Uterine cyst treatment
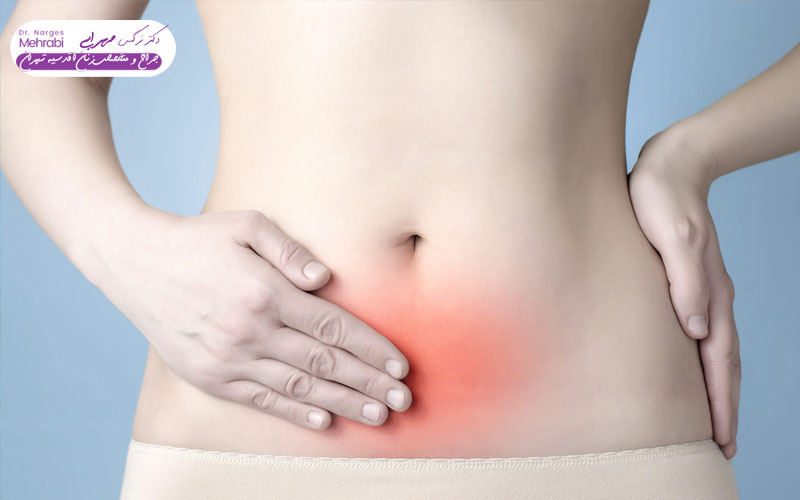
The uterus, this complex and vital organ in the female reproductive system, sometimes hosts small structures called cysts. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that often form on the ovaries (also incorrectly called uterine cysts) or the uterine tissue itself. Diagnosis can come with concerns about fertility, pain, and the possibility of serious conditions. However, it should be known that the vast majority of these cysts are functional and are completely benign and resolve on their own. Functionally, the important role of treatment of uterine cysts should not be overlooked in cases that cause severe symptoms or have malignant potential. The main challenge here is to distinguish between cysts that require immediate intervention and those that should only be observed. An effective treatment approach requires careful examination of the patient's type, size, clinical symptoms, and medical history in order to avoid overtreatment or, on the contrary, delay in necessary interventions.
The aim of this article is to provide a specialized yet understandable overview of the various methods of uterine cyst treatment. We will cover everything from watch-and-wait approaches to pharmacologic interventions and advanced surgical procedures. Focusing on important aspects such as pain management, fertility preservation, uterine cyst treatment cost and uterine cyst aftercare, we strive to provide the information needed to make an informed decision and reduce the anxiety associated with this diagnosis.
What you read
Types of uterine cysts (ovaries) and time of treatment
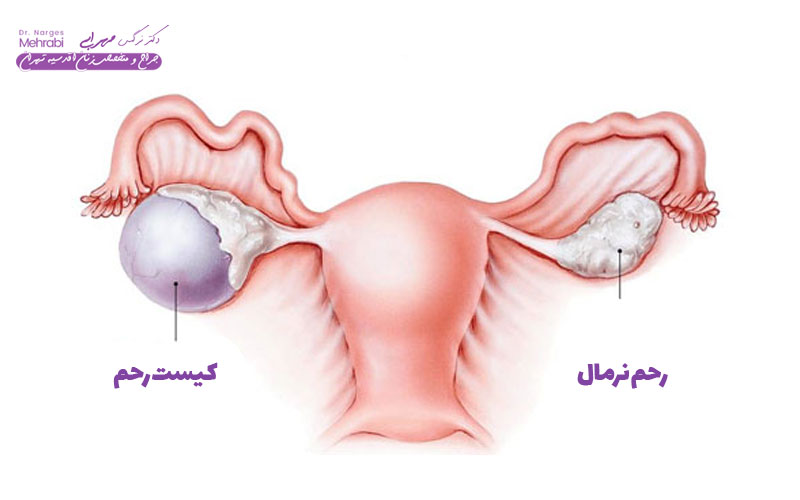
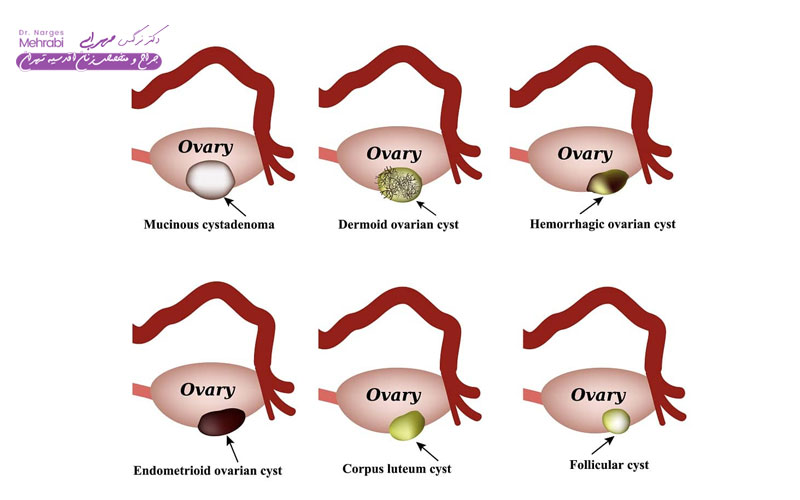
The first step in Treatment of uterine cysts, which are mainly ovarian cysts, is to diagnose the type. The most common type, functional cysts include follicular cysts and corpus luteum cysts, which often form during the normal menstrual cycle. These cysts usually have no symptoms and resolve on their own within a few weeks to months and do not require invasive treatment.
However, there are other types of cysts that require investigation and sometimes intervention in uterine cyst treatment. These include dermoid cysts (cystic teratoma), which contain tissue such as hair, fat, or teeth, endometrioma cysts (which are caused by endometriosis), and cystadenomas (which arise from the surface of the ovary). Dermoid cysts and endometriomas rarely go away on their own and often require surgery.

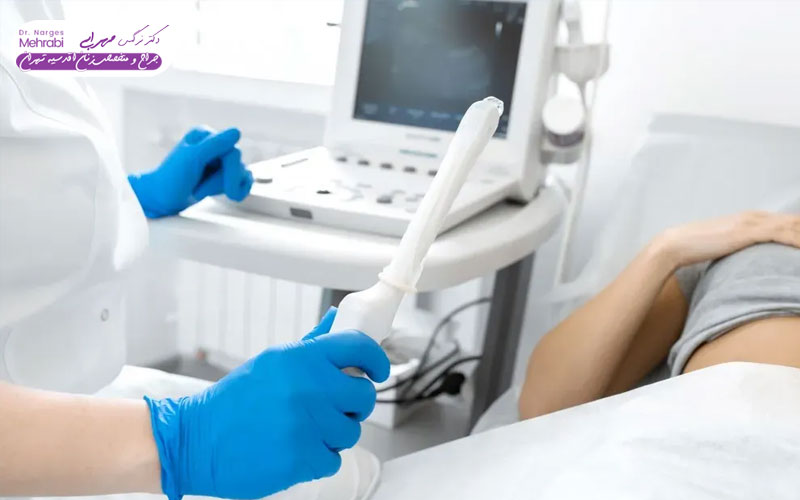
time The need for active uterine cyst treatment (drug or surgery) is determined based on several main criteria: cyst size (especially if it is more than 5 to 10 cm in diameter), severe symptoms such as chronic pain, bloating, or pelvic pressure, and suspicious features on ultrasound that raise the possibility of malignancy. The presence of internal septa (walls), solid component and abnormal blood flow are warning signs. Finally, the sudden occurrence of acute complications such as ovarian torsion or cyst rupture, which is accompanied by severe and sudden abdominal pain, requires emergency intervention and is another opportunity for conservative approaches in uterine cyst treatment. does not remain The doctor evaluates the situation using Doppler ultrasound and blood tests (such as CA-125).
Watchful Waiting approach as the first treatment of cysts Uterus
For the majority of ovarian cysts, especially those that are smaller than 5 cm and appear benign on ultrasound, the watch-and-wait approach is considered the first and best uterine cyst treatment. This treatment method does not mean doing nothing, but rather closely monitoring the condition of the cyst for a certain period of time, usually 1 to 3 months.
This strategy is based on the principle that functional cysts, which are caused by natural hormonal changes, will disappear on their own when the menstrual cycle is completed and hormones reset. During this period, the patient is called back regularly (usually once a month) for a repeat ultrasound to make sure the cyst is shrinking or at least not getting bigger. This close monitoring is a vital part of Uterine Cyst Treatment by the wait method.
During the watch and wait period, managing the patient's symptoms is very important. If you have pelvic pain, your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen to control the pain. The goal is for the patient to continue his daily life without severe discomfort until the cyst is removed, and to prevent the negative impact of uterine cyst on the quality of life.
If the cyst does not disappear after 3 menstrual periods, or if it becomes larger or has suspicious features in subsequent ultrasounds, the doctor will change his approach and consider more active methods for uterine cyst treatment, such as drug or surgical treatments. Therefore, this stage is an ongoing risk assessment in which medical patience is combined with careful monitoring.
The role of drug therapies in the management and treatment of uterine cysts
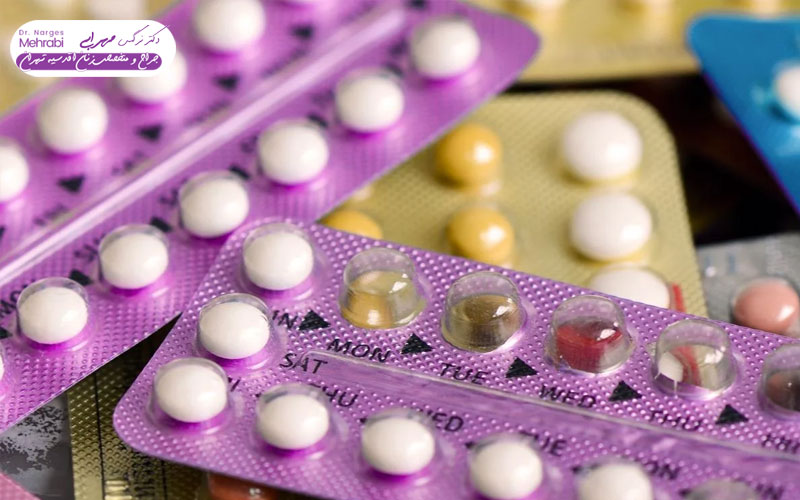
Functional cysts frequently recur, or in cases where there is a need to prevent new cysts from forming, treatment Uterine cyst becomes an effective option with the use of drugs. The most commonly used medications are oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), which work by regulating or suppressing hormones.
Contraceptive pills do not directly shrink or destroy an existing cyst; Rather, by preventing ovulation, they prevent the formation of follicular cysts or corpus luteum in subsequent cycles. This method is especially beneficial for women who frequently have functional cysts and can be used as a preventive strategy in uterine cyst treatment.

Drug therapy can also help control cyst-related symptoms. For example, in endometrioma cysts (caused by endometriosis), drugs such as GnRH agonists or other hormone therapies can be prescribed to shrink the endometriosis tissue and reduce the size of the cyst. However, the use of hormonal drugs for uterine cyst treatment should be done with the careful consultation of a doctor and consideration of possible side effects.
In certain cases, such as cysts caused by infection (inflammatory cysts), antibiotics may be prescribed to eradicate the underlying infection as part of uterine cyst treatment. However, it should be emphasized that most cysts are not infectious in nature, and drug treatment primarily focuses on hormonal regulation and prevention rather than direct treatment of the cysts that have formed. Uterus
Surgical intervention in uterine cyst treatment is recommended only when the cysts cause severe and persistent symptoms, are large in size (usually more than 7-10 cm), do not shrink during the period of care and waiting, or show worrisome symptoms on ultrasound or blood tests that suggest malignancy. Emergency surgery is also necessary in case of twisting or rupture of the cyst.
Before the uterine cyst treatment surgery, a comprehensive preparation stage is necessary. This stage includes a complete evaluation by the surgeon and the anesthesiologist. Preoperative tests include a complete blood count, blood chemistry, and coagulation tests. If present, tumor marker tests such as CA-125 may also be repeated to gain a more accurate understanding of the nature of the cyst. One of the most important preparations before surgery for uterine cyst treatment is to stop taking blood thinners. Medications such as aspirin and ibuprofen should be stopped at least 10 days before surgery to minimize the risk of bleeding during and after surgery. The doctor should be informed about all medications, even herbal medications.
The patient should also carefully follow the instructions regarding fasting before the surgery. Mental preparation is also important; The patient should discuss with the surgeon the type of surgery (laparoscopy or laparotomy), the amount of tissue to be removed (only the cyst or the entire ovary), and the possible implications for fertility. Full knowledge of the uterine cyst treatment process reduces anxiety.
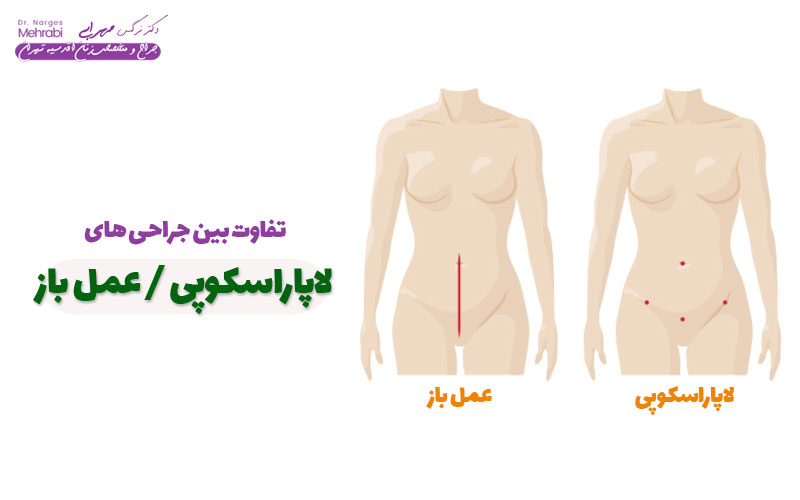
Modern surgical methods: laparoscopy and cyst laparotomy
two main surgical methods for Treatment of uterine cyst (ovary) is: Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) and Laparotomy (open surgery). Period Recovery is longer and more painful.

Evaluation of the cost of uterine cyst treatment and its influencing factors
The cost of uterine cyst treatment is an important concern for patients and it is difficult to determine a single amount for it because several factors affect this cost. At first, if uterine cyst treatment is a wait-and-see type, the costs will be limited to periodical examinations, ultrasounds and pain medications.
But if surgical intervention is required, the cost of uterine cyst treatment will increase significantly. Factors affecting cost include: type of surgery (laparoscopy is usually more expensive due to specialized equipment), surgeon and anesthesia team fees (which vary based on experience and geographic location), and hospital charges (including operating room use and length of stay).
The critical part about uterine cyst treatment cost, Check insurance coverage. Since ovarian cyst surgery is necessary to relieve symptoms and prevent complications or treat malignancy, usually a major part of the expenses is covered by health insurance, both basic and supplementary. However, the patient should be aware of the amount of the deductible (the patient's share of the cost) and the limit of his insurance obligations. Also, he should remember the side costs such as the cost of post-operative drugs, the cost of special surgical equipment (such as disposable laparoscopic instruments) and the cost of pathology (examination of the removed cyst tissue). It is recommended that you get a clear and written financial estimate from your hospital and surgeon before performing uterine cyst treatment surgically.
Care after treatment of uterine cyst and prevention From recurrence
Care after uterine cyst treatment, especially after surgery, play an important role in accelerating recovery, reducing complications and preventing cyst recurrence. In both laparoscopic and laparotomy procedures, a rest period is necessary, although this period is shorter (several days to a week) for laparoscopy. The patient should refrain from lifting heavy objects and vigorous sexual activities until the doctor's approval. Pain management is an important part of the care after uterine cyst treatment. The doctor will prescribe painkillers that must be taken as directed. Also, paying attention to the place of cuts and keeping them clean is essential to prevent infection. In case of redness, swelling or discharge from the suture site, the doctor should be informed immediately.
To prevent recurrence of cysts, especially functional cysts, the doctor may recommend the use of oral contraceptive pills. These drugs greatly reduce the possibility of new cyst formation by stabilizing hormone levels and inhibiting ovulation. This preventive approach is considered an essential part of uterine cyst treatment in the long term.
Regular follow-ups and periodic ultrasounds are also an essential part of care after uterine cyst treatment. These visits allow the doctor to monitor the healing process and intervene quickly if any signs of recurrence are observed. In addition, maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress can also help with hormonal balance and overall pelvic health. Long-term
One of the biggest concerns when treating a uterine cyst, especially with surgery, is the effect on future fertility. Fortunately, in most cases, ovarian cyst surgery is performed with the aim of preserving healthy ovarian tissue (cystectomy). Especially in laparoscopy, the surgeon tries to remove only the cyst and leave the normal tissue of the ovary intact as much as possible in order to preserve reproductive function. However, in situations where the cyst is very large, has completely destroyed the ovary, or is suspected of malignancy, it may be necessary to remove the entire ovary and fallopian tube (Oophorectomy). Even if one ovary is removed, the remaining ovary can usually perform its normal function and make pregnancy possible, although fertility is slightly reduced. Discussing these outcomes is an important part of the uterine cyst treatment process.
In terms of long-term health, uterine cyst treatment, especially removal of large cysts or endometriomas, can significantly improve the patient's quality of life. By removing the source of chronic pelvic pain and pressure, women often experience permanent relief. Also, if uterine cysts caused by endometriosis are treated, the symptoms associated with this disease are also reduced.
It is important that after uterine cyst treatment, the patient consults with their doctor about a long-term follow-up plan to manage any risk of recurrence, especially if there is a history of endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Active management of these underlying conditions is key to ensuring long-term health and fertility after surgery.
Conclusion
Uterine cyst treatment, which mainly refers to ovarian cysts, is a wide range of medical approaches that range from simple observation to advanced surgery. takes For functional and small benign cysts, a watch-and-wait approach with close ultrasound monitoring is often the most effective and least invasive approach, while oral contraceptives play a key role in preventing the recurrence of functional cysts.
In cases where the cysts are large, symptomatic, or suspected to be malignant, laparoscopic surgery or, in more complex cases, Laparotomy is chosen. Success in uterine cyst treatment is not only limited to removing the cyst, but also includes careful care after uterine cyst treatment, especially washing the surgical site and regular follow-ups. A clear understanding of the uterine cyst treatment cost and its insurance coverage is also an important part of this process.
Finally, the main goal of uterine cyst treatment is not only to resolve the acute problem, but also to preserve the health of the ovaries and fertility in the future. By choosing the right treatment method based on the type of cyst and the patient's individual characteristics, and with proper follow-up and management after treatment, it is possible to ensure that women will get rid of cysts and maintain their reproductive health and quality of life in the long term. href="https://drmehraabi.com/%d8%af%da%a9%d8%aa%d8%b1-%d9%85%d8%aa%d8%ae%d8%b5%d8%b5-%d8%a7%d9%86% d8%af%d9%88%d9%85%d8%aa%d8%b1%db%8c%d9%88%d8%b2-%d8%af%d8%b1-%d8%aa%d9%87%d8%b1%d8%a7%d9%86/">