Table of contents
Listen to the summary of this article in this podcast:
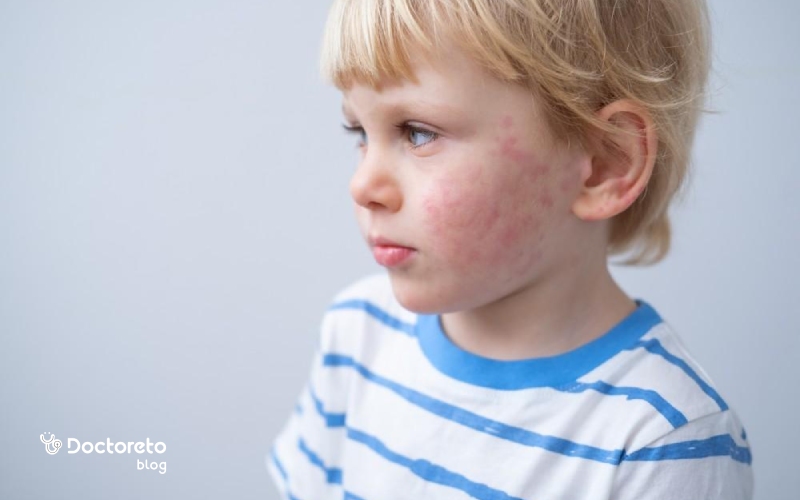
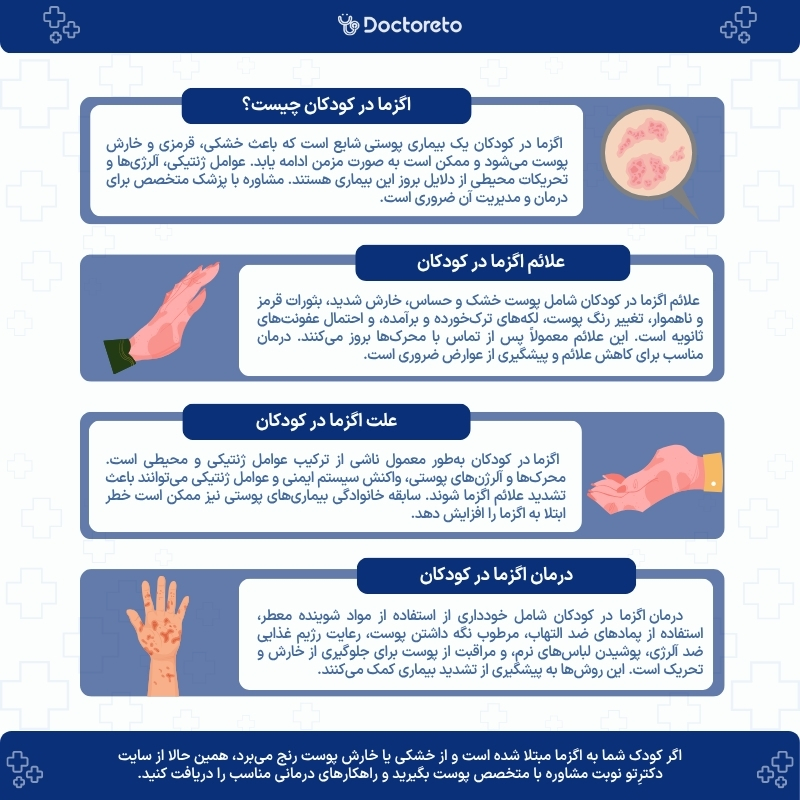
What is eczema in children?
Eczema in children is one of the common skin diseases that causes red, dry and itchy spots on the skin. These spots usually appear on areas such as the face, behind the knees and elbows. Eczema in children is often chronic and experiences periods of improvement and relapse. This type of eczema usually starts at a young age and may continue into adulthood. Factors such as genetics, allergies and environmental irritations can play a role in the occurrence of eczema.
| Characteristics | Eczema in children | Eczema in adults |
|---|---|---|
| Age of onset | Usually at a young age (under 5 years) | Can start at any age |
| Location Symptoms | Face, back of knees, elbows and hands | Usually on dry areas of the body such as hands, feet and neck |
| Severity of symptoms | May be more severe and cause more discomfort | Symptoms may be milder, but some people have severe symptoms |
| Cycle Disease | Periods of remission and relapse, can last into adulthood | Symptoms may improve or worsen over time, especially in response to environmental factors |
| Precipitating factors | Genetics, allergies, environmental stimuli, and hormonal changes | Similar factors such as allergies, stress, and changes Hormonal |
| Treatment | Moisturizers, steroid creams, and antiallergic medications | Treatment similar to children, but stronger medications may be needed |
| Prognosis | Many cases persist into adulthood | Symptoms may be controlled, but may be persistent Treatment is needed |
What are the symptoms of eczema in children?
Eczema symptoms in children begin after interacting with triggers that irritate their skin. These symptoms may vary based on the type of stimulus, the child's age, and the severity of the eczema. Typically, the symptoms of eczema in children include the following:
- Dry and sensitive skin: The baby's skin may become dry, rough and very sensitive, especially in areas that are subject to irritation.
- Severe itching: itching is one of the most common symptoms of eczema, which may be very uncomfortable for the child and cause restlessness and insomnia.
- Uneven and red rashes: skin rashes appear as red and inflamed spots on the skin of the body and face. These rashes may last temporarily or in long-term periods.
- Discoloration of the skin: In some cases, the skin of the affected area changes color and may become red or darker than the normal skin color. This condition is known as hyperpigmentation.
- Raised and cracked skin: In some children, eczema causes raised and cracked patches of skin that may be painful or bleed.
- Secondary infections: if the child burns his skin due to excessive itching, the possibility of bacterial infections such as cellulitis or herpes increases.
Eczema symptoms in children may change over time and experience periods of improvement and relapse. Appropriate treatment and skin care can help reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
form of eczema in children
Eczema in children, the most common type of which is atopic dermatitis, appears as red, dry and itchy spots on the skin and can be accompanied by peeling, surface cracks and sometimes discharge or scabs. In infants, the cheeks, forehead, and scalp are usually involved, while in older children, the folds of the elbows, behind the knees, wrists, and the neck are more affected. Severe itching is one of the main symptoms, and frequent scratching can cause the skin to thicken and darken. Affected children's skin is usually very dry and sensitive and aggravated by contact with irritants such as strong soaps, perspiration or cold air. Timely diagnosis and initiation of appropriate skin care plays an important role in controlling symptoms and preventing recurrence.
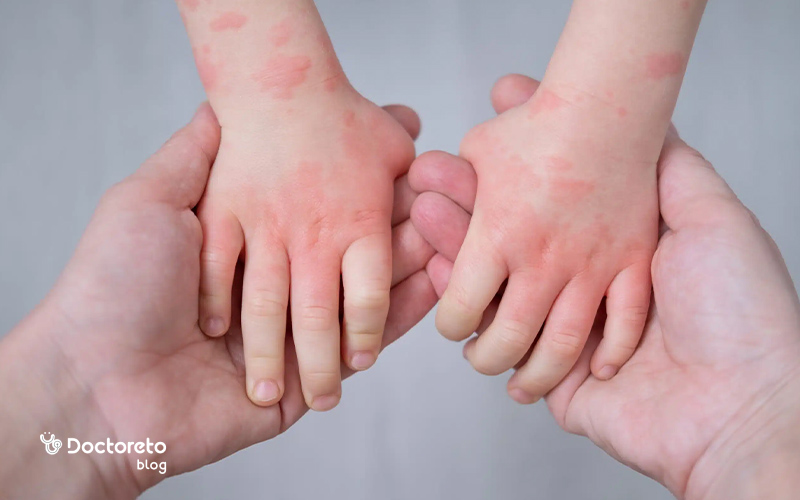
English text: Baby eczema is a common skin condition that affects infants. Eczema causes your baby's skin to become dry, bumpy and itchy Persian translation: Baby eczema is a common skin disease that affects babies and children. Eczema causes dryness, raised patches and itchy skin in the baby.
quoted from my.clevelandclinic
coined eczema in children
One of the forms of eczema in children, especially babies, is coinic eczema. The form of this eczema, which is also called nummular dermatitis, is that coin-shaped spots appear on the child's skin. These circular spots are usually red and inflamed and are accompanied by itching and discomfort.
What is the cause of eczema in children?
The exact cause of eczema in children is not fully known, but researchers believe that this disease is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the effective factors in the occurrence of eczema in children are:
- Skin irritants and allergens: contact of the child's skin with different substances such as special fabrics, soaps, detergents and some food items can irritate the skin and aggravate the symptoms of eczema.
- Immune system reaction: The child's immune system may react abnormally to some stimuli, which causes inflammation and eczema symptoms.
- Genetic factors: In some cases, genetic predisposition plays an important role in the occurrence of eczema. If there is a history of skin diseases such as eczema or allergies in the child's family, the child is more likely to get this disease.
These factors can cause eczema in children separately or in combination with each other.
diagnosis of eczema in children
The doctor diagnoses eczema after a physical examination. The appearance of rashes on your child's skin helps to accurately diagnose eczema. However, the doctor may order more tests to find out the cause of the symptoms on the child's skin. Tests to diagnose eczema can include the following:
-
Allergy test
- Blood tests
- skin biopsy
What is the treatment of eczema in children?
The treatment of eczema in children depends on the cause and severity of the symptoms. To reduce the symptoms, the following methods can be used:
- Avoid using perfumed soaps and detergents that can irritate the baby's skin.
- Using topical ointments and creams containing mild or anti-inflammatory steroids to reduce inflammation and itching.
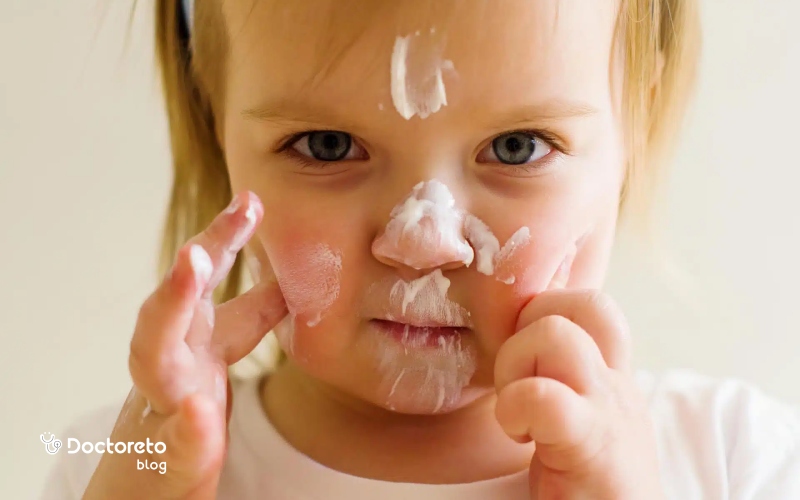
- Keeping the skin moist with appropriate moisturizing creams and ointments to prevent dryness and stretch marks.
- Following an anti-allergy diet to reduce irritation caused by allergies.
- Wear soft and breathable clothes to prevent skin irritation.
- Taking care of the skin when the symptoms appear and preventing it from scratching.

What are the types of eczema in children?
There are different types of eczema in children, which we have introduced in the following table:
| Eczema type | Main symptoms in children |
|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | Dry skin, severe itching, inflammation and redness, cracking in the skin |
| Contact dermatitis | Redness and burning From contact with an allergenic substance (such as soap or metal) |
| Seborrheic dermatitis (cradle cap) | Grey and yellow skin on the scalp, eyebrows or behind the ears |
| Disydrotic eczema | Small and itchy blisters on the palms or feet |
| Eczema Nummular | Round, dry and scaly spots on the skin |
Complications of eczema in children
Eczema in children can cause various complications that affect their daily life. Along with itchy skin, eczema can cause more severe allergies because it weakens the immune system, can cause blisters, and breaks down the skin barrier that protects against skin diseases. Some of these complications are:
- Severe and continuous itching: itchy skin can make the child restless and uncomfortable and prevent him from his daily activities.
- Sleep disturbance: itching and discomfort caused by eczema may disturb the child's sleep and cause insomnia and disturbed sleep.
- Skin cracks and sores: constant itching can cause scratching and open sores on the skin, which can lead to skin infections.
- Increased risk of skin infections: Eczema makes the skin weaker and hence, the child is more exposed to skin infections such as cellulitis and herpes.
- Skin thickening and discoloration: In areas affected by eczema, the skin may thicken and change color, causing an ugly appearance.
- Possibility of other allergies: Eczema may lead to other allergies such as asthma or allergic rhinitis.
- Decreasing self-confidence: the appearance of a child's skin can affect his self-confidence and cause embarrassment and anxiety.
Prevention of eczema in children
Although there is still no definitive treatment for eczema, but following some tips, it can be prevented or reduce its severity. To prevent eczema in children, consider the following recommendations:
- Identifying and keeping the child away from stimulating factors such as perfumed detergents, dust and smoke
- Using cotton and comfortable clothes that do not irritate the baby's skin
- Keeping the baby's skin moist with fragrance-free creams and lotions for children
- Preventing excessive sweating of the child's body
- Maintaining the ambient temperature at a cool and balanced level
- Keeping the environment around the child clean and preventing the accumulation of dust
Conclusion
Eczema in children is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that is characterized by itching, dryness and red lesions and often has a genetic and immune background. This disorder can start from the first months of life and continue with periods of relapse and remission. Although the severity of the symptoms is different in different people, its chronic nature makes it important to pay attention to the triggering factors and the general condition of the skin. All in all, eczema is part of the range of childhood allergic diseases, and knowing it correctly helps to better understand the course of the disease and possible consequences in the following years of life.
Your doctor takes care of your health!