Medical and non-surgical uterine myoma
In many women of reproductive age, there is a common problem called uterine myoma. Naturally, like any other disease, there are various treatments for this problem. Doctors consider specific treatments according to the patient's conditions, if the symptoms of uterine myoma are mild to moderate and the patient wants to preserve the uterus, priority is given to drug treatments.
It should be noted that in most cases drug treatments for myoma do not lead to complete removal of the myoma, but control the disease and reduce the symptoms. Drug treatments include hormonal and non-hormonal drugs. Birth control pills and drugs that contain hormones that temporarily reduce the activity of the ovaries relieve symptoms. Also, these drugs temporarily reduce the size of myoma. It should be noted that there is a possibility of symptoms returning after stopping these drugs. There are non-surgical and minimally invasive methods to shrink myomas and relieve symptoms, which are explained in the rest of the article. For information about this disease, read the article uterine myoma.
contents
- Objectives of medical and non-surgical treatments for uterine myoma
- Non-surgical and minimally invasive treatments
- Advantages and limitations of non-surgical treatments
- What factors are effective in choosing a non-surgical treatment method
- When are non-surgical treatments for myomas unresponsive
- Frequently Asked Questions
- summary and conclusion
- sources
Objectives of drug and non-surgical treatments for uterine myoma
Drug and non-surgical treatments for uterine myoma is one of the non-surgical and It is conservative, which aims to control symptoms and improve quality of life. This method is especially useful for women who want to preserve their uterus or plan to become pregnant in the future. Drug treatment can reduce heavy menstrual bleeding, relieve pelvic pain and menstrual cramps, and reduce pressure from myomas on the bladder. Of course, it should be noted that these treatments usually do not completely eliminate myoma and their effect is temporary, but they are very useful for controlling symptoms and postponing surgery.
Hormonal drugs
Hormonal drugs are one of the most common options for drug treatments for myoma. They are the womb. By regulating the level of estrogen and progesterone hormones in the body, these drugs slow down the growth of myomas and reduce the patient's symptoms.
Combined birth control pills: These drugs can regulate menstruation and reduce bleeding. Although their effect on reducing the size of the myoma is limited, they are effective in reducing the symptoms and improving the quality of life. and reduce severe bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Hormonal intrauterine device (IUS): The use of this device in the treatment of this disease is that it releases progesterone hormone in the uterus. This process leads to a decrease in bleeding and relieves symptoms.
The use of hormonal drugs is usually short to medium term and is adjusted based on the response of the patient's body and the severity of the symptoms.
GnRH agonists and antagonists
These drugs cause the ovaries to temporarily decrease activity and decrease estrogen production. Estrogen significantly leads to the growth of fibroids. The reduction of this hormone leads to the shrinking of myomas and finally reduces the bleeding during menstruation. They are used as monthly or quarterly injections and cause a temporary state similar to menopause.
GnRH antagonists: They have a different route, but they have the same effect of reducing the hormone and shrinking the myoma. They work faster.
The effect of these drugs is temporary and after stopping the use, myomas may grow back. For this reason, they are often used before surgery or minimally invasive procedures to reduce the size of the myoma and make the treatment easier and safer. It can be said that in many cases of myoma drug treatment, it is considered a complementary method.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen are more for reduction of menstrual pain and cramps are used. These drugs do not change the size of the myoma, but they can reduce bleeding and pain temporarily. They are often used together with hormonal drugs or other medical methods to provide better relief.
Medicines to reduce menstrual bleeding
In women who have heavy and prolonged bleeding, Drugs such as tranexamic acid or some short-acting hormonal drugs can reduce bleeding and delay the need for blood transfusions or urgent surgical procedures. These drugs are usually used together with other treatments or intermittently to achieve the best control of symptoms.
Role of myoma drug treatments before invasive interventions
1- Reducing the size of the myoma to facilitate the operation and reduce surgery time.
2- Reducing bleeding during treatment, which increases patient safety.
3- Improving the general condition of the patient, especially in women who have anemia due to heavy bleeding.
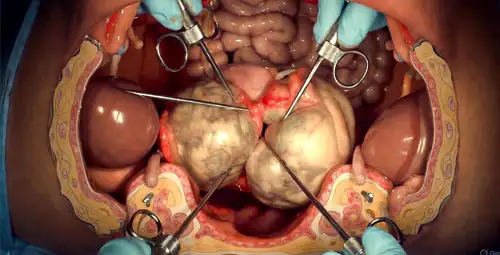
In general, drug treatments for uterine fibroids are an option are safe, adjustable and minimally invasive that can control the symptoms well and improve the patient's quality of life. However, it is necessary for patients to be regularly monitored by a doctor so that the effect of treatment can be evaluated and the treatment method can be changed if needed. Myoma, non-surgical and minimally invasive methods for the treatment of uterine myoma are offered to patients who want to avoid open surgery or are not candidates for surgery. These treatments aim to reduce symptoms, reduce myoma size and preserve the uterus and have a shorter recovery period than surgery. Choosing the right method is based on myoma size and location, severity of symptoms, patient age and future pregnancy plan.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE)
Uterine artery embolization is a minimally invasive method that It works by closing the vessels that supply blood to the myoma. In this method, the doctor uses a small needle and catheter to insert tiny particles into the uterine artery to cut off the blood supply to the myoma. When the myoma does not receive blood, its size decreases and patient symptoms such as bleeding and pain decrease. This procedure usually requires a short hospital stay and patients can return to daily activities in a few days to a week. UAE is suitable for women who wish to preserve the uterus or for whom surgery is a high risk.
Focused ultrasound waves under MRI (MRgFUS)
In this method, the doctor uses focused sound waves. It destroys. In this method, the doctor uses the MRI tool to accurately diagnose the location of the myoma. The sound waves transfer their energy to the myom and cause heat and destroy parts of the myom MRgFUS is suitable for small to medium-sized myomas and patients seeking a completely non-invasive treatment. This method is generally performed without a long hospitalization and has a short recovery period, but may require multiple sessions for complete treatment.
Other interventional procedures without open surgery
In addition to embolization procedures Uterine artery and focused ultrasound are other methods that can treat fibroids without opening the abdomen. One of these methods is removing the myoma from inside the uterus using a special tool through the vagina. There are also some guided imaging techniques where the doctor can target and treat the myoma with the help of precise images. These methods are usually suitable for myomas that are inside the uterine cavity or are small to moderate in size and can reduce bleeding and other symptoms such as pelvic pain. The main advantage of these methods is a short recovery period, preserving the uterus and reducing the need for open surgery.
Advantages and limitations of non-surgical treatments
Non-surgical treatments for uterine myoma have significant advantages. These methods do not require opening the abdomen, have a shorter recovery period, and usually the patient returns to daily activities faster. In addition, the uterus is preserved and they are considered a good option for women who intend to get pregnant. Also, many of these methods can reduce heavy bleeding and pelvic pain and limit the growth of myomas.
However, these treatments have limitations. Their effects are usually temporary and the myoma may grow back. Some methods are not suitable for large or multiple myomas and may require several treatment sessions or finally surgery. Therefore, choosing a treatment method should be done under the supervision of a specialist and experienced doctor.
What factors are effective in choosing a non-surgical treatment method
Choosing a non-surgical treatment method for uterine myoma depends on several important factors. The size and location of myoma is one of the most important factors; Small to medium-sized myomas that are in the right place respond better to non-surgical methods. The severity of the patient's symptoms is also decisive; People with heavy bleeding or a lot of pain may need stronger, less invasive methods. Age and desire to get pregnant also play an important role, because some methods are more suitable for maintaining fertility. In addition, the general health status of the patient and the presence of underlying diseases can affect the choice of treatment method. The doctor usually examines all these factors and determines the appropriate method on an individual basis.
When non-surgical treatments for myoma are not responsive
In some cases, non-surgical treatments are not effective and surgery or invasive interventions are needed. This usually occurs in large or multiple myomas that are not completely controlled by minimally invasive methods. Also, if the patient's symptoms do not decrease after treatment or bleeding and pain continue, non-surgical treatment will not be sufficient. Certain medical conditions, such as severe anemia or other co-morbidities, may also require prompt surgical intervention. In these cases, the doctor recommends the best treatment method according to the individual conditions of the patient. For information, read the article Uterine myoma surgery.
Do uterine myomas always need treatment?
No. If the myoma is small and does not cause symptoms, regular follow-up by the doctor is usually sufficient. Treatment is only necessary when symptoms affect daily life or cause health problems.
How does drug treatment for fibroids work?
What are the advantages of non-surgical treatments?
Uterine myoma mass is a benign mass and many women, especially in reproductive age, are dealing with this problem. Myoma leads to heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain and pressure on the bladder.
Medical and non-surgical treatments for uterine myoma are the first choice for patients who want to preserve their uterus or are not candidates for surgery. Hormonal medications, medications to reduce bleeding, and medications to reduce ovarian activity can control symptoms and in some cases temporarily reduce the size of the fibroid. rel="nofollow noopener">Evidence Summary – Management of Uterine Fibroids (NCBI Bookshelf)
The difference between diagnostic laparoscopy and therapeutic laparoscopy in women The difference between diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy in women is one of the important topics in...
A complete review of types, complications and post-operative care
What is hysterectomy? What are the types, uses, complications and care after hysterectomy? Hysterectomy is a surgery that...













2 answers