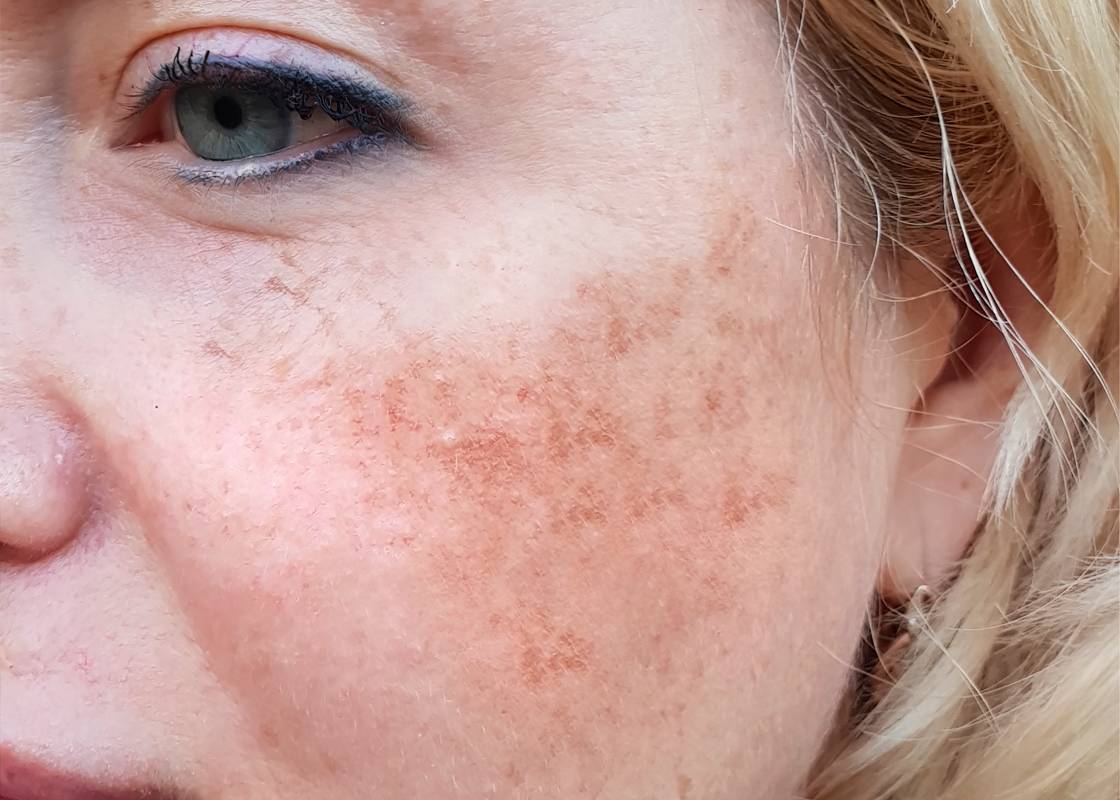
ملاسما (Melasma) یک اختلال شایع و مزمن پیگمنتیشن پوست است که با ایجاد لکهای قهوهای تا خاکستری در نواحی مانند گونهها، پیشانی، بینی و بالای لب بروز میکند. These spots are usually symmetrical and are caused by increased production or abnormal accumulation of melanin in the superficial and deep layers of the skin. Unlike simple sun spots, melasma is a more complex and multifactorial disease; For this reason, its treatment requires a precise, gradual approach based on scientific principles. This disorder usually has periods of improvement and exacerbation, and even after treatment, its control must continue to prevent spots from returning or worsening.
Research shows that melasma is closely related to hormones, sunlight, genetics, and chronic inflammation. In many people, these spots are caused or aggravated by pregnancy, taking hormonal drugs, prolonged exposure to the sun, or improper use of lasers. One of the important features of melasma is that it appears in different layers of the skin (epidermis, dermis or both) and this affects the treatment response. The deeper the pigmentation, the more time-consuming the treatment and the more conservative approach required.
How is melasma created? It means the cells that produce melanin. When these cells are hyperactive or receive wrong inflammatory messages, they produce a lot of melanin and accumulate in certain places. This process can be caused by hormonal changes, chronic exposure to sunlight or weakness of the skin's defense barrier. UV light and even blue visible light have the ability to stimulate melanocytes, and this makes even indoor light or mobile light play a role in aggravating melasma. For this reason, complete light control is one of the main pillars of treatment.
Another important factor is inflammation. In many patients, the skin is prone to chronic inflammation, and the slightest irritation, such as vigorous exfoliation, excessive heat, or improper use of lasers, can exacerbate blemishes. This feature shows that melasma, unlike surface blemishes, is not caused by a simple stimulus but is the result of an instability in the skin color regulation system. Therefore, successful treatment cannot be achieved with just one laser session or a topical product, and requires a multi-step program.
Main causes of melasma
- Sunlight and visible light
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control pills)
- Genetics and family history
- Skin inflammation and Improper peels
- Heat, oxidative stress and smoking
Types of melasma and the difference in treatment response
Melasma is divided into three types of epidermal, dermal and mixed in terms of pigment depth. In epidermal melasma, melanin accumulates in the superficial layers of the skin and usually has a faster and more predictable treatment response. But in the dermal type, the pigment is placed deeper and due to more difficult penetration, the treatment process is longer and more conservative. The mixed type—which is a combination of both—is the most common type in clinics and requires careful management to prevent spots from returning.
It is the difference in depth that determines whether a person will respond better to laser treatment, topical medications, or a combination of methods. In deep melasma, the use of thermal or high-energy lasers can aggravate the spots, while non-thermal methods such as low-energy Kioswitch and combination drug treatments are more effective. Therefore, diagnosing the type of melasma before starting treatment is very important and forms an important part of the doctor's decision-making.
Types of melasma
- Epidermal: more superficial, faster response
- Dermal: deeper, requires a conservative approach
- Mixed: The most common type requires step-by-step treatment
Symptoms and distribution patterns of melasma
Diagnosis of melasma is usually possible by observing specific patterns of spots. These spots are often symmetrical and can be seen in areas such as cheeks, forehead, nose, chin and upper lip. The color of the spots varies from light brown to bluish gray, and this color change can indicate a different depth of melanin. In some cases, mild inflammation or skin sensitivity is also associated with melasma, especially in people who have reactive skin or have used irritating products.
Another characteristic of melasma is its chronicity. Unlike simple sunspots, this disease tends to return and is usually affected by the seasons; It means that it gets worse in summer and gets better in winter. This variable nature means that melasma treatment always involves long-term control, not just spot clearing. The main goal of treatment is to manage the disease and reduce its stability, not to completely remove the spots at once.
Common patterns of melasma
- Mid-face
- Cheeks (Malar)
- Jaw and chin (Mandibular)
How is melasma treatment done?
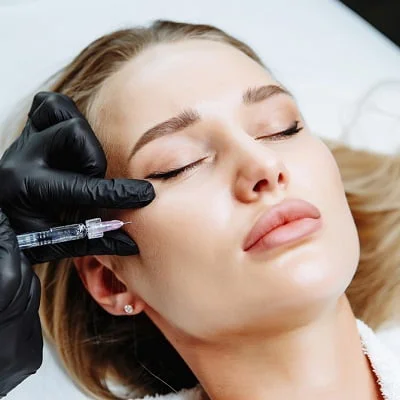
Melasma treatment is a multi-step process that must be carefully designed based on the skin type and depth of the disease. No treatment alone is sufficient; Rather, a combination of medicinal, protective methods and sometimes non-thermal lasers are used. The first and most important component of treatment is light control. Without full sun and visible light protection, no treatment—even the most professional—will last. Using a full-spectrum sunscreen, reapplying regularly, and avoiding direct heat are critical at this stage.
Aside from light protection, topical treatments including melanogenesis inhibitors (such as hydroquinone, tranexamic acid, azelaic acid, and retinoids) help reduce melanocyte activity. These treatments are the mainstay of disease control. In cases where the pigmentation is deeper, the doctor uses a combination of oral medications such as low-dose tranexamic acid and non-thermal methods such as the low-energy Kioswitch laser. Instead of creating heat, these methods reduce the pigment gradually and the risk of melasma exacerbation is lower.
The most effective melasma treatment methods
- Full protection against light
- Melanin inhibitor topical creams
- Low energy Kioswitch laser
- Oral medications Low dose according to the doctor's opinion
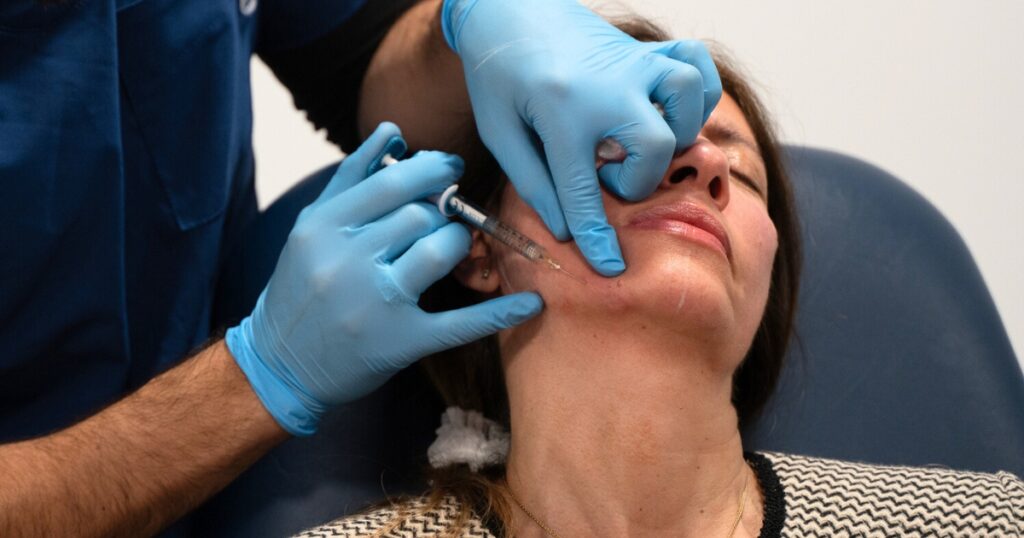
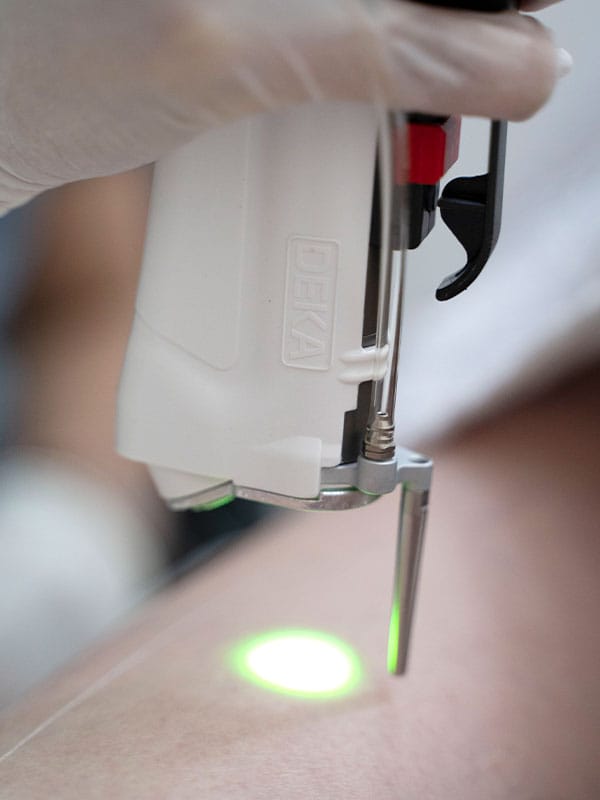
The role of the KiSwitch laser in the treatment of melasma
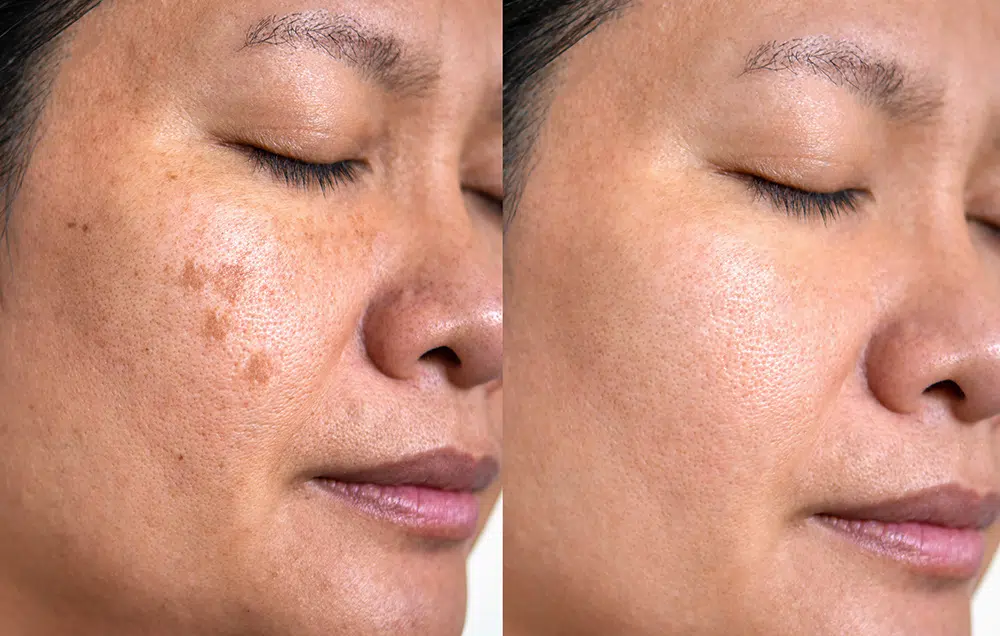
If it is used with the right parameters and a conservative protocol, the KiSwitch laser can be one of the effective options for the gradual reduction of melasma. In this method, the goal is not to reduce the activity of melanocytes; Rather, it is to crush excess melanin and help clear it. Sessions are usually performed with low energy, limited number of passes and standard time interval to minimize skin irritation and inflammation. This treatment can help to gradually lighten the skin, especially for people who have mixed or deep spots.
The results of Kyoswitch melasma treatment are usually gentle, gradual and controllable. Unlike ablative methods, this laser does not cause severe exfoliation and epidermal stimulation is limited. The goal of the treatment is only gradual "lightening" of the spots, not their sudden removal. This issue is the main criterion for the safety of melasma treatment, and this is precisely where it differs from the treatment of other skin spots.
Kioswitch advantages in melasma
- Gradual lightening without severe inflammation
- Less risk of returning or aggravating the spot
- Possibility of combining with topical and oral medications
Essential care in melasma
Care after treatment is one of the most important parts of melasma management. Even the best treatments don't last without follow-up care. Avoiding sunlight, using full-spectrum sunscreen, and heat control are vital principles. In addition, the use of creams to strengthen the skin barrier, antioxidants and anti-inflammatory products can prevent the aggravation of the disease. Patients with sensitive skin should avoid strong exfoliators or irritating products to maintain skin color stability.
During this period, the doctor usually offers a program that includes a combination of soothing, moisturizing, and skin color stabilizing treatments. This program, along with periodic review sessions, helps to stabilize the healing process and reduce the possibility of the stain returning. هرگونه درمان تکمیلی مانند لیزر یا دارو باید تنها بر اساس نظر پزشک انجام شود تا توازن پوست حفظ شود.
نکات کلیدی مراقبتی
- استفاده مداوم از ضدآفتاب طیف کامل
- پرهیز از گرما و نور شدید
- اجتناب از لایهبرداری قوی
- استفاده از محصولات ترمیمکننده و ضدالتهاب