Quick access
- Summary of gallbladder filling symptoms
- What does gallbladder filling mean?
- The most common gallbladder filling symptoms Bile
- Gastrointestinal symptoms related to gallbladder filling
- Referral symptoms of gallbladder filling
- Less known but important symptoms
- Difference between symptoms of gallbladder filling and gallstones
- Factors that increase the risk of gallbladder fullness
- When are symptoms of gallbladder fullness dangerous?
- Methods to diagnose gallbladder fullness
- Summary
- Frequently asked questions about gallbladder fullness symptoms Bile
Summary of gallbladder filling symptoms
| symbol | Description | intensity |
|---|---|---|
| pain on the upper right side of the abdomen | especially after fatty foods | moderate to severe |
| Heaviness and fullness of the stomach | No obvious bloat | light to medium |
| nausea | usually after meals | mild to severe |
| Indigestion | Difficulty digesting fat | continuous |
| radiating pain to the back or right shoulder | reference tag | Medium |
| bitter mouth | most mornings | light |
| Premature saturation | Decreasing appetite | light |
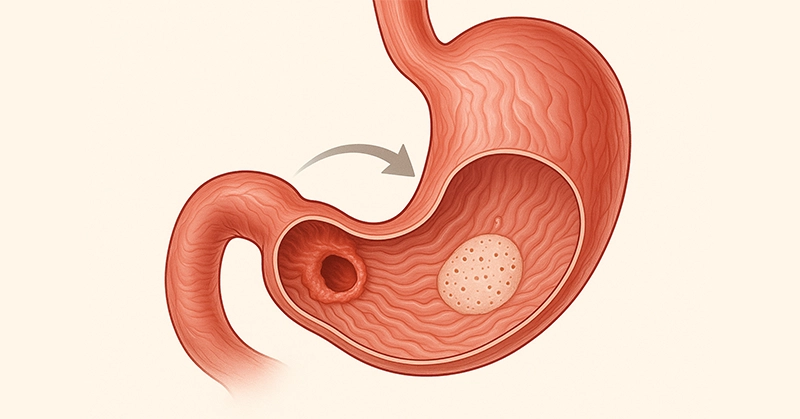
What does the filling of the gallbladder mean?
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver, and its main function is to store and concentrate bile. Bile is a liquid that is necessary for the digestion of fats Gallbladder congestion occurs when bile does not drain properly. This situation can happen for reasons such as gallbladder motility disorder, partial obstruction of the bile ducts, or changes in the composition of bile. In this case, the bile stays in the gallbladder too much and the internal pressure increases.
The most common symptoms of gallbladder filling
These symptoms are usually gradual and may seem mild at first. But in the absence of follow-up and treatment, they become more intense and annoying. Care should be taken to avoid these symptoms leading to is also annoying.
-
pain in the upper right part of the abdomen
The most common symptom is pain in the upper and right side of the abdomen. This pain usually:
-
Intensifies after consuming fatty foods
-
It may take a few minutes to a few hours
-
Sometimes it feels like pressure or heaviness
-
feeling of fullness and heaviness of the stomach
Unlike bloating, which is associated with gas, in this case, the patient feels that the stomach is "full and heavy", even after consuming a small amount of food.
-
Nausea and sometimes vomiting
Disturbance in bile secretion causes indigestion, which results in nausea, especially after heavy meals.
Gastrointestinal symptoms related to gallbladder filling
The filling of the gallbladder is directly related to the functioning of the digestive system.
Chronic indigestion
People with this problem usually complain about digesting fatty foods and feel that the food "stays in the stomach".
Change in defecation
In some people, stool may:
-
Brighter than usual
-
be greasy or smelly
which indicates a disorder in the entry of bile into the intestine.
Referral symptoms of gallbladder filling
All symptoms are not necessarily felt in the gallbladder.
Pain in right shoulder or back
This pain is caused by common nerve pathways and is one of the symptoms that is often confused with muscle problems.
Feeling of pressure in the chest
In some cases, the patient feels a vague discomfort in the chest area, which may be confused with heart problems.

Lesser known but important symptoms
Some signs are less noticed, but they are important from the point of view of diagnosis.
Bitter mouth
Especially in the morning or after waking up.
Early satiety
A person feels extremely full after consuming a small amount of food.
Chronic fatigue
Disturbance in the digestion and absorption of fats can lead to a decrease in the body's general energy.
The difference between the symptoms of gallbladder filling and gallstones
Gall bladder filling does not necessarily mean the presence of stones.
The main differences:
-
In gallbladder filling, the pain is usually milder and more persistent
-
In gallstones, the pain is often severe, sudden and colicky
-
Gallstones are more often associated with acute pain attacks
Factors that increase the risk of gallbladder filling
Some conditions make this problem more likely:
-
High-fat and low-fiber diet
-
Fast weight loss
-
Pregnancy
-
Inactivity
-
Chronic stress
-
Family history of biliary problems
When do the symptoms of gallbladder filling become dangerous?
If you see the following symptoms, it is necessary to see a doctor immediately:
-
Severe and persistent abdominal pain
-
fever or chills
-
Yellow skin or white eyes
-
Severe and frequent nausea and vomiting
Methods to detect gallbladder filling
Precise diagnosis is not possible with symptoms alone.
Abdominal ultrasound
The most common and most accessible method of checking the condition of the gallbladder.
Blood test
To investigate inflammation or dysfunction of the liver and bile ducts.
Clinical review
Detailed history of the patient plays a very important role in diagnosis.
Summary
Symptoms of gallbladder filling may be mild and non-specific at first, but ignoring them can lead to serious complications. Recognizing the signs and taking timely action is the key to preventing advanced biliary problems.
Frequently asked questions about the symptoms of gallbladder filling
1-How do we know that the gallbladder is full?
The presence of pain on the right side of the abdomen after eating, nausea, feeling of fullness and confirmation in ultrasound are the main symptoms.
2-Is it possible to fill the gallbladder without pain?
Yes, in some people, symptoms appear in the form of indigestion, bitterness in the mouth, or fatigue.
3-Does the filling of the gallbladder go away by itself?
In mild cases, it may be improved by modifying the diet, but in many cases, it requires medical examination.
4-What is the difference between stomach bloating and gallbladder symptoms?
Bloating is usually accompanied by gas and noise, but gallbladder symptoms are more common as local pain and a feeling of heaviness.
5-Does the filling of the gallbladder turn into stones?
In case of continuation and no treatment, the possibility of gallstone formation increases.