آنچه در این مقاله خواهید خواند:
تورم غدد لنفاوی گردن به چه معناست؟
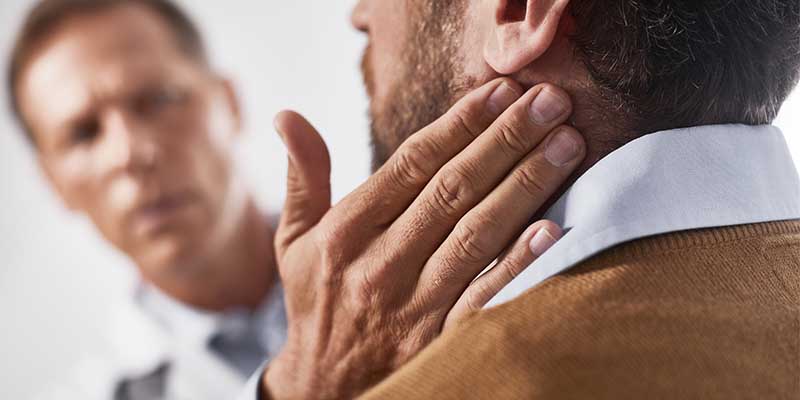
غدد لنفاوی گردنی در جلوی گردن، کنارهها و پشت گردن قرار دارند. They are important bean-shaped organs less than 1 cm in diameter that filter lymph fluid and play a vital role in the body's immune system by clearing damaged cells and microbes. You have hundreds of lymph nodes throughout your body. When these glands become larger than normal, healthcare professionals call it lymphadenopathy, or swollen lymph nodes. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are bumps that you notice when touching different areas of your neck. These bumps may be tender or painful when pressed. Swollen neck lymph nodes can occur in children and adults of any age. Neck lymph node surgery is one of the ways of treatment, which we will discuss more about various treatment methods in the following article.
A normal person does not necessarily feel the swelling of his cervical lymph nodes. However, if the neck lymph nodes are swollen, the doctor can detect one or more bumps under the skin when examining the neck area. The exact symptoms that may occur with swollen lymph nodes depend on the underlying cause; But its common symptoms are:
- Swollen and palpable bumps in the neck
- Pain or sensitivity to touch in the area of swollen glands
- Fever or chills
- General feeling of lethargy or unwellness
- fatigue
- Body pain
Swelling of neck lymph nodes
Swollen neck lymph nodes are often a sign of an upper respiratory tract infection (such as a common cold) or an infection in nearby tissues. Viral infections are the most common cause of cervical lymphadenopathy in children. These problems are usually temporary or treatable. However, there are many possible causes, some of which are more serious. These causes fall into several general categories:- Infections Cancers
- Autoimmune diseases
- Other medical conditions
- Reaction to drugs
Depending on the cause, in some cases, in addition to the neck, you will also notice the swelling of the lymph nodes in other areas of your body; such as the armpit or groin. This condition is called general lymphadenopathy.
1. Infections
A wide range of bacterial, viral and other infections can cause swollen neck lymph nodes. Some are more serious than others. For example:
- Streptococcal sore throat
- common cold and flu
- Adenovirus infection
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- chicken pox
- Shingles
- Redhead
- HIV
- TB
- Epstein-Barr virus infection such as mononucleosis or mono
- Skin infections such as staph
- Lyme disease
- Cat scratch disease
- Toxoplasmosis
2. Cancers
Cancer can cause swollen lymph nodes in more than one area of your body (generalized lymphadenopathy), and the neck may be one of these areas. Note that less dangerous diseases such as strep throat or chicken pox also cause swelling of the lymph nodes in several areas in some cases. For this reason, if you see swollen lymph nodes, it is necessary to see a doctor for further investigation.
Examples of cancers that can cause cervical lymphadenopathy include:
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Rhabdomyosarcoma Thyroid cancer Melanoma Kaposi's sarcoma
3. Autoimmune diseases
When you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system mistakes healthy body cells for invaders. As a result, a large number of white blood cells are mobilized to attack and eliminate this perceived threat. The accumulation of these cells in the lymph nodes leads to swelling. Examples of autoimmune diseases that can cause swollen lymph nodes in the neck (and often other areas) include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus Steel's disease
4. Other medical conditions
Other medical conditions that cause swollen lymph nodes in the neck include:
- Castleman's disease
- Kawasaki disease
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease
- Sarcoidosis
5. Reaction to drugs
The body's reaction to some drugs may also lead to swelling of the cervical lymph nodes. For example:
- some high blood pressure medications (such as atenolol, captopril and hydralazine)
- some antibiotics (such as penicillin and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole)
- Some seizure management drugs (such as carbamazepine and phenytoin) Allopurinol, which is used to treat gout or kidney stones
- Sulindac, which is used to treat arthritis.
- Quinidine, which is used to treat irregular heart rhythm.
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are usually temporary and harmless, and indicate that your body is fighting a minor infection, such as a cold or strep throat. Infections often resolve without treatment, and the lymph node will return to its normal size after the infection clears. But sometimes this condition can be a sign of a more serious problem. Therefore, if you see the following, be sure to see a doctor:
- Presence of severe symptoms such as severe pain, high fever or difficulty breathing
- Continuation of swelling for more than 2 weeks
- Existence of additional symptoms such as night sweats and constant fever
- Swelling of the gland without any other symptoms (could be a sign of cancer or an autoimmune disease)
- Feeling of a hard and painless mass in the lymph node
- Rapid change in lymph node size
- Swelling in more than one area of lymph nodes; For example, simultaneously in the neck and groin
The doctor usually detects the swelling of the neck lymph nodes by touching the person's neck and asks the patient about the following:
- Other symptoms of the person
- Personal and family medical history
- Used drugs and the possibility of exposure to poisons
- Lifestyle habits
- recent trips Exposure to other people with infectious diseases
He may also order additional tests to find out what is causing the swelling:
- blood test
- Throat culture to check for bacterial infections such as streptococci
- computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- X-ray photography
If necessary, the doctor will also perform a biopsy of the cervical lymph nodes to check for the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment methods for swollen neck lymph nodes directly depend on the underlying cause of the swelling. Health care professionals choose the best treatment option according to the causative agent.
1. Treatment of swelling caused by infections
In most cases, swollen neck lymph nodes are caused by the body fighting an infection. In such a situation, the gland usually returns to its normal size after the infection is cleared. Treatment in these cases includes two parts:
A) Home care (for viral infections and to reduce discomfort): Swollen lymph nodes in the neck usually do not require medical treatment; Unless it's painful. The following strategies help to reduce discomfort:
- Using a warm compress several times a day on the swollen area
- Using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) without a prescription (such as ibuprofen) for pain relief
- Adequate rest and drinking lots of fluids
B) Drug treatment (for bacterial infections): If symptoms of a bacterial infection (such as strep throat) are observed, the doctor may prescribe appropriate antibiotics to eliminate the pathogen.
2. Treatment of swollen neck lymph nodes caused by cancer
In more serious conditions such as cancer, the doctor will discuss treatment options with the patient based on the type, stage and overall health of the patient. Possible treatments for cancers that cause cervical lymphadenopathy include:
- Chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
- Immunotherapy (treatment based on the activation of the immune system)
- Surgery: This procedure, mainly used to manage head and neck cancers (such as throat, mouth and tongue cancer, thyroid cancer, and melanoma), involves performing a lymphadenectomy (complete removal of the involved lymph nodes) to prevent the disease from spreading.
3. Treatment of swollen neck lymph nodes caused by HIV
For people with HIV, antiviral drugs are prescribed to manage the virus. These drugs reduce the amount of virus in the blood and body fluids until it reaches an undetectable level. By reducing the activity of the virus and strengthening the immune system, the swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck will be removed or greatly reduced.4. Treatment of swelling caused by autoimmune diseases
Swollen lymph nodes caused by autoimmune diseases (such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis) occur when the immune system becomes overactive and attacks healthy tissue. The treatment of this type of swollen lymph nodes is directly focused on controlling the underlying autoimmune disease. With the successful management of the underlying disease, it is expected that the swelling of the lymph nodes will also decrease. These treatments may include:
- Immunosuppressant drugs: to reduce overactive immune system
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: to reduce inflammation throughout the body, including the lymph nodes
5. Treatment of swollen lymph nodes caused by a reaction to drugs
. In this case, the main treatment consists of stopping the use of the relevant drug (under the supervision and at the discretion of the doctor) or replacing it with another drug. After stopping or changing the medicine, the swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck usually disappears gradually.
Swelling of neck lymph nodes is not always preventable and often happens suddenly; For example, when a person gets a viral or bacterial infection. In other cases, swelling is caused by diseases that affect the whole body. However, you can prevent many contagious infections that are the main cause of swollen neck lymph nodes by following a few simple tips:
- Washing your hands: Be sure to wash your hands when necessary, including after touching common items or caring for a sick person.
- Disinfect surfaces: Disinfect surfaces such as desks, counters, and doorknobs at home and at work.
- Strengthening the immune system: Strengthen your immune system by consuming nutritious foods and having enough sleep.
- Injecting vaccines: Get the vaccines your doctor recommends (such as the flu shot).
Since the lymph nodes of the neck are directly related to the health of the head and face areas, prevention of infections in that area is also of particular importance:
- Oral hygiene: Use a toothbrush and floss regularly. Tooth and gum infections are one of the common causes of swollen lymph nodes under the jaw and neck.
- Avoid contact with sick people: As much as possible, avoid close contact (such as kissing or sharing utensils) with people who have infections such as mononucleosis or a severe cold.
- Scalp protection: Take care of skin wounds and scratches in the head and neck area that can be a way for bacteria to enter.