Table of contents
- What is tdcs electrical brain stimulation?
- Tdcs electrical brain stimulation is used to treat what disorders Does it?
- Who are tdcs electrical brain stimulation suitable for?
- What are the advantages of tDCS?
- How to perform tdcs electrical brain stimulation
- Preparation before tdcs electrical brain stimulation
- Care after tdcs electrical brain stimulation
- What are the complications of tdcs electrical brain stimulation?
- Conclusion
tdcs electrical brain stimulation is a way to stimulate the brain. In this method, a weak electric current (usually 1 to 2 milliamps) is passed through electrodes on the scalp. This flow does not directly cause neurons to fire, but it makes the activity of neurons in the brain a little more or less and prepares the brain to learn or do a certain task. For more information about tdcs brain electrical stimulation, stay with us in the rest of this article from your doctor.
What is tdcs electrical brain stimulation?
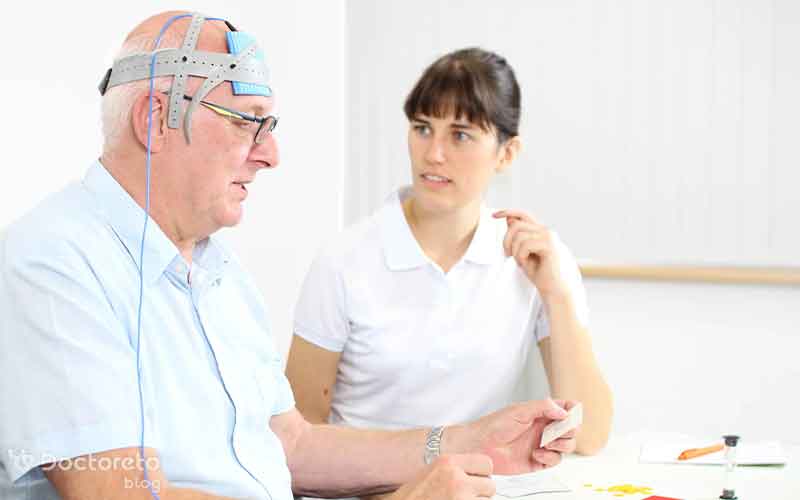
tDCS or Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation is a non-invasive way to stimulate the brain. In this method, a weak current is sent to the brain through the scalp. Current is transmitted by a battery-powered device through special electrodes and conductive gel or sponge. According to the location and type of current, tDCS can increase (anodic) or decrease (cathodic) the activity of neurons and thus affect brain function.
The table below summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of tdcs electrical brain stimulation.
| Benefits | Complications |
|---|---|
| Possibility of improving mood and reducing symptoms of moderate to severe depression | Mild headache or temporary dizziness |
| Improving sleep quality | Fatigue or feeling sleepy after the session Treatment |
| Increased nerve flexibility | Skin irritation such as itching or redness at the site of the electrodes |
| Enhancement of working memory and cognitive function | Tingles or mild warmth |
| Improved language function and cognition after stroke | Rare mood changes or confusion Temporary |
| Reduction of neuropathic pain symptoms after spinal cord injury | No severe or permanent complications reported |
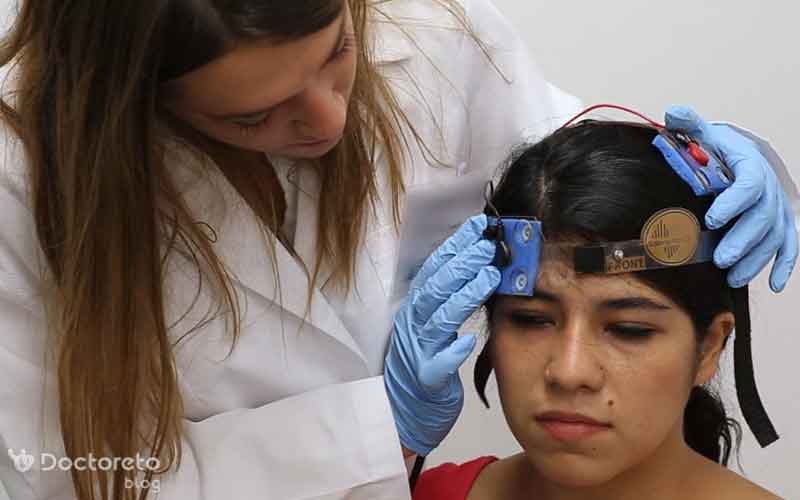
Tdcs electrical brain stimulation is used to treat what disorders?
Electrical brain stimulation as tDCS is currently used to treat or improve a wide range of clinical disorders. From depression, schizophrenia, aphasia, addiction, epilepsy to chronic pain relief, attention problems and motor rehabilitation. In addition to medical applications, tDCS is also used in non-medical fields to enhance learning, increase concentration, relaxation and meditation:
-
Treatment-resistant depression
- Anxiety
- Chronic nerve pains
- Improving cognitive performance Addiction disorders
Who are the tdcs electrical brain stimulation suitable for?
tDCS can be useful for people who need to improve their cognitive, motor or speech functions, especially in patients with neurological disorders such as MS, Parkinson's disease, stroke, dementia or head injuries. This method may be practical and effective and help the rehabilitation process and improve the quality of life of patients by strengthening the activity of neurons.
English text:
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a portable, wearable brain stimulation technique that delivers a low electric current to the scalp.
Persian translation:
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a portable and wearable brain stimulation technique that delivers a weak electric current to the scalp.
neuromodec
What are the advantages of tDCS?
English text:
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a portable, wearable brain stimulation technique that delivers a low electric current to the scalp.
Persian translation:
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation (tDCS) is a portable and wearable brain stimulation technique that delivers a weak electric current to the scalp.
tDCS is a non-invasive method that delivers a weak electrical current to the brain and usually causes a mild tingling sensation. This technique is easily combined with other treatment methods to have faster effects. Due to these characteristics, tDCS is considered a promising treatment method in the rehabilitation of stroke patients and improvement of brain functions and quality of life.
how to perform tdcs brain electrical stimulation
tDCS is a transcranial electrical stimulation technique that involves applying a weak electrical current (1 to 2 mA) through 2 or more electrodes on the scalp. In the traditional method, one electrode acts as the target electrode and the other as the reference electrode. A weak current changes the activity of neurons without generating an action potential and can enhance or modulate brain function.
In general, how to perform this method should be explained as follows: to prepare for tDCS, a cap is placed on the patient's head to keep the location of the electrodes fixed. Then, two cup-shaped electrodes are prepared with conductive gel and inserted between the cap and the skin. Then, one electrode is placed on the target area (such as epileptic focus or seizure site) and another on the opposite side to direct the current to the target area.
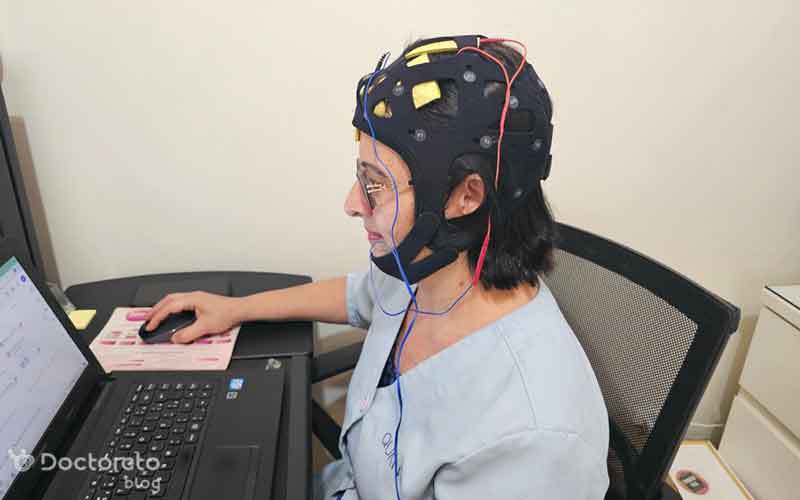
Preparation before tdcs electrical brain stimulation
It is important to observe some points before tdcs brain electrical stimulation to increase safety, effectiveness and reduce side effects. These items include:
- Examining the general health condition of the person and the history of diseases
- Investigating the presence of metal implants in the skull area
- Avoidance of caffeinated drinks, alcohol or drugs that affect brain activity
- Cleanliness of the scalp at the location of the electrodes
- Using wet gel or sponge to improve conductivity and prevent skin irritation
- sitting or lying down in a comfortable and stable position
- Avoid sudden movements during the session to prevent moving the electrodes
tdcs-electrical-brain-stimulation-duration
The duration of tDCS electrical brain stimulation is usually between 10 and 30 minutes per session, depending on the treatment goal and protocol. Treatment plans are adjusted based on the severity of the disease and the patient's response.
care after tdcs electrical brain stimulation
After tDCS electrical brain stimulation sessions, simple care is necessary to improve results and reduce complications. To maintain effectiveness, regular follow-up with a physician, such as weekly assessments of cognitive function or mood, is helpful.
Following some tips can help reduce possible side effects and increase effectiveness:
- Examination of the patient's physical condition
- Allocating time to rest after tdcs electrical brain stimulation
- Avoid intense physical or mental activities
- Drink enough water to help improve the general condition of the body
- Paying attention to any unusual symptoms such as severe headache or dizziness and informing the doctor if needed
- Record mood, cognitive or motor changes after the session to help evaluate treatment
English text:
tDCS is a widely-used tool to induce neuroplasticity and modulate cortical function by applying weak direct current over the scalp.
Persian translation:
tDCS is a widely-used tool to induce neural plasticity and modulate cortical function by applying weak direct current over the scalp. href="https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychology/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00685/full" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">frontiersin
What are the side effects of electrical brain stimulation with tdcs?
tDCS is usually safe and painless, but some mild side effects may occur. The most common side effects of electrical stimulation of the brain with tdcs are:
- Pingling feeling under the electrodes
- Fatigue after treatment session
- Slight itching in the area of electrodes
- Mild skin problems
Conclusion
tdcs electrical brain stimulation is a non-invasive method to enhance brain activity that helps improve cognitive, motor and emotional functions in various disorders. Despite the mild and temporary side effects, this method is considered a promising option for the treatment of patients with neurological and brain problems. Studies have shown that tDCS is effective in improving memory, increasing concentration, improving motor learning, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety, and even in post-stroke rehabilitation. But it is better to consult a neurologist before starting the treatment.
Your doctor takes care of your health!