best pill for uterine infection
Gynecological diseases and infections of the reproductive system, especially uterine infections, are among the most common and at the same time the most sensitive problems. are that a significant part of women are involved with during their lives. These complications can not only disrupt the quality of daily life, but if not treated properly and on time, they greatly increase the risk of more serious problems such as infertility or the spread of infection to other parts of the pelvis. In such a situation, finding an effective treatment solution and identifying the best pill for Uterine infection is a major concern. It turns out that it requires accurate knowledge and expert advice. Unfortunately, the cyberspace is full of contradictory and sometimes unscientific information about treatment methods for women's infections, which can confuse people and even lead to dangerous self-treatments. While many different types of infections (such as fungal, bacterial, or viral infections) can affect the uterus, the treatment protocol and type of medication prescribed are completely different for each. The purpose of writing this article is to go beyond general recommendations and focus on scientific analysis and introduction of drugs that are usually prescribed by specialists, so that by providing a comprehensive and documented view, it will help you in the way of knowing the best pill for uterine infection.
We in this article We try to provide you with a complete and reliable guide by examining various aspects of uterine infections, from symptoms and diagnosis to the detailed introduction of common drug categories and important points in their use. Don't forget that no prescription is safe and effective without an expert doctor's opinion, but being armed with enough knowledge will double your power in interacting with the doctor and following the treatment process. So stay with us until the end of this article to follow the path of diagnosis and treatment with a deeper insight and finally get a correct understanding of the concept of the best pill for uterine infection.
What you are reading
common signs and symptoms of uterine infection that require medication
Uterine infections often appear with a set of clinical symptoms that can vary from person to person, but some symptoms are very common and warning signs. Abnormal vaginal discharge, which may have a different color, odor, and concentration (such as cheesy, yellowish-green, or foul-smelling discharge), is one of the main indicators of the need for medical treatment. Burning, itching or pain in the genital area are also other annoying symptoms that can be a sign of the need to identify and take the best pill for uterine infection.
These warning signs should not be ignored, because the lack of treatment can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and long-term complications. Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, especially chronic pain or pain during sex (dyspareunia), can indicate the spread of infection to deeper parts. Fever, chills, and extreme fatigue also occur in more severe cases, in which case, after examining the situation, the doctor will prescribe a specific type of antibiotic or antifungal, which may be the best pill for uterine infection.

Early and accurate diagnosis of symptoms by the patient plays a vital role in the treatment process. Faced with mild symptoms, many women turn to home remedies or over-the-counter medications, often delaying proper diagnosis. While similar symptoms may be seen in several types of infection, the treatment approach is quite different. For example, fungal infections (candidiasis) are characterized by itching and a cheesy white discharge and require antifungal medication, while bacterial infections require antibiotics.
Finally, any abnormal bleeding outside of your period or spotting after sex can also be a sign of inflammation or ulceration of the cervix due to infection. These conditions require immediate medical evaluation and often the prescription of a strong course of treatment. In these cases, deciding which drug is really the best pill for uterine infection depends entirely on the type of pathogen and the severity of the symptoms, which can only be determined after an examination and perhaps additional tests. In the choice of medicine
The choice of the type of medicine is directly dependent on the cause of the infection, that is why it is absolutely vital to differentiate between bacterial, fungal and viral infections. Bacterial infections, such as bacterial vaginosis or chlamydia, are the most common and are characterized by thin, foul-smelling discharge. Treatment of these types of infections almost always involves the use of antibiotics. In this group, the doctor may prescribe special drugs, which can include penicillins, cephalosporins, or other broad-spectrum antibiotics. In contrast, fungal infections (often caused by the fungus Candida albicans) have different symptoms, such as severe itching and thick, cheesy discharge. In this case, antibiotics not only have no effect, but can make the condition worse by killing the beneficial bacteria in the vagina. These types of infections are treated with antifungal drugs (such as fluconazole or clotrimazole). So, in this particular case, the best pill for uterine infection is an antifungal drug, which is completely different from a bacterial drug, and a misdiagnosis will completely disrupt the treatment. style="border-width:15px">
The third category are viral infections that are less common, such as genital herpes (HSV). Treatment for viral infections usually includes antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, which are aimed at controlling symptoms and reducing the number of relapses, rather than completely eradicating the disease. These drugs have a completely different mechanism of action than antibiotics or antifungals, and in the case of uterine infections, they are less considered as the best pill for uterine infection caused by bacteria or fungi.
The importance of this distinction is that the wrong use of antibiotics for a fungal or viral infection will not have any positive results, except for drug resistance and damage to the body's normal flora. For this reason, gynecologists always emphasize the need for careful examination and, if necessary, microscopic tests (such as vaginal culture) before prescribing any medicine, even claiming to find the best pill for uterine infection, to ensure targeted and effective treatment.
antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment in the face of uterine infections of bacterial origin, and their role in eradicating harmful pathogens is undeniable. Infections such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), often caused by bacteria such as chlamydia or gonococci, require strong doses and full courses of antibiotics to prevent damage from spreading to the fallopian tubes and ovaries. In these situations, the doctor may prescribe a combination of antibiotics to ensure that all pathogens are targeted.
Choosing the right antibiotic depends on several factors; including the type of bacteria, the severity of the infection, and the history of the patient's sensitivity. Medicines such as doxycycline, azithromycin, or ceftriaxone taken orally or by injection are among the most commonly used antibiotics. By disrupting the vital processes of bacterial cells, these drugs lead to their death, thus paving the way for treatment. The goal is to control inflammation and infection in the shortest possible time to prevent complications.
The best pill for uterine infection The best pill for uterine infection The best pill for uterine infection
However, taking antibiotics without a prescription and arbitrarily to find the best pill for uterine infection can lead to a serious problem called antibiotic resistance. Drug resistance occurs when bacteria mutate and no longer respond to a drug, which makes future treatments much more difficult and complicated. For this reason, it is emphasized that the course of treatment should be completed exactly as prescribed by the doctor, even if the symptoms have improved before the medication is finished.
Finally, it should be noted that despite the effectiveness of antibiotics in fighting bacteria, these drugs have no effect on fungal or viral infections. In addition, their consumption can upset the balance of the natural flora of the vagina and automatically lead to secondary fungal infection. For this reason, sometimes, along with prescribing antibiotics as the best pill for bacterial uterine infection, taking probiotic supplements is also recommended to restore the balance. (Metronidazole) is one of the most well-known and widely used drugs in the field of treating genital and pelvic infections, and it is often discussed in the discussion of the best pill for uterine infection. This drug is a strong antibiotic and antiprotozoal, which is particularly effective against anaerobic bacteria and protozoa such as Trichomonas vaginalis (the causative agent of trichomoniasis) as well as bacterial vaginosis. The wide effectiveness of metronidazole in eliminating the main pathogens of uterine infections has led to it being prescribed as the first line of treatment by specialists in many cases. By penetrating the DNA of pathogenic cells and disrupting it, this drug causes the death of microorganisms and can quickly relieve annoying symptoms. The use of metronidazole can be taken orally (tablets) or topically (vaginal suppository or gel), which is more useful for more advanced or systemic infections.

However, calling metronidazole the best pill for uterine infection is correct only when the infection is of bacterial (especially anaerobic) or protozoan origin. If the infection is caused by a fungus, metronidazole is completely ineffective and antifungal drugs should be used. Also, this drug can cause certain side effects such as metallic taste in the mouth, nausea and severe sensitivity to alcohol, which the patient should be aware of before starting to use. As a result, while metronidazole is a key and very effective drug for certain types of uterine infections, it cannot be absolutely the best pill for uterine infection in all cases. The final decision is made based on the accurate diagnosis of the type of pathogen, by a specialist doctor and taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, and this makes the need to avoid self-medication even more evident. Searching for the best pill for uterine infection, accurate diagnostic methods such as vaginal culture and antibiogram play a very vital role. Vaginal culture is a process in which a sample of vaginal or cervical secretions is taken and cultured in a laboratory environment to identify the exact type of pathogen (bacteria, fungus or protozoa) that is causing the infection. This helps the doctor to avoid speculation and make a definitive diagnosis.
Once the cause of the infection (usually bacteria) is determined, the next step is to perform an antibiogram test. In this test, the sensitivity of the grown bacteria to a wide range of available antibiotics is examined. In other words, this test determines which antibiotic is able to kill the bacteria in question most effectively. This approach is especially necessary in cases of treatment-resistant and recurrent infections, where the bacteria may not respond to common drugs.
Without culture and antibiogram, the doctor may be forced to prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics that, in addition to harmful bacteria, destroy a large population of beneficial bacteria in the body and increase the risk of side effects and resistance. But with the exact result of the antibiogram, the doctor can choose a specific and targeted drug that has the least side effects and guarantees the highest success rate. In fact, the result of the antibiogram directly tells the doctor which of the dozens of available drugs is exactly the best pill for uterine infection of the patient with that particular type of bacteria. This work not only leads to faster and more effective treatment, but also prevents the indiscriminate and inappropriate use of antibiotics, which is one of the global health problems, and helps in the management of drug resistance.
side effects and important points in taking prescription drugs for uterine infection
Although prescription drugs such as best pills for uterine infection are vital for eradicating the infection, like any other drug, they can come with side effects. Knowledge of these complications and how to manage them is essential to successfully complete the treatment course. Common side effects of antibiotics include gastrointestinal problems such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Also, some drugs may cause mild to severe allergic reactions such as hives or shortness of breath. One of the most important points in the use of antibiotics is drug and food interactions. For example, some antibiotics (such as doxycycline) should not be taken with dairy products or calcium supplements because their absorption is reduced. Also, as previously mentioned, taking metronidazole with alcohol can lead to a very unpleasant reaction that includes nausea, headache and low blood pressure, so absolute abstinence from alcohol during treatment is essential.
The best pill for uterine infection The best pill for uterine infection The best pill for uterine infection
Completing the entire course of treatment, regardless of the feeling of improvement, is a key point that must be strongly emphasized. Stopping the drug early as soon as the symptoms improve is the most common reason for the recurrence of the infection and the development of drug resistance. Bacteria that are weakened but not completely killed remain and grow more vigorously, defying subsequent treatments. Therefore, to ensure the full effectiveness of the best pill for uterine infection, it is vital to follow your doctor's instructions exactly.
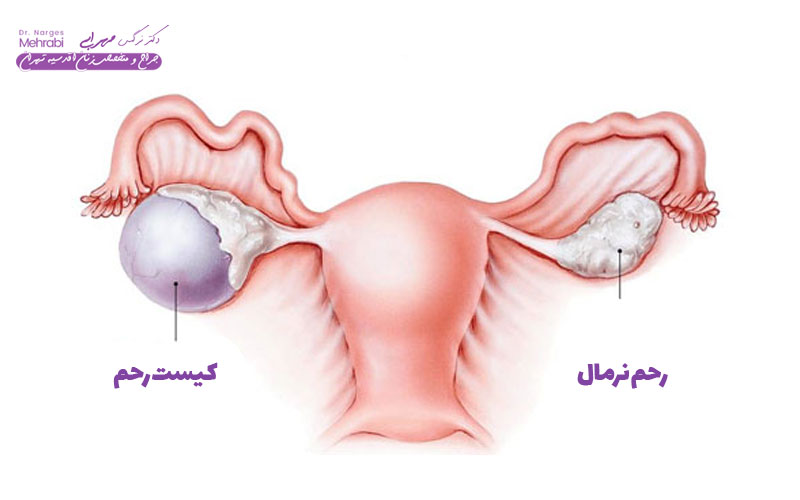
Finally, the occurrence of a secondary fungal infection (such as vaginal candidiasis) following the use of antibiotics is a common side effect. Antibiotics also destroy the beneficial bacteria in the vagina and provide room for fungal overgrowth. If symptoms of fungal infection (such as severe itching and cheesy discharge) are observed while taking antibiotics, the doctor should be informed immediately so that antifungal medication can be added to the treatment regimen. It is mainly based on the main drugs (antibiotics or antifungals), but the use of complementary and alternative drugs can help speed up the healing process and reduce the recurrence of the disease. These drugs are usually used as adjunctive treatments and should never replace best pills for uterine infection prescribed by a doctor. The aim of these treatments is to strengthen the body's immune system and support the return to normal balance in the genital area. One of the most common auxiliary supplements is the use of boric acid in the form of vaginal suppositories. Boric acid can be especially effective in cases of bacterial vaginosis and resistant fungal infections (other than Candida albicans). This substance helps to regulate the pH of the vagina and makes the environment unfavorable for the growth of pathogens. However, it should be noted that oral consumption of boric acid is toxic and should only be used in the form of suppositories and with complete caution. In addition, supplements containing vitamin D and C can also help strengthen the immune system. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of infections in women, and supplementation can improve the body's immune response. Also, some plant extracts such as garlic extract (Allicin) or tea tree oil may be used in topical formulations or supplements due to their antibacterial and antifungal properties, but their scientific evidence is often less than that of standard drugs.
Attention to diet and lifestyle changes is also necessary as a therapeutic supplement. Reducing the consumption of sugar and refined carbohydrates, which can be the perfect food for the growth of fungi, and increasing the consumption of water and fiber, will help maintain the balance of the body and reduce inflammation. Combining these changes with the main drugs is a comprehensive strategy to defeat the infection and prevent its recurrence.
Role of probiotics in maintaining the balance of natural flora after treatment
Using probiotics, especially after completing the course of the best pill for uterine infection (antibiotics), has become a common recommendation. Antibiotics not only kill pathogenic bacteria, but also destroy significant populations of beneficial vaginal and intestinal bacteria, such as lactobacilli. These beneficial bacteria are responsible for maintaining the acidic pH of the vagina and thus preventing the excessive growth of pathogens and fungi. A sharp decrease in the number of lactobacilli after antibiotic treatment leads to the occurrence of side effects such as secondary fungal infection or recurrence of bacterial vaginosis. Probiotics, which include live, beneficial microorganisms, are prescribed to replace these lost bacteria and restore the natural microbial balance. Studies have shown that the consumption of probiotics containing specific strains of lactobacilli (such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri) can be very effective in this matter. accept Vaginal suppositories directly deliver lactobacilli to the target site, while oral capsules first strengthen the intestinal flora and then indirectly affect the vaginal flora as well. In both cases, the ultimate goal is to restore the body's natural defense system against infections.
In fact, probiotics act as an "insurance" after using the best pill for uterine infection to minimize the destructive effects of antibiotics on the body's natural balance. It is very important to consult with your doctor to choose the right dosage and type of probiotic, because not all probiotics are beneficial for vaginal health and proven strains should be chosen in order to achieve the best results for maintaining health after getting rid of the infection. id="conclusion-giri">conclusion
This article comprehensively investigated the different dimensions of uterine infections and how to choose the best pill for uterine infection. We found that the success of the treatment depends not on a single and miraculous drug, but on the accurate diagnosis of the type of pathogen (bacteria, fungus or protozoa) and the prescription of the targeted drug (antibiotic, antifungal or protozoan) by the specialist. It was emphasized that metronidazole, while very effective for bacterial and protozoal infections, is only one option among a wide range of treatments and cannot be called absolutely "best" without a definitive diagnosis.
Common symptoms such as abnormal discharge and itching are warnings that should not be ignored and should lead to immediate medical attention. Meanwhile, the importance of vaginal culture and antibiogram in determining the most accurate and effective drug was highlighted. Also, the need to fully complete the treatment course, even after feeling better, in order to prevent drug resistance and recurrence of infection, is a non-negotiable principle.
Finally, the treatment of uterine infection is a multifaceted process that includes managing side effects, paying attention to drug interactions, and using supplements such as probiotics to restore the natural flora after taking the best pill for uterine infection. Awareness and cooperation with the doctor, armed with the correct information and continuous follow-up, are the main keys to return to health and maintain it. Remember that women's health is a long-term investment that deserves scientific attention and the most precise treatment approaches. href="https://drmehraabi.com/%d8%af%da%a9%d8%aa%d8%b1-%d9%85%d8%aa%d8%ae%d8%b5%d8%b5-%d8%a7%d9%86% d8%af%d9%88%d9%85%d8%aa%d8%b1%db%8c%d9%88%d8%b2-%d8%af%d8%b1-%d8%aa%d9%87%d8%b1%d8%a7%d9%86/">
FAQ
Can I take pills for uterine infection without seeing a doctor?
No, it is not recommended at all to do without seeing a doctor and getting an accurate diagnosis. Stop taking pills for uterine infection. As explained in the article, uterine infections can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or protozoa, and each requires a completely different drug (antibiotic, antifungal, or protozoan). Taking the wrong medicine not only does not help, but can lead to drug resistance, worsening of symptoms and serious side effects.
If the symptoms of infection go away after taking the pills, can I stop taking the medicine?
No, stopping the drug arbitrarily even if the symptoms have completely resolved is very dangerous. Courses of treatment (especially antibiotics) are designed to completely eliminate all pathogens from the body. Stopping the drug early allows the weakened bacteria to grow again, this time resistant to that particular drug, making subsequent treatments very complicated. Be sure to complete the course of treatment as prescribed by your doctor.
Why did my doctor prescribe vaginal suppositories or gels instead of an oral pill?
Vaginal suppositories and gels are topical medications that directly They work at the site of infection (vagina and cervix). These methods are usually used for milder or localized infections such as fungal infections (topical clotrimazole) or bacterial vaginosis (topical metronidazole). Their advantage is that they have less systemic side effects (in the whole body) than oral drugs and can be very effective.
What complications do uterine infections have for pregnancy?
Uterine infections Untreated, especially pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) caused by bacteria such as chlamydia, can have very serious complications for fertility and pregnancy. PID can lead to permanent damage to the fallopian tubes and greatly increase the risk of tubal infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain. During pregnancy, some infections can increase the risk of premature birth and neonatal infections, so timely and complete treatment is vital. ">
Yes, diet can be especially effective in cases of yeast infections. Fungi (like Candida) feed on sugar. Excessive consumption of sugar, refined carbohydrates and alcohol can promote the growth of fungi and increase the risk of recurring yeast infections. During and after treatment, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of sugar and processed foods and increase the consumption of probiotics and healthy foods to help maintain the balance of the body's flora. Go away?
Uterine infection pills (antibiotics or antifungals) usually work quickly. Many patients notice significant relief of their symptoms (such as burning, itching, or discharge) within 24 to 48 hours of starting treatment. However, it may take several days to a week for the symptoms to disappear completely. It is important to finish the full course of the drug even after you feel a rapid improvement to ensure complete eradication of the pathogen.
The best pill for uterine infection.
This article is being updated and expanded to meet the SEO standard.