Motivation in children is an internal force that encourages them to achieve their goals, try and act. Motivation and motivation in children play a very important role in progress, growth and learning.
Motivation can come from two external and internal sources in children. External resources include encouragement and praise for successful work, material and non-material rewards or rewards, praise and encouragement from parents and teachers, role models, and providing a stimulating environment. On the other hand, the internal sources of motivation include personal growth, the feeling of satisfying the child's desires and personal goals, self-knowledge and the feeling of control over his life.
Motivation in children has a great impact on their behavior, desires, mood and performance. They are with AWhich children have motivation problems?
Motivation in children may be lost or reduced in some diseases and disorders. Some of these diseases and disorders include the following:
Children with depression may lose the motivation to do things. They usually have less desire to achieve their desires and get tired of performing daily activities. 4- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD):
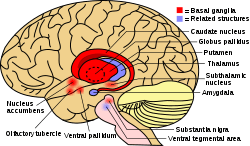
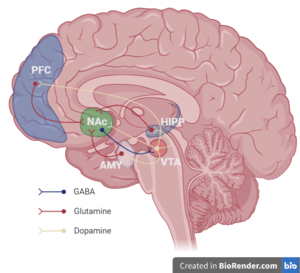
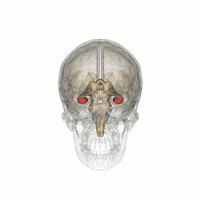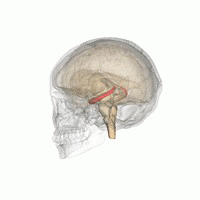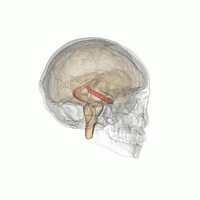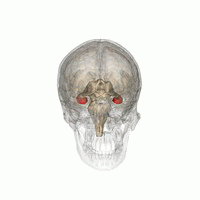
In some children with Spectrum disturbance Autism, motivation may decrease. This disorder can have a negative effect on children's communication and social interaction and affect them. Some neurological disorders can reduce motivation in children. For example, patients suffering from neurological diseases such as hearing impairment vision suffer, the motivation and desire to perform activities may decrease in them. Motivation (Motivation) is the result of the interaction between several brain regions, collectively called the limbic region, this region consists of two main parts: The basal_ganglia region of the brain plays an important role in motivation and reward, among a wide variety of other functions. This area is involved in the regulation of factors such as reward, encouragement, and attention to the results of actions and desires. Also, it plays an important role in controlling motor function and regulating limbic area activities. reward system, including areas such as the midbrain, forehead (Prefrontal cortex) and hippocampus (Hippocampus). This system is related to the induction of pleasant feeling and rewards to strengthen performance and motivation. Through the release of noradrenaline and norepinephrine (norepinephrine) and dopamine, the performance reward system With activities related to the motivation area, you can give your children the spirit to learn and strive. Activating the areas related to the limbic area requires complex functions at the brain level. Here we will examine some strategies to make the limbic area more active: Exercise and physical activity usually increase blood flow to the brain and increase the release of happy hormones. These factors can make the limbic areas more active and help increase motivation and happiness. 4- Meaningful social relationships:
Establishing meaningful social relationships and feeling connected and spreading positive and polite emotions with others, as well as having strong social support, can make the limbic areas more active and have a positive effect on the child's mood and motivation. A sufficient and good quality sleep can improve the nervous system and help the limbic areas become more active. It is recommended that children have at least 9 hours of sleep every night. Using exercises that enhance memory, concentration, attention and critical thinking can stimulate the limbic regions. This can include doing puzzles, mind games, math games and analytical games. Encouraging positive behaviors and offering rewards helps children to activate the limbic regions. For example, encouraging and praising children's good performance and successes can help increase children's motivation and happiness. Establishing warm and close relationships with children and providing emotional support can help the limbic areas become more active in children. This includes accepting and loving children, showing interest and attention to them, and sharing happy moments. If needed, it is best to consult with a child development specialist such as a child psychologist, speech therapist or occupational therapist so that you can examine the child's specific concerns and needs. Movement exercises such as skipping, jumping, walking on similar shapes and balance can help stimulate the basal ganglia. At the same time, these exercises strengthen the neural integration. Occupational therapists can give specialized exercises in this field. Using sensory devices such as balls and trampolines to practice balance and motor control can stimulate the basal region. For example, you can practice walking on a line to strengthen the child's balance. Occupational therapy specialists can provide more complete and comprehensive exercises in this field. Occupational therapists can help stimulate the basal area with special methods, which generally include using materials such as different balls, shaking the balance device, and placing the child in different sensory environments. Dancing, singing, and other interactive games that require movement and coordination between the body and auditory perception can help stimulate the basal region and the interaction between different areas of the brain. If the child has specific problems in movement control, it is better to consult with rehabilitation specialists in the field of movement (occupational therapist) so that you can provide appropriate exercises to your child. Stimulation reward system in the children's brain can be done through various solutions and activities. Below I will review some strategies to stimulate the reward system in children's brains: Using alternative rewards such as labels, badges, or a rating system can help children achieve desired achievement and behavior. For example, you can create a chart for desirable behaviors and give a badge every time the child succeeds. Creating games or challenges that improve children's motivation and performance can facilitate stimulation of the reward system. For example, setting small, achievable goals for children and rewarding them when they achieve them can increase motivation. Movement exercises and sports games that allow children to cooperate, pay attention and try, can activate the reward system. Improving movement skills and achieving goals in sports can make children feel more rewarded and satisfied. Providing encouragement and praise to children for their efforts, successes, and progress in some skills and tasks can help regulate the reward system in children's brains. Also, be sure to pay attention to the needs and concerns of each child's personality and personalize the encouragement and rewards based on them.1-Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD):
2- Depression disorder:
3-Relation between anxiety disorder and motivation enhancement:
5- Nervous or neurological disorders and motivation enhancement:
Brain areas effective in enhancing motivation
1-Basal Ganglia:
2-Reward System:
Most stimulation of these functions is done through reward circuits. When a person receives a positive and pleasant result from doing something, this system is activated and motivates the person to repeat it.How can the child's motivation be raised?
A: stimulating the limbic area:
1- Exercise and physical activity:
2-Mental training and meditation:
Exercises such as meditation can help relax and balance the nervous system, as well as increase focus and integrity of mind. These activities help the limbic areas in the central nervous system. 3- Music and art:
5- Sufficient sleep:
6-Mental and cognitive exercises:
7- Positive behaviors and encouragement:
8-Warm and close relationships:
Remember that every child is unique and the appropriate strategies to improve the functioning of the limbic region may vary according to the child's individual needs and situation.
Since the basal region of the brain is effective in children's motivation, ways of stimulating the basal ganglia in children can help improve motor function and motor control, and on the other hand, improve motivation in children. Below I review some exercises that can stimulate the basal ganglia in children to boost motivation:
1- Physical movements:2-sensory exercises:
3-occupational therapy:
4- Interactive games:
It is important to always pay attention to the child's ability and use age-appropriate exercises.Ways to stimulate the reward system in the brain:
1- Reward system and indirect rewards:
2- Making games and encouraging challenges:
3- Movement exercises and sports games:
4-Encouragement and praise:
If, as a parent of a child, you feel that you need help with the child's development and the child's motivation to change,Aba's experts will be by your side to resolve your concerns.
Key words: occupational therapy, motivation, motivation improvement
Book introduction

The hidden logical drive that shapes our motivations

Creating motivation in children

Happiness, confidence and success of children

The miracle of encouragement in increasing students' motivation

The keys to raising hopeful and successful children