in women who had regular monthly period. Of course, a little bleeding may happen to the mother in the first months of pregnancy, which is a sign of the implantation of the fetus. In the 12th week of pregnancy, the uterus enters the abdomen in a spherical shape from the pelvis.
3. Changes in the breast and skin
Increased pigmentation (darkening and yellowing of the breast) and changes in the appearance of abdominal striae (abdominal cracks) are seen in pregnancy.
4. Fetal movement
In the first pregnancy, the mother feels the first movements of the fetus between 18 and 20 weeks. From the second pregnancy onwards, the mother can feel the movements of the fetus between the 16th and 18th week.
Diagnosis of pregnancy with ultrasound
With transvaginal TVS ultrasound, the gestational sac can be seen in 4-5 weeks of pregnancy. The yolk sac can be seen in the middle of the fifth week, and the fetus with a heartbeat can be seen in the sixth week. Abdominal ultrasound can see the heartbeat of the fetus in the 7th week.
Duration of normal pregnancy
The average duration of pregnancy calculated from the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) is nearly 280 days or 40 weeks. One of the methods of determining the expected time of delivery is adding 7 days to the date of the first day of the last natural period and subtracting three months from the date. For example, if a woman's last period started on January 20th, the time used for giving birth is considered to be October 27th of the following year.
Pregnancy trimesters
Pregnancy period is divided into 3 equal trimesters, each of which is 14 weeks. The first trimester is up to the end of the 14th week, the second trimester is up to the end of the 28th week, and the third trimester is up to the 29th week to the 42nd week of pregnancy.
Previous and current health status
A detailed history of medical diseases and surgical history should be obtained from the pregnant woman.
Also, we must have detailed information about the previous birth because there are many complications of the previous pregnancy. They usually recur in subsequent pregnancies.
Using tobacco and alcohol during pregnancy
Using tobacco has definite adverse consequences. The risk of placenta previa, placental abruption, and premature rupture of the water sac is doubled in women who smoke.
Babies born to smoking mothers are more likely to be born prematurely, have low birth weight, and sudden infant death syndrome.
Also, the risk of miscarriage and fetal death and fetal finger abnormalities increases in smoking mothers.
In addition Children who were in contact with tobacco during intrauterine life are at an increased risk of asthma, colic in infants and childhood obesity.
If smoking is stopped early in pregnancy or preferably before pregnancy, the best results will be achieved and smoking cessation at any stage of life improves maternal and fetal outcomes.
Alcohol consumption causes fetal alcohol syndrome. Its characteristics include facial deformity and anomalies, dysfunction of the central nervous system, and fetal growth restriction. Pregnant women or women who intend to become pregnant should avoid consuming any alcoholic beverages.
Also, the use of heroin and other narcotics, cocaine, amphetamines, and marijuana (flower) is very dangerous for the mother and the fetus. right;">1. Full medical history and general physical examination of the pregnant woman (including blood pressure, weight, pelvic examination, uterine height and fetal heart rate)
2. Gestational age check
3. Laboratory test including: blood cell count, blood group and RH, HIV Ab antibody screening, hepatitis B, syphilis and immunity against rubella, urine test and urine culture, fasting blood sugar (FBS) and TSH thyroid test
4.Pregnancy risk assessment
There are many factors that can have an adverse effect on the health of the mother or the fetus and cause a so-called "high-risk pregnancy". Some of the most important factors include (some of the most important factors are fully explained in the high-risk pregnancies article. )
Heart disease, diabetes mellitus, family or personal history of genetic disorder
high blood pressure, kidney failure,
lung diseases, AIDS, history of pulmonary embolism or deep vein thrombosis, autoimmune disorders, weight loss surgery (bariatric), epilepsy, cancer, structural or chromosomal disorders of the fetus in the past or present, contact with harmful drugs. teratogen), infection or contact with microorganisms that cause congenital infection, multiple pregnancy, severe amniotic fluid volume disorders
In some of the cases mentioned, it may be necessary to involve maternal-fetal medicine specialists, geneticists, pediatricians, anesthesiologists or other medical specialists in the process of examining and caring for women and their fetuses.
Contact number: 02166933869 and 02166933906
Online consultation at WhatsApp Messenger
Thank you site management Hera Clinic