Infections
Infections are considered one of the most important and serious problems in the field of orthopedics. Infection of the skin and other soft tissues can lead to infection of the bones (osteomyelitis) and joints (septic arthritis). If not treated on time, orthopedic infections may become chronic and cause irreversible complications. Even small scratches on the tip of the finger, depending on the type of bacteria causing the infection, have the ability to cause permanent hand disability.
Fortunately, with early diagnosis by an orthopedic specialist, proper antibiotic treatment, and surgery if needed, most infections can be completely cured and permanent damage prevented.
Prevention of orthopedic infections
To control and reduce the spread of infections in medical environments, doctors and nurses use gloves and gowns and wash their hands continuously.
Prevention of skin wound infection
To prevent wound infection, it is necessary to observe the following:
- First control the bleeding and then wash the wound with soap and water.
- Avoid removing objects embedded deep in the wound.
- For initial dressing, be sure to use sterile equipment.
For final washing and specialized examination of the wound, it is recommended to visit Dr. Hooman Kokbi, the best orthopedic surgeon in Tehran.
The cause of bone and joint infections
Infections usually enter the body through skin injuries, especially deep, perforating wounds that are difficult to clean. After entering the body, pathogenic bacteria, viruses and parasites can destroy healthy tissue, reproduce and spread through the bloodstream.
Transmission of infection may occur through direct contact with an infected person or indirect contact through infected objects.
Some chronic diseases, such as HIV, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, hemophilia and sickle cell anemia, reduce the power of the immune system and increase the risk of infection. In some patients, joint infection develops around knee or hip replacement prostheses. The knee is the most common joint involved, and these types of infections require immediate examination by an orthopedic specialist in Tehran.
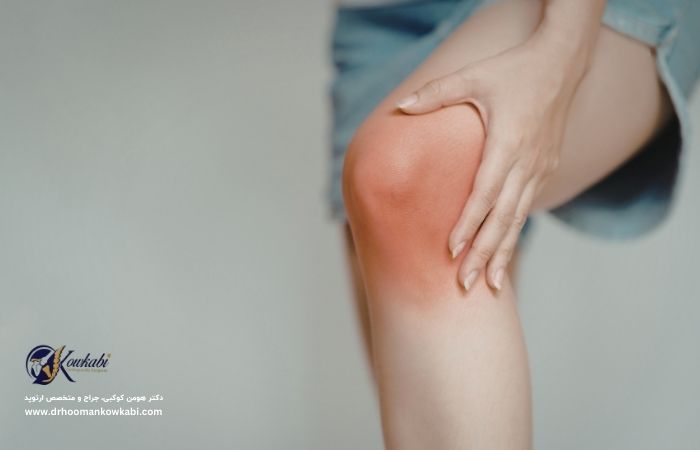
Symptoms of orthopedic infections
Infections are usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Redness, warmth and inflammation in the affected area
- joint or limb dryness, pus discharge and reduced range of motion
- Fever and chills in more advanced cases
Orthopedic infections in infants and children
Children under 3 years of age are at the highest risk of infection because their immune system is not yet fully developed and their skin is more damaged due to frequent falls.
Why is infection more dangerous in children?
- The infection spreads quickly in the child's circulatory system and bone structure.
- Infection of the hip joint in children is considered a surgical emergency.
Warning symptoms of infection in children
- Restlessness, lethargy, anorexia or vomiting in infants
- Child limping or refusing to walk
- Pain or swelling in the limbs, spine, or pelvis
Examination and diagnosis of infection by orthopedic specialist
If you see signs of infection in yourself or your child, it is very important to go to Dr. Homan Kokbi, an orthopedic surgeon and specialist in Tehran for early diagnosis.
Physical examination
- The doctor asks about underlying diseases.
- Time of onset of symptoms and history of injury or surgery are checked.
- Moving the affected area is done to check the intensity of pain.
- In children, the whole body is examined for other foci of infection.
In some cases, bone infection may be asymptomatic (subclinical osteomyelitis).
Tests
The orthopedic specialist will usually use X-ray imaging and, if necessary, order additional imaging tests such as an MRI to check the extent of bone and soft tissue involvement. It is also possible to take a blood sample or drain the fluid from the infected area using a syringe and needle (aspiration). Laboratory tests on these samples help to identify the cause of infection.
Treatment of orthopedic infections
Treatment may include antibiotics administered intravenously (intravenously) or orally.
Soft tissue infections
Different types of infections involve the skin and soft tissue, the most common of which are the following:
- Paronychia: an infection that occurs around the edge of the nail.
- Furuncle: infection of the hair follicle.
Treatment of soft tissue infections
In some cases, soft tissue infections are treated only by placing in warm water and using a dry, sterile dressing. In other cases, an orthopedic surgeon in Tehran may drain the infection after local anesthesia. Sometimes there is a need to use topical ointments or use antibiotics.
Bone infections
Depending on the severity of the infection and the condition of the patient, osteomyelitis can cause irreversible destruction of bone cells (necrosis).
treatment of bone infection
The orthopedic specialist usually prescribes antibiotics. In many cases, surgery is necessary to drain the infection and remove dead bone and tissue. In very severe and resistant cases, sometimes amputation will be the only treatment.
joint infections (septic arthritis)
Like osteomyelitis, the treatment of septic arthritis also often requires the use of antibiotics and rapid evacuation and joint surgery to remove infected tissues.
treatment
The doctor may aspirate the joint several times; In this method, joint fluid is removed using a syringe and needle. In some cases, surgical procedures are used to open the bone and remove the inflammatory cells.
Antibiotic resistance and the importance of correct drug use
Antibiotics often successfully treat bacterial infections, but some microorganisms are developing resistance to common treatments.
Every time an antibiotic is used, resistant bacteria may survive and multiply. These bacteria can cause infections for which there is no effective treatment and can also be transmitted to others, which is a serious threat to public health.
If an oral antibiotic is prescribed for home use, it is very important to follow the instructions of Dr. Homan Kokbi, an orthopedic surgeon and specialist in Tehran and complete the entire course of treatment, even if you feel better before the medication is finished. In other words, no medication should be left unless the doctor has explicitly ordered to stop or change the medication.