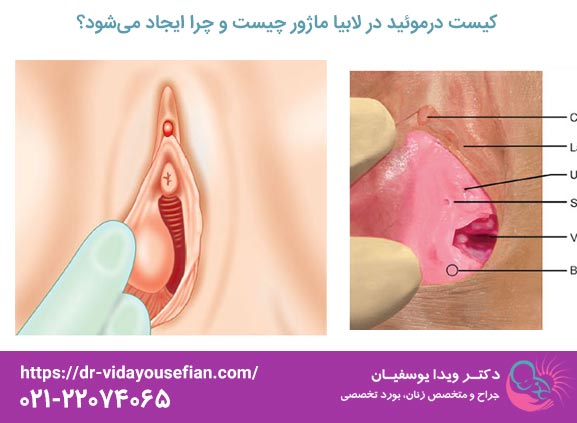
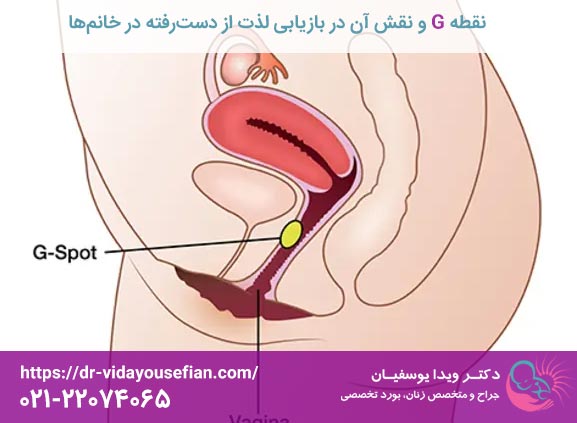
کیست درموئید (Dermoid Cyst) یکی از انواع نادر تودههای خوشخیم (Benign) در ناحیه تناسلی زنان است که اغلب در بافتهای نرم لابیا ماژور (لب بزرگ دستگاه تناسلی) مشاهده میشود. این تودهها از نظر ریشهشناسی، منشأ اکتودرمی دارند و در حقیقت تومورهای مادرزادی یا تکاملی محسوب میشوند که به دلیل باقی ماندن سلولهای نابهجای بافتی در مسیر رشد غدد جنینی ایجاد میگردند.
ماهیت اصلی کیست درموئید در محتویات غیرعادی آن نهفته است. برخلاف کیستهای ساده که تنها حاوی مایع شفاف هستند، کیستهای درموئید حاوی ترکیبات بافتی متنوعی هستند که از سه لایه زایا (اکتودرم، مزودرم و اندودرم) مشتق شدهاند. این محتویات میتواند شامل موارد زیر باشد:
- بافتهای پوستی: شامل فولیکولهای مو، غدد چربی (سباسه)، غدد عرق و کراتین بیش از حد.
- بافتهای سخت: در موارد نادر، ممکن است حاوی بقایای بافت دندانی یا قطعات کوچک استخوانی باشند.
- مایع غلیظ: ترکیبی از چربی، سبوم و سلولهای مرده پوست.
از منظر پاتولوژی، این کیستها همیشه خوشخیم هستند و خطر تبدیل شدن به سرطان (بدخیمی) در آنها بسیار پایین است (کمتر از ۲٪ موارد گزارش شده). Their growth is usually slow and gradual, and they may remain asymptomatic in the genital area for years until they grow to a size that causes physical discomfort or cosmetic concern. These cysts have a distinct capsular wall that needs to be completely removed to prevent recurrence.
The main root of the formation of dermoid cysts goes back to developmental abnormalities during the fetal period. During fetal development, cell migration and the formation of reproductive structures must be done precisely. A dermoid cyst is formed as a result of the entrapment or retention of stem or epithelial (skin) cells in the path of cell migration or tissues that should not be there.
More precisely, these cysts arise from primordial cells that have the potential to give rise to all tissue components. In the area of the labia majora, these cells may begin to produce and secrete skin substances (such as fat and hair) due to defects in normal development and accumulate in an enclosed structure (capsule).
Accelerating factors or factors that cause the cyst to appear (even if it is congenital):
- Hormonal changes: Extreme hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation or pregnancy can stimulate the activity of the glands in the cyst and accelerate its growth.
- Local trauma (injury): Repeated blows or injuries from childbirth, rough waxing, or old surgical incisions in the perineum can stimulate latent cells and activate cyst growth.
- Chronic inflammation: Long-term inflammatory conditions in the surrounding tissues may act as triggers.
- Genetic factors: Although a strong genetic link has rarely been proven, certain syndromes that affect tissue development may increase the risk of developing congenital masses.
In clinical practice, most dermoid cysts diagnosed in adult women are cysts that have been present since birth but are not noticed until puberty or even later (in the 30s and 40s) due to slow growth.
Dermoid cyst of the labia majora is often a "silent" lesion and does not cause any specific symptoms. Symptoms appear when the cyst becomes large enough or becomes complicated.
The most important clinical findings are:
- Existence of a palpable mass: The patient or doctor feels a subcutaneous mass on one side of the labia majora.
- Consistency and Appearance: The mass is usually firm but slightly elastic (not quite firm like bone, not quite sac like a Bartholin's cyst), round or oval and often mobile (ie not attached to deeper tissues).
- Initial Painlessness: Normally, these cysts are not painful because they are not infected or inflamed.
- Slow growth: Patients often notice that the lump has become slightly larger over several months or years.
- Infection (rare): If the contents of the cyst become inflamed or infected, symptoms similar to an abscess appear: severe redness (erythema), swelling, increased local heat, acute pain, and sometimes pus discharge.
- Pressure and discomfort: If the cyst grows to the size of a walnut or larger, it can cause mechanical pressure and discomfort when walking, wearing tight underwear, or during intercourse (dysparony).
- Change in appearance (Cosmetic Concern): In many cases, the main motive for referral is concern about the asymmetry created in the genital area.
Dermoid cyst with other similar masses in the genital area
The female external genital area is susceptible to various types of masses. Accurate differential diagnosis is critical for choosing the appropriate treatment method. The following table shows the key differences between the most common masses:
Type of mass, origin and main characteristic, common location, consistency, usual risk of malignancy, dermoid cyst,embryonic origin, containing hair, fat, hard tissue of the labia majora (usually one-sided), firm, relatively mobile, very low Bartholin's cyst,obstruction of Bartholin's gland duct, entrance to vaginal vestibule (near 4 or 8 o'clock), soft, not filled with fluid Epidermoid Cyst (Sebashe) Entrapment of superficial skin cells anywhere on the skin of the genital area is soft, sometimes it does not have a central black dot (exit point) Lipoma (fat mass) Benign tumor of fat tissue in subcutaneous areas and more fat tissue is very soft, "pasty" and cannot be pressed easily Fibroma or submucosal tumor Connective tissue Fibrosis of the deeper areas of the labia or the pelvis is very hard and not deformable very rarely
Clinical diagnosis usually begins with palpation of the mass; A firm mass with the possibility of hair or hard material is highly suspicious for dermoid, while a mass that is only at the entrance to the vagina and very painful is often an infectious Bartholin's cyst.
- Anesthesia: Depending on the size and depth of the cyst, local anesthesia (for small and superficial masses) or light general anesthesia (for larger masses or in cases where the patient has severe anxiety) can be used.
- Skin incision (Incision): The surgical incision must be made very carefully and usually along the natural lines of the skin (Langer's lines) in the labia majora. The goal is to create the least possible scar.
- Dissection: Using delicate tools, the surgeon must separate the cyst from the surrounding healthy tissues (fat, superficial muscles). The most important step is to maintain the complete integrity of the cyst capsule. Rupture of the capsule causes fatty contents and hair to enter the subcutaneous space and lead to severe inflammatory reaction or local recurrence.
- Closure and repair: After ensuring complete resection, the remaining cavity is carefully sutured. In labia majora, it is very common to use very fine and absorbable sutures (such as nylon or polyglactin) to achieve an optimal aesthetic result.
The recovery period is usually short, but strict adherence to the instructions is necessary to avoid complications:
- Medication: Taking antibiotics to prevent infection (especially in the sensitive genital area) and anti-inflammatory/analgesic drugs as prescribed by the doctor.
- Wound care: The area should be kept clean and dry. Washing should be done with lukewarm water or very mild antiseptic solutions prescribed by the doctor.
- Activity restriction: Avoiding intense activities, lifting heavy objects, strenuous sports and especially sexual activity (vaginal and external) for a period of at least 3 to 6 weeks until the underlying tissues are fully restored.
- Prohibited pressure: The patient should avoid sitting for a long time or applying direct pressure on the operated area as much as possible.
(Cosmetic Reconstruction)
In cases where the cyst is very large and its removal leads to significant indentation or asymmetry in the labia majora, plastic surgeons or aesthetic gynecologists can use auxiliary methods:
- Repair with the patient's own fat tissue (Fat Grafting): Fat is taken from another area of the body and injected into the sunken area to compensate for the lost volume and restore symmetry.
- Laser use: After the initial wound is completely healed, skin lasers can be used to improve the quality and reduce the redness of the remaining scar.
Many skin masses are treated by the public with traditional or home remedies, which are completely ineffective or dangerous in the case of dermoid cysts:
- Warm compresses and massage: These methods are useful for improving blood flow and reducing inflammation in sebaceous gland cysts, but they cannot destroy the cells that make up a congenital dermoid cyst. This only leads to more irritation and the possibility of capsule rupture.
- Aspiration with a needle: Evacuation of the liquid or fatty contents of a dermoid cyst with a needle is almost always associated with failure. If the contents contain hair or hard substances, it is impossible to empty. In case of incomplete evacuation, the cyst wall will remain and the cyst will form again (recurrence).
- Using ointments or topical medications: There is no known topical medication that can penetrate deep into the labia tissue and destroy the cyst capsule.
Strict advice: Any pressure, bursting or draining of a dermoid cyst by a non-specialist can lead to its transformation into a severe infection, fistula formation or permanent and deformed scar.
Effects Psychological and sexual presence of mass in the genital area
The genital area is a very sensitive area psychologically and emotionally. The presence of an abnormal protrusion, although benign, can have significant negative effects on the patient's mental health:
- Decreased self-confidence and anxiety: Patients may feel that their genitals are "defective" or "sick", which causes severe anxiety, especially at a younger age or before sexual intercourse.
- Avoidance of examination: Fear of the doctor's judgment or facing the nature of the mass causes a delay in referral and diagnosis.
- Effect on sexual function (Dyspareunia): If the cyst is large, pressure during intercourse can be painful and make sexual intercourse difficult or impossible.
The doctor should provide a safe and non-judgmental environment and reassure the patient that these conditions are relatively common and treatable. Psychological counseling before and after surgery can be very effective in restoring a positive body image.
Since the dermoid cyst is an evolutionary and congenital lesion, it is not possible to prevent its "formation" in the basic state. However, factors that cause activation or inflammation of existing cysts and prevent the formation of similar cysts (such as epidermoid cysts) can be avoided:
- Gentle hygiene: Washing daily with lukewarm water and mild detergents and keeping the area dry after washing.
- Avoidance of mechanical irritation: Limit the use of very tight underwear, clothing containing synthetic fibers and reduce irritation from intense sports or long-term cycling.
- Hair removal methods: The use of hair removal methods (such as waxing or laser waxing) should be done carefully to avoid damage to the hair follicles and the possible trapping of cells in the lower layers of the skin.
- Periodic examinations: Regular female examinations (Pap smear and pelvic exam) provide an opportunity to detect any new lumps in the early stages.
Choosing a doctor for dermoid cyst surgery in the labia majora is crucial, because this area has a very high functional and aesthetic importance.
The doctor's role includes the following:
- Precise diagnosis: Differentiate between dermoid, Bartholin cyst, abscess and other masses.
- Conservative surgical planning: While complete excision is essential, the surgeon should employ techniques that cause minimal damage to healthy tissue.
- Aesthetic Approach: A skilled surgeon must not only remove the cyst completely, but also ensure that the sutures are placed in such a way that the natural symmetry of the labia majora is preserved and deep scarring is minimized. This skill becomes more important in cosmetic reconstructive surgeries.
1. Can dermoid cyst be treated with laser?
no Laser is a thermal tool and is not effective for removing subcutaneous structures such as cysts. Although laser can be used after surgery to improve the quality of scars, the main treatment should be excision surgery.
2. Is there a possibility of recurrence?
Only if the surgery is performed incompletely and a part of the capsule (especially the parts containing stem cells) remains in the body, there is a possibility of recurrence. With the complete removal of the capsule, the chance of recurrence is almost zero.
3. What is the difference with Bartholin's cyst?
Bartholin's cyst is a glandular cyst that occurs as a result of obstruction of the duct of one of the two Bartholin's glands (near the opening of the vagina). Its contents are usually mucous fluid and become very painful when infected. The dermoid has an embryonic origin, it is often located in the deeper tissue of the labia majora, and its contents are more complex.
4. Does a scar remain after surgery?
Yes, every skin surgery leaves a scar. But with modern surgical techniques, fine incisions, and the use of absorbable sutures in the underlying layers, the scar left behind is very small, thin, and often barely noticeable within months, especially if the incisions are made along natural skin lines.
Final summary class="ez-toc-section-end">
A dermoid cyst of the labia majora is a rare but manageable finding in women. Its benign nature should not be ignored; Because secondary complications such as infection and physical discomfort are predictable. Accurate diagnosis through imaging and the final treatment, which is surgical removal of the complete capsule, completely resolves this problem. The success of the treatment depends not only on the removal of the mass, but also on the skill of the surgeon in maintaining the beauty and symmetry of the genital area. Awareness and timely referral to an experienced gynecologist is the key to achieving satisfactory therapeutic and cosmetic results.