LASIK, LASIK surgery and their differences - Dr. Mohammad Periman

Dr. Mohammad Periman
TabrizSurgeon and ophthalmologist
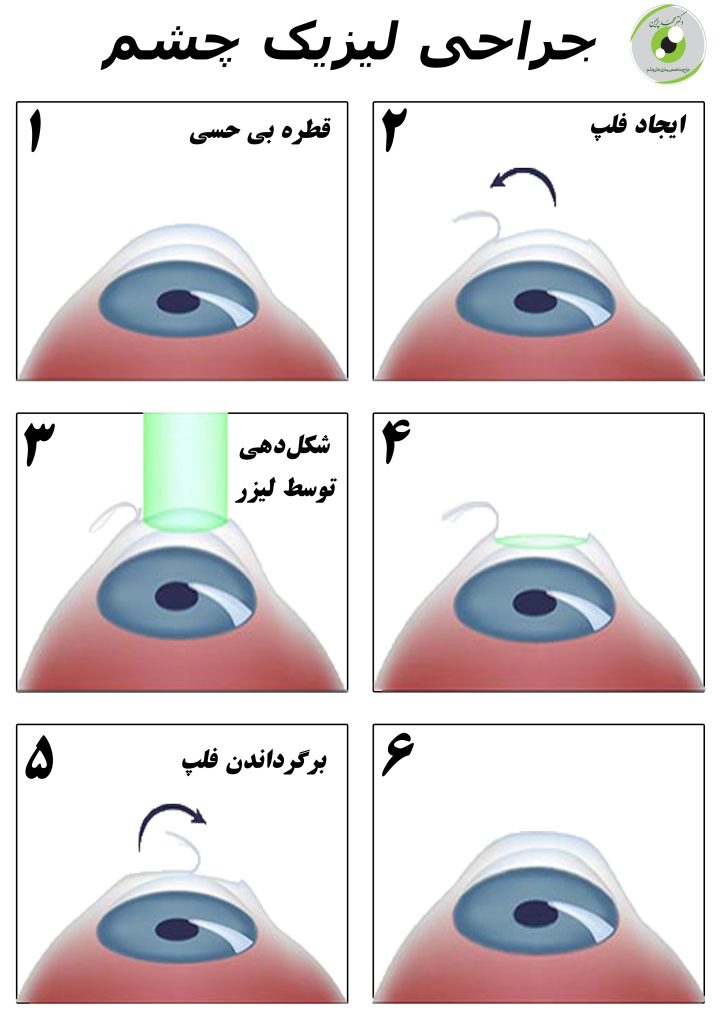
Lasik or LASIK stands for Laser-Assisted In-Situ Keratomileusis. This surgery has been used by ophthalmologists around the world for nearly 20 years and has helped improve the vision of millions of people with eye problems. This treatment method is so effective and efficient that even NASA has approved it and uses it to treat the eyes of its astronauts. Currently, LASIK is the most widely used and popular laser eye surgery. LASIK is the term "in-situ keratomyelosis using a laser" and is performed in such a way that the surgeon removes a thin flap (layer), about 100 to 180 microns thick, from the corneal tissue. The flap contains both layers of epithelium (upper layer) and a part of the stroma layer.
The popularity of LASIK is not without reason, the efficiency of this method is great for most patients. Patients who prefer LASIK to PRK are satisfied with the shorter recovery period and faster recovery of vision. In addition, the regression rate of LASIK is very low and only 5 to 10% of patients need secondary treatment in the coming years

risks and side effects
However, it also has its own complications. If there is a severe blow to the head, the flap of corneal tissue is displaced, this complication is an emergency and may cause long-term damage to the eye. Of course, such an occurrence is very rare. Once the flap has healed in place, it is unlikely to move. Also, many patients complain of dry eyes, which is one of the side effects of surgery. Damage to the corneal nerve during surgery also causes dry eyes.
The vision of some patients is also disturbed at night. Patients' vision decreases at night for the following reasons:
- Swelling of the cornea sometimes causes the loss of the patient's vision at night and causes problems such as nasal aura or "star" vision at night.
- Night vision sometimes decreases because the pupil dilates too much and its size is not proportional to the size of the corrected eye area. Many patients experience night vision problems immediately after surgery, but this condition usually resolves within the next few months.
This surgery carries more serious risks. Serious and permanent injuries, for example, corneal protrusion, scarring, abnormal correction, sensitivity to certain lights and blindness, are among the serious complications that rarely occur. The surgical recovery period is very short and most patients notice an immediate improvement in vision and enjoy its full benefits from the day after the operation. This operation is a good choice if you have a thin cornea or if your eyes have special conditions that make laser eye surgery difficult. During this surgery, instead of using two lasers that are used in LASIK, only one laser is used to improve and correct your vision.
This operation (keratomileusis epilitum with laser) has the advantages of both LASIK and PRK methods, and at the same time, the probability of complications after that is low. Then the surgeon carefully cuts the tissue with a knife without using a laser and lifts a thin flap from the tissue. The thickness of the flap in the LASIK method is about 50 microns and in the LASIK method it is 100-180 microns. In the next step, the surgeon reshapes the surface of the cornea with a laser and then returns the epithelium to its place. At the end, like the PRK method, a dressing lens is placed on the eye so that the epithelium is gradually restored and covers the eye.
It may seem a little confusing, but the main difference between LASIK and LASIK is related to the thickness of the cut tissue. In the LASIK method, the epithelium and a part of the stroma layer are cut and lifted. But in LASAK and PRK methods, only the epithelium layer is removed.

What is the difference between these two methods?
The main difference between these two surgeries, as mentioned above, is in the way the cornea is opened for laser radiation on its underlying layer.
Sometimes the unique characteristics of your eyes can determine which of these two methods is suitable for you. For example, if you have a thin cornea, you are not a suitable candidate for LASIK treatment, and LASIK treatment is recommended as an alternative.
To examine and treat your eye problems by Dr. Mohammad Periman through option
















