Table of Contents
- Is electrical brain stimulation effective for treating depression?
- Advantages of using electrical brain stimulation in treating depression What is it?
- For whom is electrical brain stimulation to treat depression suitable?
- How to perform electrical brain stimulation to treat depression
- Precautions before treating depression with electrical brain stimulation
- Care after electrical brain stimulation to treat depression
- Complications of electrical brain stimulation to treat depression
- Conclusion
Depression is one of the most common mental disorders and many people do not respond well to common treatments such as drug therapy and psychotherapy. In such circumstances, electrical stimulation of the brain for the treatment of depression is proposed as a new and promising approach. This method regulates the activity of certain parts of the brain by using mild electric currents and helps to reduce symptoms resistant to treatment. Depending on the type of technique used, electrical stimulation of the brain may be performed non-invasively or through implantable devices and play a complementary or alternative role to traditional treatments. In the rest of this article, your doctor will explain more about this method of treating depression.
Is electrical brain stimulation effective for treating depression?
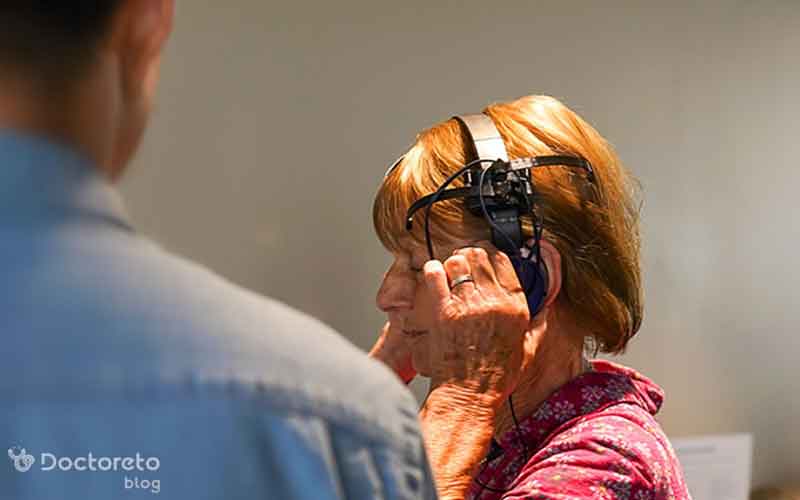
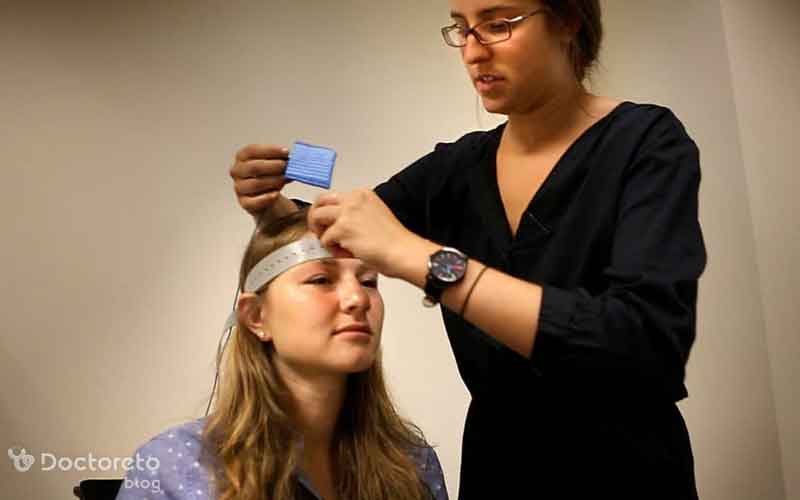
Magnetic brain stimulation for the treatment of depression is usually performed using rtMS rTMS (repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation). During each session, an electromagnetic coil is placed on the scalp and sends short, controlled magnetic pulses to the brain. These pulses specifically stimulate nerve cells in areas of the brain that control mood and regulate emotions.
Stimulation of these areas can re-regulate neural activity, strengthen brain networks related to depression and help improve treatment-resistant symptoms. This non-invasive method is performed without the need for anesthesia and with minimal side effects, and is usually applied in short daily sessions over several weeks.
What are the advantages of using electrical stimulation of the brain in the treatment of depression?
Electrical brain stimulation for drug-free depression treatment could have several key benefits. Research shows that this method not only improves mood, but that its effects are sustained during 2-week and 4-week post-treatment assessments. In addition to reducing the symptoms of depression, this treatment significantly increases a person's daily functioning, energy, motivation and ability to concentrate. Its other advantages include non-invasiveness, low side effects, and the possibility of use in people who do not respond to antidepressants. These features make rTMS a safe and effective option for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Mood improvement | Temporary headache or scalp pain |
| Sustained effects at 2- and 4-week assessments | Dizziness and nausea Short-term |
| Increased daily performance, energy and motivation | Temporary muscle pain or fatigue |
| Non-invasiveness and few side effects | Effects are usually short-term and manageable |
| Can be used for people resistant to antidepressants | – |
| A safe option and Effective for treatment of resistant depression | – |
For which people is brain stimulation suitable for treating depression?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) for the treatment of depression involves the permanent placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain through surgery. This electrode sends low-level electrical pulses that help regulate mood and reduce symptoms of depression. This method will be experimentally effective for people who have severe depression and do not respond to usual drug treatments. This method is still in the study phase and the standard non-invasive treatment for resistant depression is rTMS.
Who should not do electrical brain stimulation for the treatment of depression?
Using Electrical brain stimulation to treat depression may not be suitable for everyone and consultation with a doctor is essential before any treatment. Certain medical conditions, implants, and individual factors can pose serious risks and make this procedure inappropriate. In the following, we have explained who should not undergo electrical brain stimulation to treat depression. People who:
- Active implants such as pacemakers, defibrillators or other active devices have in the body. Are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. Of course, pregnancy is not an absolute prohibition.
- They suffer from neurological disorders, including a history of seizures, epilepsy and dementia.
- Suffering from infections or tissue problems including tuberculosis, osteomyelitis, bladder or vaginal infection, tissue recently undergoing radiation therapy or a recent fracture.
- Metal or electronic implants in the head and neck (such as aneurysm clips, cochlea, implants)
How to perform electrical stimulation of the brain to treat depression
In treating depression with electrical brain stimulation, an electromagnetic coil is placed on the scalp and sends weak magnetic pulses to an area of the brain that controls mood and emotions. These pulses stimulate the nerve cells and help to reset the brain activity to reduce the symptoms of depression. The patient is awake during the treatment and does not need anesthesia. This type of treatment is completely non-invasive.
English text:
mayoclinic
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of major depression.
Persian translation:
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain to improve symptoms of major depression.
Number of sessions of electrical stimulation of the brain for treatment of depression
The initial course of treatment usually includes 5 sessions per week for 6 weeks; That means a total of about 36 sessions. After electrical stimulation of the brain, the patient does not need hospitalization or long-term rest.
Duration of electrical stimulation of the brain for treatment of depression
A session of electrical stimulation of the brain usually lasts between 3 and 40 minutes. The length of each session varies depending on the intensity of the stimulation, the person's response, the target location and of course the diagnosis of the specialist doctor. This treatment is usually done in short and regular sessions to get the best results.
Precautions before treating depression with electrical brain stimulation
Before starting the treatment, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the types of brain stimulation methods and how they work. Patients should avoid activities that can cause electromagnetic interference, such as placing devices containing permanent magnets (loudspeakers, magnetic watches, etc.) near the coil. Also, the doctor may check the use of some drugs or supplements so that there is no interference with the treatment.
Care after electrical stimulation of the brain to treat depression
After the treatment, it is necessary to follow the instructions of the treatment team. Most patients can return to normal daily activities within a few days. Patients should not leave the hospital until they are able to perform basic tasks such as sitting, standing and walking. Incisions require care and pain is usually mild; In this situation, painkillers are prescribed and it is recommended to gradually change to non-prescription drugs such as acetaminophen. To reduce the risk of complications, it is very important to fully follow the instructions of the treatment team for a successful recovery.
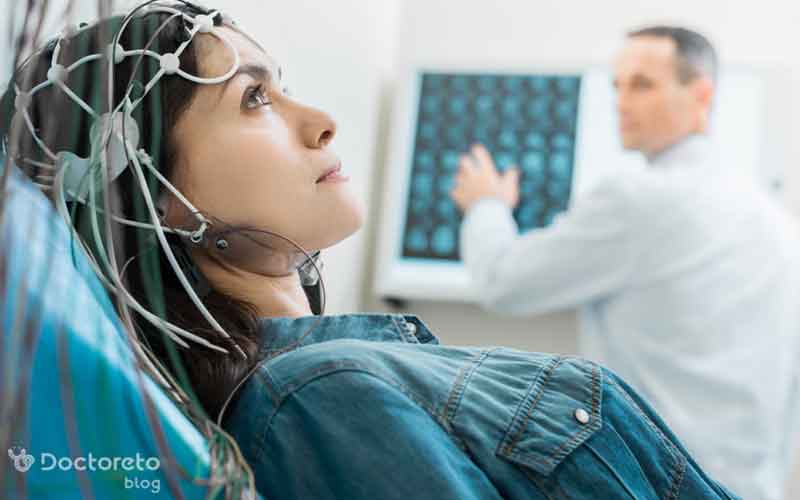

Complications of electrical stimulation of the brain for the treatment of depression
Electrical brain stimulation to treat depression is generally safe, but some mild and temporary side effects may occur. These side effects include headache or scalp pain and dizziness. Usually, these effects are short-term and decrease after the end of the treatment session, and they can be managed with simple control methods.
English text:
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) has shown mixed results for depression treatment. rel="noreferrer noopener">pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
Conclusion
Electrical brain stimulation for the treatment of depression is a new non-invasive method that is effective for people who do not respond to antidepressants. This method helps to re-regulate brain activity and improve depression symptoms by targeted stimulation of nerve cells in areas related to mood. Treatment of depression with electrical stimulation of the brain is low-risk and does not require anesthesia and can improve the patient's mood, energy and daily performance. In general, electrical stimulation of the brain has been proposed as a safe and reliable option in the management of treatment-resistant depression and significantly increases the quality of life of patients.
Your doctor takes care of your health!