Hysterectomy what is it Types, uses, complications and post-operative care
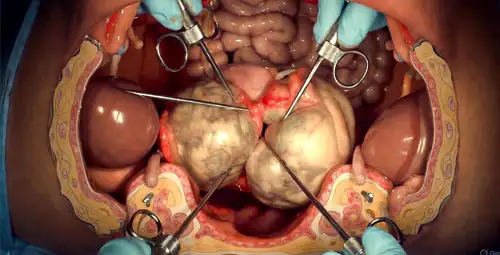
What is hysterectomy? Hysterectomy is a surgery in which part or all of the uterus is removed from the patient's body. This operation is one of the most common surgeries among women. The doctor chooses this method when minimally invasive or drug treatments are not effective. In this surgery, the cervix, ovaries and fallopian tubes may be removed. Deciding on this depends on the results of the tests and the decision of the specialist doctor.
The applications of this operation include a wide range of benign and malignant diseases; including treatment-resistant uterine fibroids, severe abnormal bleeding, advanced endometriosis, uterine prolapse and some cancers of the female reproductive system. Choosing the type and method of surgery depends on factors such as the age of the patient, the desire to maintain hormonal function, the severity of the disease and the risk of malignancy. These complications can include short-term problems such as pain, infection, and bleeding, as well as long-term consequences such as hormonal changes or impact on quality of life. For this reason, post-operative care and informed decision-making with the expert doctor's opinion play a key role in improving the treatment results. 600;">
What is hysterectomy?
Definition of hysterectomy in plain language
What is hysterectomy? It is a surgical operation in which the uterus is completely or partially removed from the body. The uterus is an organ that plays a major role in menstruation and pregnancy; Therefore, after doing it, the possibility of pregnancy is permanently lost. This surgery can be performed for various therapeutic reasons and is usually recommended when other treatment methods such as drug therapy or minimally invasive interventions have failed to control the patient's symptoms.
This operation may be used as a definitive treatment for chronic uterine problems, or as part of the treatment of malignant gynecological diseases. Deciding to perform this surgery requires a detailed assessment of the patient's condition, age, clinical symptoms, and treatment goals.
What parts of the uterus does hysterectomy include?
Depending on the type, Different parts of the female reproductive system are removed. In general, this practice includes two main models. It is a type of total hysterectomy in which the uterus and its opening are completely removed. The second type is subtotal or partial, in which the surgeon only removes the uterus, but the cervix is preserved.
In some special cases, especially in malignant diseases, a radical type is performed, in which, in addition to the uterus and cervix, surrounding tissues and parts of the vagina are also removed.
A hysterectomy may also be performed along with the removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This decision has a direct impact on the patient's hormonal status and can lead to surgical menopause. The choice of surgical extent depends on the doctor's diagnosis and the patient's clinical conditions, and plays an important role in the occurrence or prevention of hysterectomy complications.
Does menstruation continue after hysterectomy?
After the procedure, menstruation stops permanently, because the uterus, which is the source of monthly bleeding, no longer exists. does not have Even in cases where the cervix is preserved, menstruation will not occur. In some surgeries, the ovaries are kept in the body. In this case, it is likely that the natural symptoms and effects of hormones will continue in the body.
On the other hand, if the ovaries are removed, menopause will occur immediately after the surgery, which can be accompanied by symptoms such as hot flashes and mood changes. Awareness of this issue is very important to reduce the anxiety of patients and to properly manage complications.
Why is hysterectomy performed?
Common reasons for performing hysterectomy and target groups
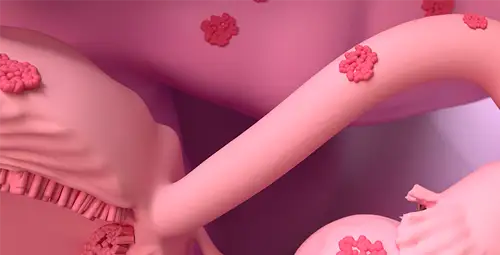
This surgery is recommended when Uterine problems can cause a significant disruption in the patient's health or quality of life. The most common reasons for performing this procedure include symptomatic uterine fibroids, abnormal and severe uterine bleeding, advanced endometriosis, adenomyosis, chronic pelvic pain, and uterine prolapse. In these conditions, the symptoms may not respond to drug treatments or minimally invasive methods, and the continuation of the disease brings the risk of anemia, chronic pain, or reduced daily functioning.
In addition to benign diseases, hysterectomy plays an important role in the treatment of some malignancies such as cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and in certain cases, ovarian cancer. The diagnosis of this group of diseases in the patient can convince the doctor of the need for hysterectomy.
When is hysterectomy the last treatment option?
In many cases, this solution is proposed as the last treatment option when conservative methods such as drug therapy, hormonal treatments or Minimally invasive interventions have failed to control symptoms or the disease has relapsed. Also, in patients who do not want to preserve fertility or pregnancy is dangerous for them, performing hysterectomy can be a definite and effective solution. In this situation, accurate evaluation of benefits and side effects is of fundamental importance for informed decision making.
Types of hysterectomy
Different types of this surgery are defined based on extent of tissue removal and treatment goals. Choosing the type of surgery depends on the doctor's diagnosis, underlying disease, patient's age and hormonal considerations. Understanding the difference between these types helps patients to better understand what hysterectomy is and what consequences each method can have, especially in terms of complications and quality of life after the operation. In this method, the entire uterus is removed along with the cervix. This type is usually done to treat symptomatic fibroids, abnormal bleeding resistant to treatment, adenomyosis, and some women's cancers. It should be said that full menopause symptoms do not appear after this procedure. Due to the presence of ovaries, the patient will have hormonal function.
Subtotal or partial hysterectomy
In the subtotal method (Subtotal or Supracervical Hysterectomy), the body of the uterus is removed, but the cervix is preserved. This method is chosen in some patients in order to reduce the duration of surgery or maintain pelvic support.
Although menstruation usually stops after this operation, in rare cases, slight bleeding may remain. Clinically, no significant difference in the rate of complications between the complete and subtotal type has been reported, and the choice of method depends more on the patient's individual conditions.
Radical hysterectomy
Radical type is usually performed in the treatment of invasive cervical cancer or other pelvic malignancies. In this method, in addition to the uterus and cervix, tissues around the uterus, ligaments and the upper part of the vagina are removed. For this reason, it is usually performed only in special circumstances and according to oncological protocols.
Hysterectomy with removal of ovaries
In some cases, this operation is performed with removal of one or both ovaries. This decision has a direct impact on the patient's hormonal status and can lead to surgical menopause.
hysterectomy with ovary preservation
In this case, the uterus is removed but the ovaries are preserved. The doctor chooses this method for young women or patients who do not suspect the risk of malignancy in the ovary. Keeping the ovaries continues to secrete female hormones and reduces the risk of long-term complications such as osteoporosis and heart diseases.
Hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy
In hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy (Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy), both ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. This procedure is often performed in cases of cancer, high risk of malignancy or severe ovarian diseases. This method has certain complications such as immediate menopause. Usually, the doctor fully explains the complications of this method to the patient before the operation.
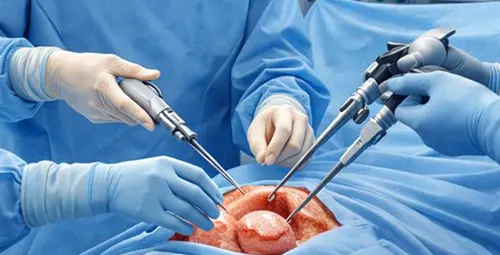
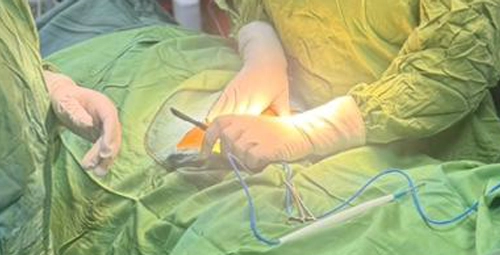
Hysterectomy procedures
The procedure depends on several factors such as the type of disease, the size of the uterus, the history of previous surgeries, the general condition of the patient and the skill of the surgical team. Choosing the right method can have a direct impact on the amount of pain, the length of the recovery period, and the possibility of complications.
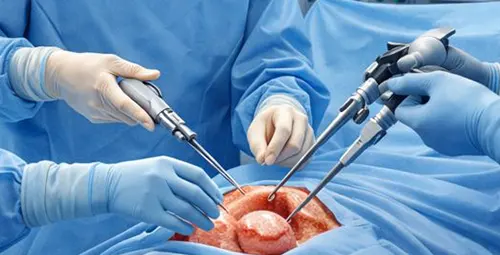
How is abdominal hysterectomy performed?
In abdominal hysterectomy, the surgeon accesses the uterus through an incision in the abdomen. This method is usually used when the uterus is large, there are pelvic adhesions, or there is a need for an extensive examination of the abdominal cavity.
Although this method provides a direct view and more control for the surgeon, it is associated with more postoperative pain, a more pronounced skin scar, and a longer recovery period than other methods.
What is vaginal hysterectomy?
In vaginal hysterectomy, the uterus is removed through the vagina and no external incision is made on the abdomen. Usually, the doctor chooses this method in cases such as uterine prolapse and when the size of the uterus is not too large.
Its main advantages include less pain, shorter hospitalization and faster return to daily activities. However, this method is not suitable for all patients and is limited in some physical conditions or specific diseases. href="https://drzahrasabokru.com/%d9%84%d8%a7%d9%be%d8%a7%d8%b1%d8%a7%d8%b3%da%a9%d9%8 Hysterectomy Laparoscopic surgery is performed using small incisions and delicate instruments. In this method, the surgeon separates the uterus with the help of a laparoscope camera and usually removes it through the vagina. In general, vaginal and laparoscopic hysterectomy have the least postoperative pain and the shortest recovery period. Abdominal hysterectomy causes the most pain and the longest recovery time, but it is unavoidable in some situations. Choosing the right method plays an important role in reducing hysterectomy complications and improving the patient experience. Problems after hysterectomy They are divided into two categories, short-term and long-term. In the short term, the most common side effects include pelvic pain, mild vaginal bleeding, infection, fatigue, and nausea after anesthesia. These complications usually subside within a few days to a few weeks and can be controlled with proper care. One of the common concerns of patients is what a hysterectomy is and how it affects sexual function. Studies show that in many women, after full recovery, the quality of sex improves; Especially in patients who had chronic pelvic pain or severe bleeding before surgery. However, in the first weeks after the operation, a decrease in libido or temporary discomfort is normal and usually resolves after the recovery period is complete. If the ovaries are preserved, the secretion of female hormones continues and the patient does not enter menopause immediately. In contrast, bilateral removal of the ovaries leads to surgical menopause, which can be accompanied by symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. Proper management of these changes is very important to reduce hysterectomy complications. Many women report a significant improvement in their quality of life after hysterectomy. Reducing pain, stopping heavy bleeding and removing daily restrictions are among the effective factors in this improvement. Of course, psychological support, patient education and regular medical follow-up play an important role in better adaptation to post-surgery changes. Pregnancy is not possible after hysterectomy, because the uterus, which is the place of embryo implantation, is removed. However, if the ovaries are preserved, it is theoretically possible to use assisted reproduction methods with a surrogacy, which requires a specialized review. class="faq-item">
Compared to abdominal hysterectomy, this method is associated with less pain, less bleeding, and a shorter recovery period, and today it is considered one of the common options for many patients. For more information Comparison of methods in terms of pain, recovery period and complicationsComplications and post-operative care
Short-term and long-term complications
In the long term, some patients may experience hormonal changes, pelvic floor disorders, or changes in quality of life. This type of surgery has risks for the digestive system and urinary excretion, but this risk is very low. Most of these injuries occur in radical hysterectomy. Hormonally, if the ovaries are preserved, menopause does not occur immediately, but bilateral removal of the ovaries will lead to surgical menopause and related symptoms. They reduce the complications of hysterectomy. In the first days after surgery, pain control, prevention of infection, gentle movement and adherence to medication instructions are very important. The recovery period usually varies between 2 to 6 weeks and depends on the surgical method and the individual conditions of the patient.
The return to daily activities should be gradual and heavy activities or lifting objects should not be done until the doctor's approval. Warning signs such as fever, severe bleeding, severe pain and abnormal secretions require immediate medical attention. Observance of these principles helps to recover faster and reduce long-term consequences.Life after hysterectomy
Hysterectomy effect on relationship Sexual
Hysterectomy and quality of life
Is pregnancy possible after hysterectomy?
What is hysterectomy and is it considered a common operation?
Does menstruation continue after hysterectomy? Does it?
How serious are the complications of a hysterectomy?
How long is the recovery period after hysterectomy?
Is it possible after hysterectomy Is there a pregnancy?
On the other hand, the complications of hysterectomy should also be carefully considered. Permanent loss of the ability to conceive, surgical risks, possible hormonal changes and psychological consequences are among the disadvantages that can be clinically important in some patients. The severity of these consequences depends on the type of surgery, the condition of the ovaries, and the individual conditions of the patient.
Informed decision with the opinion of a specialist doctor
The decision to perform a hysterectomy should be based on a careful medical evaluation and a clear conversation between the patient and the gynecologist. Examining alternative treatment options, considering fertility goals, patient's age and balance between benefits and complications of hysterectomy are key principles of this process. Informed choice based on scientific evidence can play an important role in achieving the best treatment result and patient satisfaction. ltr; "Methods of hysterectomy: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMJ.
تفاوت لاپاراسکوپی تشخیصی و درمانی در زنان | بررسی کاربرد، مزایا و تفاوتها
تفاوت لاپاراسکوپی تشخیصی و لاپاراسکوپی درمانی در زنان تفاوت لاپاراسکوپی تشخیصی و درمانی در زنان یکی از موضوعات مهم در…
لاپاراسکوپی هیسترکتومی؛ چه زمانی توصیه میشود؟
لاپاراسکوپی هیسترکتومی؛ When is it recommended that laparoscopic hysterectomy is one of the minimally invasive methods for removing the uterus, which in certain circumstances...
A complete review of types, complications and post-operative care
What is hysterectomy? What are the types, uses, complications and care after hysterectomy? Hysterectomy is a surgery that...













A reply