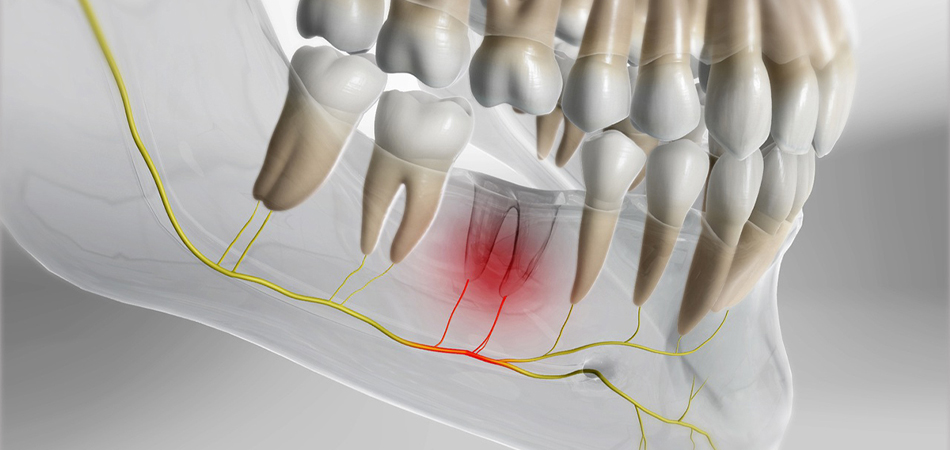
دندان عقل دردسرهای زیادی دارد. We all know this. Either it remains latent and does not come out naturally and we have to do surgery, or it may rot very quickly and we have to remove it again. Wisdom teeth may press against other teeth in the jaw and cause them to become misaligned. Another problem related to wisdom teeth is pericronite or operculitis. What is perichronite? How dangerous is it and how is it treated? In this article from Dentistry Magazine, we provide a complete explanation about this problem and answer all questions about wisdom tooth infection treatment methods.
What is pericronite?
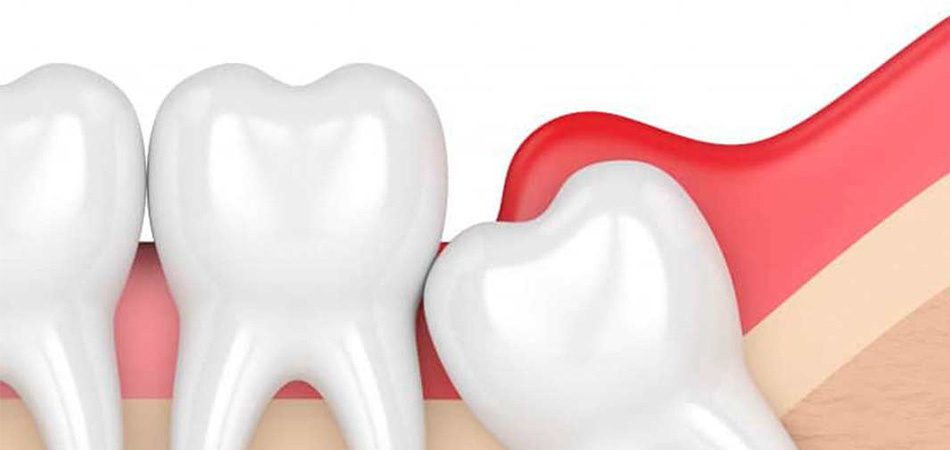
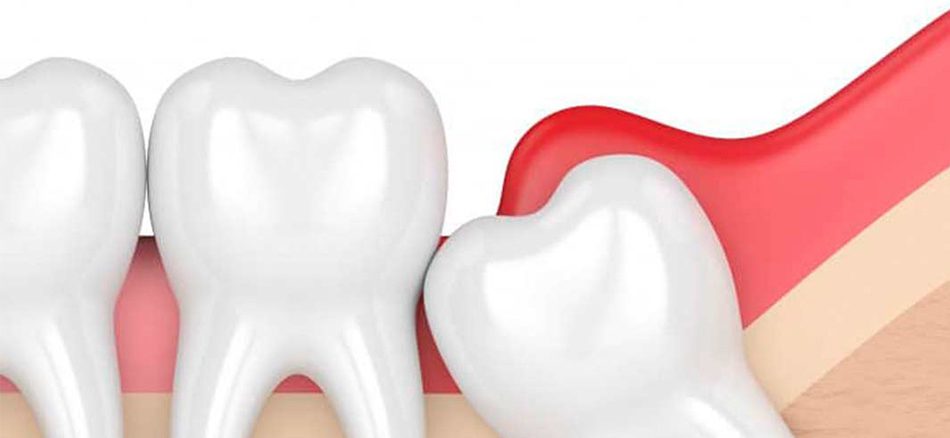
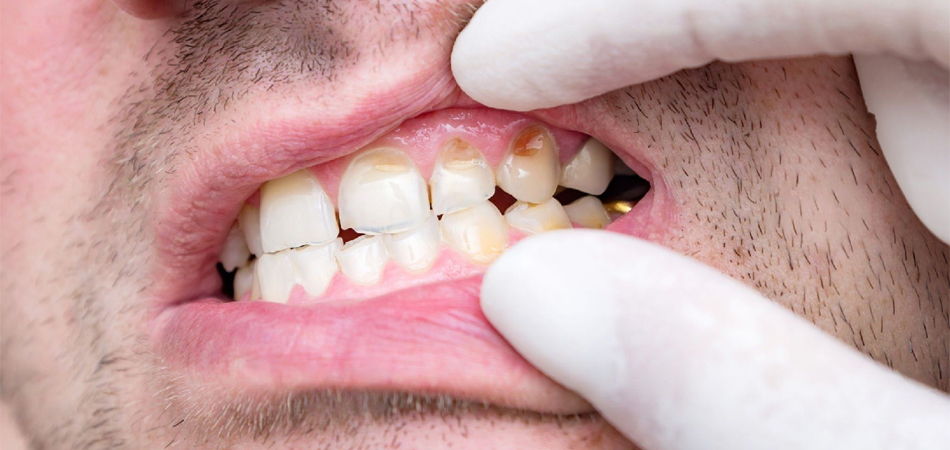
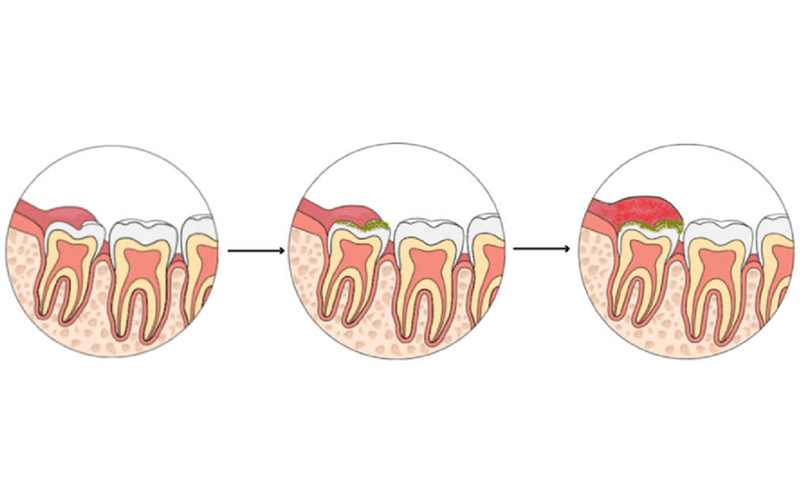
Pericoronitis is the inflammation of the gums around the wisdom tooth that is partially hidden and has not fully emerged from the gums. This condition occurs when bacteria, food debris and plaque get stuck around the wisdom tooth and cause infection and inflammation of the gums.
Perichronitis, which is also called operculitis, has various signs and symptoms:Gum pain and swelling in the area around the wisdom teeth, Redness and sensitivity in the gums, bad breath, difficulty opening the mouth and discharge of pus from the site of infection.
Not taking care of oral and dental hygiene and the accumulation of food particles and bacteria around the semi-hidden wisdom tooth is the most important reason that causes perichronitis. A wisdom tooth infection may be mild or severe. If pericoronitis is severe, wisdom teeth are usually pulled.
But in mild cases, they treat it with methods such as rinsing the mouth with salt water or disinfectant mouthwashes and using a toothbrush and floss to clean the wisdom teeth completely.
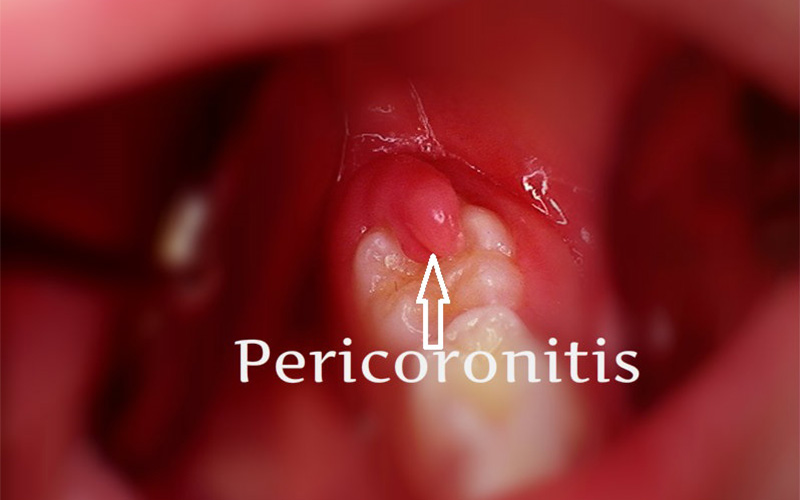
How common is perichronitis and who does it affect?
Perichronitis is one of the common dental problems that occurs mostly in people aged 17 to 25. Because it is during this period that wisdom teeth start to grow. Research has shown that almost 60 to 80 percent of people will suffer from perichronitis (mild or severe) at some point in their lives and about 20 to 30 percent of emergency visits to the dentist are related to perichronitis.
These people are more at risk of wisdom tooth infection:
-
- 17 to 25 years old,
- Those with semi-hidden wisdom teeth (because the gum does not completely cover the tooth and becomes a place for bacteria to accumulate)
- Those who do not observe oral and dental hygiene,
- Those who have a smaller jaw (because there is not enough space for wisdom teeth to fully erupt)
- Women who are pregnant or menstruating (due to hormonal changes that can aggravate gingivitis)
- People who have a weak immune system (such as diabetics or those undergoing chemotherapy)
Is pericronite contagious?
No, perichronitis is not a contagious disease. This complication is caused by the accumulation of bacteria around the semi-implanted wisdom tooth. But this type of infection is not transmitted from one person to another. If oral and dental hygiene is not observed, it may get worse and spread to other tissues of the mouth and even the jaw.
Perichronitis may be acute (transient infection) or chronic (persistent infection). The acute type requires immediate treatment, while the chronic type may continue for a long time and gradually cause damage to the gums and adjacent teeth.
Comparison of transient and permanent infection in teeth
| property |
Transient (acute) infection |
Persistent (chronic) infection |
| Duration |
Short term, a few days to a few weeks |
Long term, it may last for months or years. |
| Severity of symptoms |
sudden, severe and painful |
mild, but persistent and recurring |
| Symptoms |
Severe pain, swelling, redness, discharge of pus and fever |
Mild pain, persistent inflammation, intermittent discomfort |
| Examples |
Acute perichronitis and sudden dental abscess |
chronic perichronitis and persistent gingivitis |
| treatment |
Antibiotics, mouth wash and in severe cases tooth extraction |
Continuous health care and in some cases wisdom tooth surgery |
| Probability of recurrence |
Usually resolves with appropriate treatment. |
If not treated, it will recur frequently. |
What causes Pericronite?
Perichronitis occurs when bacteria and food residue accumulate around the partially erupted wisdom tooth, causing infection and inflammation of the gums. The most important causes of wisdom tooth infection are as follows:
1. Incomplete eruption of wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth often grow semi-recessed, meaning that part of it remains under the gum. This situation creates a suitable environment for the accumulation of bacteria and food particles that may lead to infection. If implanted wisdom teeth, with surgery It comes out and doesn't cause any problems.
2. Failure to observe oral and dental hygiene
It is more difficult to clean the wisdom tooth, especially if it is partially hidden, than the rest of the teeth. As a result, bacterial plaques and food debris accumulate around it and cause gum inflammation and infection.
3. Forming a gum flap on the wisdom tooth
When the wisdom tooth is not completely removed from the gum, a thin layer of gum tissue (flap) remains on it. This tissue is a good place for food to get stuck and bacteria to grow, which causes infection.
4. Weakness of the immune system
People who have a weak immune system, such as patients with diabetes, people undergoing chemotherapy or those suffering from stress and lack of sleep, are more susceptible to oral infections such as perichronitis.
5. Wisdom tooth pressure on adjacent teeth
If an erupted or partially erupted wisdom tooth grows, it may put pressure on the adjacent teeth. This condition irritates and inflames the gums and creates a suitable environment for the growth of bacteria.
6. Hormonal changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation or puberty may cause more sensitive gums and increase the possibility of wisdom tooth infection.
7. Stress and improper nutrition
Excessive stress and improper diet weaken the immune system and increase the possibility of oral infections.
What are the signs and symptoms of wisdom tooth infection?
Perichronitis appears in two types acute (sudden and severe) or chronic (mild but persistent). In severe cases, fever and chills (which is a sign of the spread of infection), severe pain in the ear and throat or severe swelling and breathing problems may be added to the following signs and symptoms.
In both cases, some of the following symptoms are observed in the person:
-
- Pain and gum inflammation around wisdom teeth
- Redness and swelling of the gums (especially in the area where the wisdom tooth is growing)
- sensitivity and pain when chewing or closing the mouth
- Halitosis due to the accumulation of bacteria
- Feeling an unpleasant taste in the mouth
- Pus discharge from the infected area
- difficulty and difficulty in opening the mouth (trismus)
- swelling of lymph nodes under the jaw and neck
Acute and chronic perichronitis are compared in the table below.
| Pericronite type |
Features |
| Acute |
Sudden pain, severe inflammation, pus, fever |
| chronic |
mild but persistent pain, low inflammation, periodic recurrence of pain and symptoms |
When should you see a dentist?
Not treating the wisdom tooth infection on time may cause the infection to spread to other parts of the mouth and even the jaw. If you have any of the following symptoms, it is better to see a dentist immediately:
-
- Severe and continuous pain in the wisdom tooth area
- High fever or chills
- Swelling (causing difficulty swallowing or breathing.)
- Pus discharge or smelly discharge from the gums
What factors can increase the risk of wisdom tooth infection?
There are some conditions and habits that increase the probability of perichronitis. Factors such as not observing oral hygiene, hormonal changes, weak immune system and lack of jaw space increase the risk of this infection. Next, we will explain more about these factors.
1. Having sensitive gums or susceptible to inflammation
Some people naturally have more sensitive gums that are more vulnerable to irritation and infection.
2. Small jaw or lack of enough space for the growth of wisdom teeth
In some people, there is not enough space for wisdom teeth to grow, which can cause abnormal growth or teeth to get stuck in the gums and risk Increase perichronitis.
3. Stress and unhealthy lifestyle
Continuous stress, poor nutrition, and lack of sleep weaken the immune system and make the body more vulnerable to various infections, including pericronitis.
4. Having a history of previous perichronitis
If a person has previously suffered from perichronitis, the possibility of its recurrence increases - especially if the wisdom tooth is still partially erupted.
How does perichronite affect oral health?
If wisdom tooth infection is not treated in time, it has serious effects on oral health. Therefore, perichronitis is serious and you should not lose time to treat it. The most important effects of pericronite on oral health are as follows:
1. Increased risk of infection in the mouth and chronic pain and inflammation
When bacteria and food residue get stuck under the gum tissue and around the wisdom tooth, an infection occurs. This infection spreads and causes problems such as:
-
- tooth abscess and accumulation of pus in the gums,
- More severe infections in the soft tissues around the mouth and even the jaw,
- gum inflammation and severe pain in the area of wisdom teeth,
- And in acute cases, there is difficulty in opening the mouth, chewing and swallowing food.
The possibility of infection spreading to other parts of the body is the most important and dangerous complication of wisdom tooth infection. In severe cases, the infection caused by pericronitis spreads through the bloodstream and may lead to more serious infections such as cellulitis or sepsis (blood infection).
2. bad breath (halitosis) and impact on the health of nearby teeth
The accumulation of bacteria and food residue under the gum tissue produces foul-smelling sulfur compounds that cause bad breath. In addition, the pressure of a partially erupted wisdom tooth can damage the adjacent teeth and cause crooked teeth.
Inflammation caused by perichronitis may spread to the gum and bone around the adjacent teeth and the possibility of Periodontitis (infection) gum and jaw bone).
How is perichronite diagnosed?
Dentist diagnoses wisdom tooth infection by clinical examination and review of the client's history and other necessary measures. The methods of diagnosing this infection are as follows:
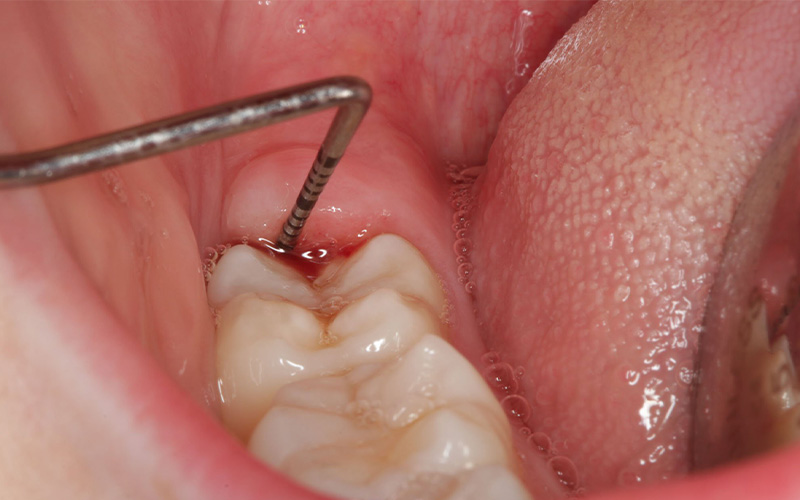
1. Clinical examination
The dentist first checks the condition of the person's gums and teeth. In this examination, he pays attention to the following symptoms:
-
- Inflammation, redness and swelling of the gums in the wisdom tooth area
- Pus or smelly discharge from under the gum
- sensitivity or pain when touching the gums
- restriction and difficulty in opening the mouth
- bad breath or unpleasant taste in the mouth
2. Examining the patient's medical history and symptoms
The dentist asks the person the following questions:
-
- How long have you been in pain?
- Is the pain severe?
- Do you have problems such as difficulty chewing, swallowing or opening your mouth?
- Do you have a history of perichronitis or other gum diseases?
- Do you have a fever or feel weak?
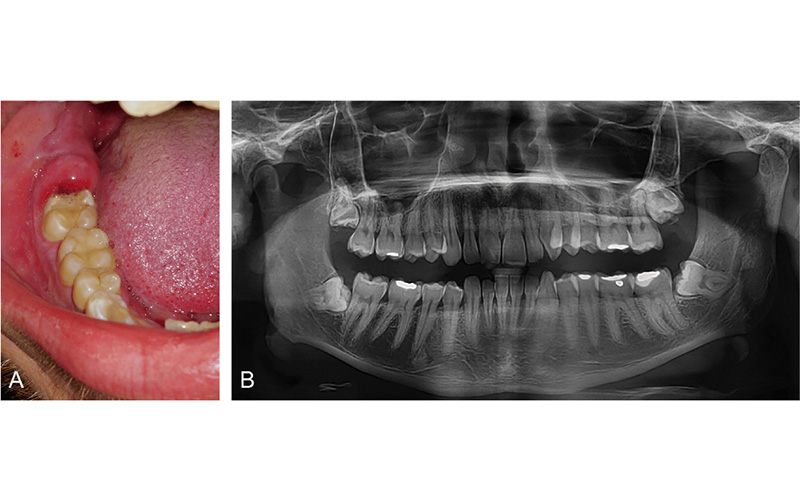
3. X-ray imaging (dental radiography)
To confirm the diagnosis, the dentist may ask the client to have a panoramic or periapical radiograph. These images show that:
-
- The wisdom tooth is partially buried or has not erupted properly.
- Does the wisdom tooth put pressure on the adjacent teeth?
- What is the degree of inflammation and the possibility of spreading the infection to the jaw bone?
4. Additional tests (in severe cases)
If perichronitis is severe and there are symptoms such as fever or extensive swelling in the patient, the dentist may prescribe a blood test to check the status of the infection and its level in the blood and its spread in the body.
پری کرونیت چگونه درمان میشود؟
درمان پریکرونیت به شدت و گسترش عفونت بستگی دارد. روشهای مراقبتی، دارویی و در برخی موارد جراحی گزینههای درمان این عفونت محسوب میشوند. درادامه، هر روش را توضیح میدهیم.
۱. درمانهای خانگی و مراقبتی (در موارد خفیف)
اگر علائم خفیف باشند، با رعایت بهداشت دهان و دندان و بعضی روشهای درمان خانگی میشود التهاب را کاهش داد. درمانهای زیر در این دسته قرار میگیرند:
- شستوشوی دهان با آب نمک گرم که برای کاهش التهاب و پاکسازی باکتریها مفید است.
- استفاده از دهانشویههای آنتیباکتریال (مانند کلرهگزیدین) برای کنترل عفونت است.
- استفاده از کمپرس سرد یا گرم به کاهش درد و تورم کمک میکند.
- مسواکزدن ملایم اطراف دندان عقل که از تجمع پلاک و باکتری جلوگیری میکند.
۲. Drug treatment (in moderate to severe cases)
If the infection has spread or symptoms become more severe, the dentist may prescribe the following medications:
-
- Antibiotics (such as amoxicillin, metronidazole, or clindamycin) to control infection
- analgesics and anti-inflammatories (such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen) to reduce pain and inflammation
- disinfectant mouthwashes to prevent further growth of bacteria
3. Dental treatments (in severe or recurring cases)
If perichronitis recurs or does not respond to home remedies and medications, the dentist may choose one of the following methods for treatment:
-
- Deep cleaning of the infected area: The dentist uses professional tools to remove infected tissues and food residues from under the gum flap.
- Surgical removal of the gum flap (opercolectomy): If the gum flap remains on the wisdom tooth and causes the accumulation of bacteria, it may be surgically removed to prevent the recurrence of the infection.
- Wisdom tooth extraction: If the wisdom tooth is partially buried and constantly causes infection, usually the best solution is wisdom tooth extraction.
4. Emergency treatment in very severe cases
If the infection has spread to other parts of the mouth, jaw, or neck, the person may need emergency treatment. In this situation, emergency treatments are as follows:
-
- dental abscess drainage or
- Injection of intravenous antibiotics in the hospital in case the infection spreads to the blood (sepsis).
What precautions should you take after possible surgery for pericoronitis?
Care after perichronitis surgery (wisdom tooth extraction or gum flap removal) helps speed up healing, reduce pain, and prevent infection. After perichronitis surgery, maintaining oral hygiene, taking prescribed medications, getting enough rest and avoiding hard foods are among the most important cares that help speed up the healing process.
If a person has any of the following abnormal symptoms after surgery, they should see a dentist immediately:
-
- Severe and persistent pain that does not decrease with painkillers.
- Severe bleeding which is not controlled and reduced after 24 hours of surgery.
- Severe swelling or pus which can be a sign of infection.
- Persistent bad breath and bitter taste which may be due to dry socket.
In the following, we will describe the post-operative care of pericronitis.
1. Bleeding control
30 to 60 minutes after surgery, keep the sterile gauze on the surgical site and press it gently. If bleeding continues, insert new sterile gauze and press it again. Avoid spitting, gargling or sucking liquids with a straw to keep the blood clot on the wound.
2. Reducing pain and swelling
For the first 24 hours, apply an ice pack on your cheek every 20 minutes (10 minutes each time). Take prescribed pain relievers (such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen) as directed and Avoid eating very hot, spicy or hard foods that irritate the ulcer.
3. Prevent infection
If the dentist has prescribed antibiotics, be sure to take them as directed. Do not wash your mouth for 24 hours after surgery; After that, you can use a warm salt water solution (a teaspoon of salt in a glass of water) to gently rinse your mouth. Avoid touching the wound with your tongue or fingers.
4. Proper nutrition after surgery
On the first day, consume only cool and soft liquids such as water, natural juice, lukewarm soup and smoothies. Avoid eating chewy and hard foods such as nuts, chips and toast. Foods rich in protein and vitamin C, such as yogurt, eggs, bananas and mashed potatoes, help heal wounds faster.
5. Compliance with oral and dental hygiene
Do not use toothbrush and floss for the first 24 hours. After that, start brushing the teeth (except the surgical site) with gentle movements. Avoid alcohol-based mouthwashes, as they may irritate the ulcer.
6. Avoiding heavy activities
Do not exercise or heavy physical activity for 48 hours after surgery, as it increases bleeding. When sleeping, put your head a little higher than the body level to avoid swelling and bleeding.
How to prevent perichronitis?
If you have any of the symptoms of perichronitis, it is better to see a dentist as soon as possible to avoid more serious complications. To prevent the occurrence of perichronitis, it is necessary to observe the following:
-
- regular brushing (especially around the wisdom teeth)
Using dental floss and antiseptic mouthwash
- Regular visits to the dentist to check the status of wisdom teeth
summary and conclusion
Perichronitis or wisdom tooth infection is called inflammation of the gums around the wisdom tooth that is partially hidden and has not completely come out of the gum. This condition occurs when bacteria, food debris, and plaque get stuck around the wisdom tooth, causing infection and inflammation of the gums. Perichronitis is very common and many 17 to 25 year olds experience mild or severe forms of it.
Not observing oral and dental hygiene, The formation of a gum flap on the wisdom tooth, Weakness of the body's immune system and Hormonal changes are among the most important causes of wisdom tooth infection. will be
pain and inflammation of the gums around wisdom teeth, redness and swelling of the gums, bad breath (halitosis) and feeling an unpleasant taste in the mouth are symptoms of this infection. A wisdom tooth infection does not heal by itself and must be treated because the infection may spread to other parts of the body. Treatment methods for pericronite in mild cases are home treatments and in severe cases surgery and wisdom tooth extraction.
The most important way to prevent perichronitis and treat it in time is to regularly visit a dentist for wisdom teeth examination.
FAQs about operculitis or wisdom tooth infection
1. What is perichronitis?
Pericronitis, Opercolitis or wisdom tooth infection is called inflammation and infection of the gums around the semi-hidden wisdom tooth.
2. What factors cause perichronitis?
The factors that cause perichronitis are: the accumulation of bacteria and food residues under the gums of semi-hidden wisdom teeth, improper oral hygiene and insufficient space for teeth to grow.
3. What are the symptoms of perichronitis?
Symptoms of pericrownitis include: pain, swelling, redness of the gums, bad breath, discharge of pus, difficulty in chewing and sometimes fever.
4. How is perichronitis diagnosed?
Wisdom tooth infection is diagnosed by dental examination and in some cases, X-ray imaging to check the position of the wisdom tooth.
5. Is perichronitis contagious?
No, this infection is caused by the accumulation of bacteria in a person's mouth and is not transmitted from person to person.
6. What is the treatment of perichronitis?
Mouthwash, taking antibiotics, painkillers, and in severe cases, removing a gum flap or pulling a wisdom tooth are the treatment methods for perichronitis.
7. Is perichronitis serious and dangerous?
Yes, if left untreated, the infection can spread to the jaw, neck, or bloodstream and cause serious problems.
8. Does Pericronite go away on its own?
No, perichronitis may improve temporarily, but it will not go away completely and permanently on its own.
9. Do you need to see a dentist for peri-crownitis?
Yes, you should see a dentist for peri-crownitis.
10. How to prevent perichronitis?
Pericronitis can be prevented by observing oral hygiene, using antibacterial mouthwashes and visiting the dentist regularly for a wisdom tooth examination.
11. Is it always necessary to extract wisdom teeth?
No, extraction is recommended only if pericoronitis occurs frequently or the wisdom tooth is partially erupted and causing problems.
12. What care is needed after the treatment of perichronitis?
It is necessary to use salt water, avoid eating hard foods, take prescribed medicines, observe oral hygiene and avoid heavy activities.