Knee swelling is called fluid accumulation in the knee joint. This condition can be caused by injuries like sports injuries or diseases like knee arthritis. The knee is one of the most commonly injured joints. In most cases, initial treatment of knee swelling can be started with rest and over-the-counter medications at home.
What is knee swelling?
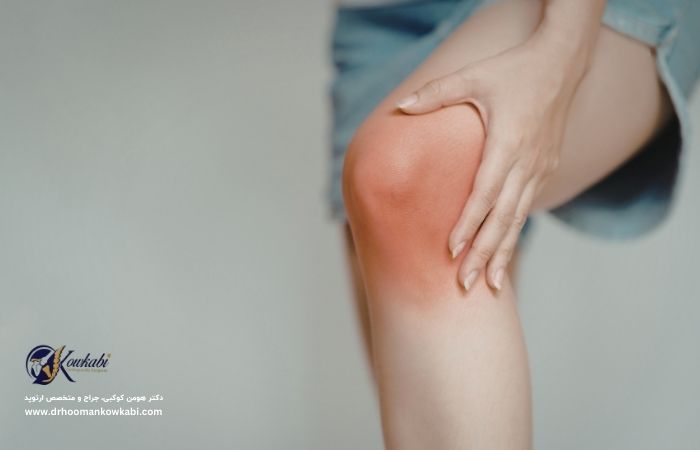
Knee swelling is a symptom and indicates that fluid has accumulated in or around the knee joint. The knee joint connects the thigh bone (femur) to the leg bone (tibia) and the kneecap (patella). The knee is the largest joint in the body and includes cartilage, muscles, ligaments and nerves.
Knee swelling occurs when excess fluid collects in or around the knee joint. The orthopedic specialist may refer to this condition as "knee joint effusion".
Knee swelling can be caused by trauma, overuse injuries to the joint, or an underlying disease or problem. To accurately diagnose the cause of swelling, the best orthopedic surgeon in Tehran may need to examine a sample of the fluid inside the joint to determine the presence of infection, disease, or bleeding from the injury.
Removing some of this fluid can help reduce knee pain and dryness. Once the root cause is identified, the appropriate treatment process will begin. Any factor that causes injury or irritation to the knee can lead to knee swelling. If your knee is injured or a disease causes damage to the tissues around the knee, the knee may become swollen.
symptoms of knee swelling
If you have knee swelling, you may experience the following symptoms:
- knee pain
- dryness or stiffness in the joint
- Redness or change in skin color
- Heat feeling in the knee area
In many cases, knee swelling can be treated with rest and over-the-counter medications. If you have suffered a sports injury or injury, you should visit Dr. Hooman Kokbi, surgeon and orthopedic specialist in Tehran.
- Joint stiffness: When there is excess fluid in the knee joint, you may not be able to fully bend or straighten your leg.
- Pain: Depending on the cause of fluid accumulation, the knee may be very painful; To the extent that it becomes impossible to bear the weight of the body on it.
Also, if the swelling of the knee does not improve within a few days, you have severe pain or you are unable to move the knee, it is necessary to see an orthopedic specialist.
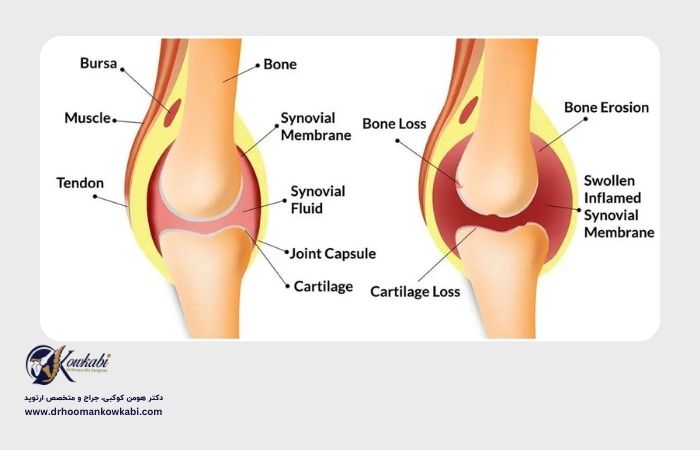
Possible causes of knee swelling
What are the most common causes of knee swelling?
Orthopedic experts divide knee edema into two types traumatic (caused by injury) and non-traumatic (not caused by injury).
traumatic knee edema
Traumatic knee swelling usually means that a person has suffered an injury. Sports injuries are the most common cause of knee swelling, including:
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) tear
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) tear
- torn meniscus
- Excessive opening of the knee (Hyperextension)
- twists
- bone fracture
- joint dislocation
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS)
Anterior cruciate ligament injury
The anterior cruciate ligament or ACL is one of the main ligaments that help stabilize the knee joint. This ligament connects the thigh bone (femur) to the leg bone (tibia). ACL tears occur more often in sports that involve sudden stops and rapid changes of direction; such as basketball, football, tennis and volleyball.
Torn Meniscus
Meniscus is a strong and flexible cartilaginous piece in the shape of the letter C, which is located between the femur and the lower leg and plays the role of a shock absorber. If the knee suddenly rotates while bearing body weight, the meniscus may be torn.
Non-traumatic knee swelling
Non-traumatic knee swelling is usually caused by arthritis. erosive arthritis (osteoarthritis) and inflammatory arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis Psoriatic) can cause knee swelling.
Other diseases that can cause non-traumatic swelling of the knee include:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Infections
- Bursitis
- tendonitis
Diseases and background conditions
Some diseases and conditions can cause fluid to build up in or around the knee joint, including:
- Osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
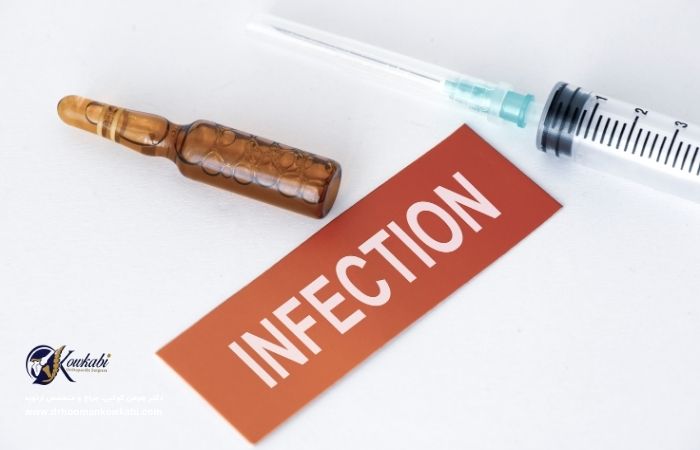
- joint infection
- Gout
- Pseudogout
- Bursitis
- Cysts
- Tumors
Is knee swelling dangerous?
Knee swelling is not considered a disease by itself, but is a sign of an underlying problem in the joint or its surrounding tissues. In many cases, knee swelling can be caused by overuse, heavy sports activity, or mild trauma, which is usually not dangerous and will improve with rest. In this situation, the body naturally responds with an increase in joint fluid or a mild inflammatory reaction.
However, in some situations knee swelling can be a serious warning. Swelling accompanied by severe pain, redness, joint warmth, fever, or inability to move the knee may indicate a joint infection, internal bleeding, torn ligament, or progressive inflammatory disease. If neglected, these types of swellings can lead to permanent damage to the joint.
Therefore, the dangerousness of knee swelling depends on the cause of it. Transient and mild swellings are usually not dangerous, but persistent, progressive swellings or with systemic symptoms should be taken seriously and need to be examined by an orthopedic specialist.
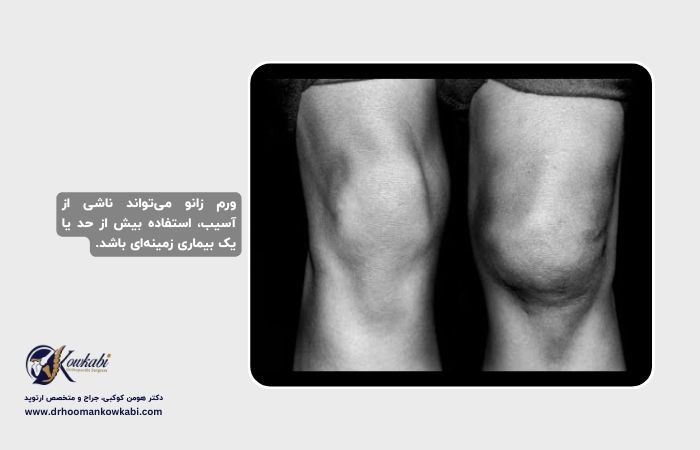
care and treatment
How is knee swelling treated?
The method of treating knee edema depends on its type. If you are injured or traumatized, you should immediately visit Dr. Homan Kokbi, an orthopedic surgeon in Tehran.
In non-traumatic cases, initial treatment can be started at home. Avoid sports or activities that put more pressure on the knee. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation. Before taking painkillers for more than 10 consecutive days, consult an orthopedic specialist.
RICE method
As soon as you notice pain or other symptoms, use the RICE method:
- Rest: Avoid the activity that caused the injury and avoid excessive pressure on the knee.
- Ice: Place a cold compress or ice wrapped in a thin towel on the knee several times a day for 15 minutes each time.
- Compression: Closing the knee with a bandage can help reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Place the knees and feet as high as possible above the heart level.
Additional treatments recommended by an orthopedic specialist
If there is a specific injury or disease, the orthopedic specialist may suggest the following treatments:
- Using a cane
- knee brace or brace
- Physiotherapy
- corticosteroid injection
Treatment of knee swelling at home
In mild to moderate cases, home remedies can be effective in reducing knee swelling and inflammation. The first and most important action is resting the knee joint and avoiding activities that put direct pressure on the knee. Continued activity during inflammation can aggravate the swelling and prolong the healing process.
Using cold compress is one of the scientific and effective methods to reduce inflammation. Cold causes contraction of blood vessels and reduces fluid accumulation and inflammation. It is recommended to put a cold compress on the knee several times a day, for 15 to 20 minutes each time. Keeping the leg elevated also helps to drain excess fluid.
Also, wrapping the knee with a standard bandage can help control swelling, provided it is not too tight. Home treatment is only suitable when the swelling is mild and there are no warning signs such as fever or severe pain; Otherwise, it is necessary to see a doctor.
The best ointment for knee swelling
Topical ointments are one of the most common options for reducing knee pain and inflammation and are usually used in mild to moderate cases. Ointments containing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help reduce swelling and pain by inhibiting the inflammation process.
These ointments create a local effect by being absorbed through the skin and have less digestive side effects than oral medications. Regular and correct use of ointment, especially along with rest and cold compresses, can be very effective in improving symptoms.
However, it should be noted that ointments do not treat the root cause of knee swelling and only reduce the symptoms. In case of persistent swelling or its frequent return, long-term use of the ointment is not recommended without specialist examination.
What should we eat for knee swelling?
Nutrition plays an important role in controlling joint inflammation and choosing the right foods can accelerate the healing process of knee swelling. Consuming foods with natural anti-inflammatory properties reduces the production of inflammatory substances in the body and helps repair the joint tissue.
Foods rich in Omega 3 fatty acids such as fatty fish, walnuts and flax seeds have a positive effect on reducing joint inflammation. Also, spices such as turmeric and ginger are effective in reducing swelling due to their active anti-inflammatory compounds.
Besides these things, adequate consumption of water, fresh vegetables, fruits rich in antioxidants and vitamin C helps to maintain joint health. Reducing consumption of processed foods, sugar and unhealthy fats also plays an important role in controlling knee inflammation.
Surgery for knee swelling
Most people who develop knee swelling do not need surgery.
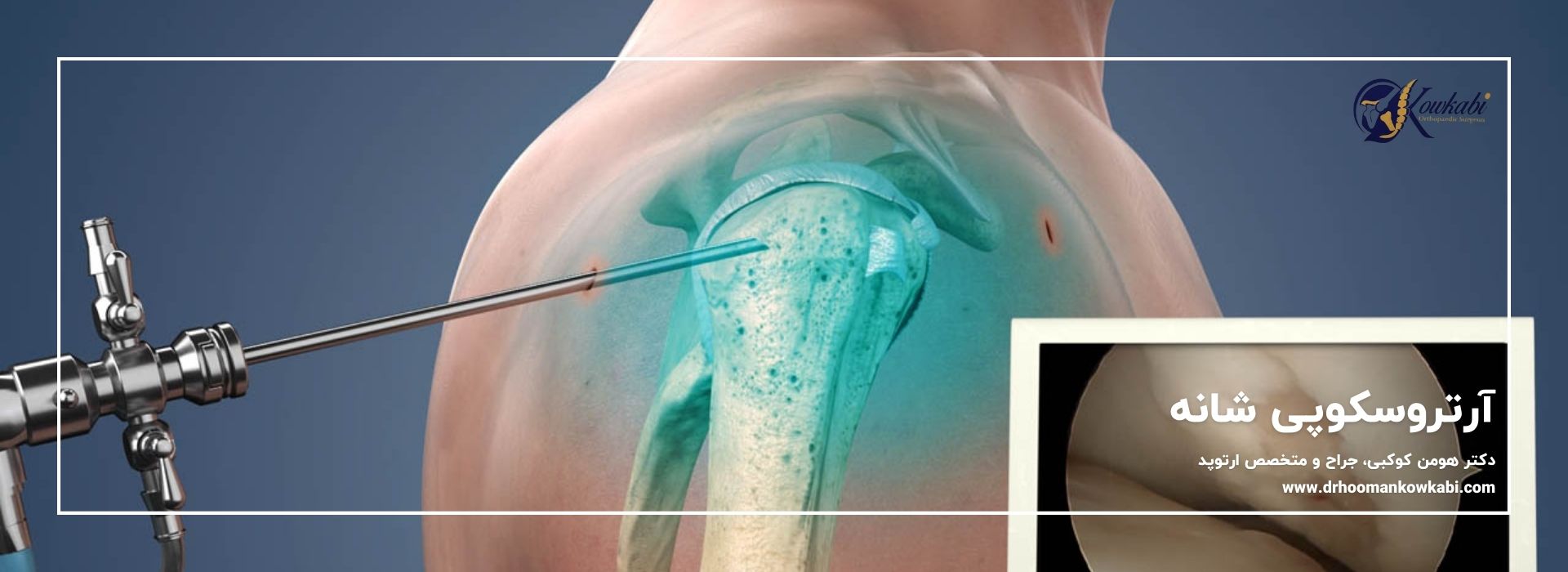
However, if the swelling is caused by an injury such as a torn ligament or meniscus tear, knee arthroscopy is necessary to repair internal injuries.
If you have arthritis and have symptoms such as severe pain and swelling that make daily activities difficult or impossible, an orthopedic surgeon may knee replacement (Arthroplasty) Surgery is usually recommended when other treatment methods have not been effective.
risk factors
Some factors increase the probability of knee swelling:
- Age: With increasing age, the probability of knee swelling caused by arthritis increases.
Complications of knee swelling
Knee swelling can cause complications if not properly treated, including:
- Reduction of muscle volume: The presence of fluid in the knee can disrupt the normal function of the muscles and cause thigh muscle weakness.
- Baker cyst formation: Fluid accumulation in the knee may lead to the formation of a Baker cyst behind the knee. This cyst can be painful but usually heals with ice and compression bandages. In severe cases, it may be necessary to drain the fluid with a needle.
Prevention of knee swelling
Knee swelling is often the result of an injury or a chronic illness. To maintain knee health and reduce the possibility of injury:
- Strengthening the muscles around the knee: Strong muscles around the joint reduce the pressure on the knee.
During exercise or physical activity:
- Use appropriate protective equipment.
- Do not continue exercising if you feel pain.
- Give your body enough time to rest and recover.
General safety tips:
- Clean the home and work environment from dangerous factors.
- Use the appropriate tool to access the height.
- If you are in danger of falling, use a cane or a walker.
The difference between swelling of the knee and swelling of the knee
Knee swelling is a general term that refers to increasing the volume of the joint or its surroundings and can be caused by various reasons including inflammation, trauma, infection or joint diseases. This swelling may be caused by tissue inflammation, bleeding, or fluid accumulation, and it does not always mean there is a lot of fluid in the joint.
On the contrary, knee effusion or knee joint effusion is specifically referred to as excessive accumulation of synovial fluid inside the joint space. This fluid usually increases due to internal inflammation of the joint, arthritis, infection, or internal injuries such as torn meniscus or ligaments.
In short, any swelling of the knee is considered a form of swelling, but not every swelling of the knee is necessarily swelling. Accurate diagnosis of this difference is usually done by clinical examination and, if necessary, imaging or joint fluid sampling.
When should you see a doctor?
In case of injury or trauma, see an orthopedic specialist. If knee swelling occurs without damage and does not improve with home treatment within a few days, you should be examined by Dr. Homan Kokbi, orthopedic surgeon and specialist in Tehran.
Also, if one of the knees has a change in skin color and is warmer than the other knee, you should immediately undergo a medical examination; Because this condition can be a sign of infection inside the joint.
Refer to the emergency room immediately in case of:
- Severe pain
- Inability to move the knee
- Severe injury such as a fall from a height or an accident
Frequently Asked Questions
What to do if your knee swells after running?
Exercise can put a lot of stress on the joints, especially if the intensity of the exercise is suddenly increased. If you develop knee swelling after running, use the RICE method and rest the knee. Despite the pain and swelling, do not continue running.
Replace running shoes every 6 to 9 months (or after 250 to 500 miles). If the symptoms do not improve, see an orthopedic specialist.
Knee swelling can be annoying, especially when it's accompanied by pain or dryness. Do not ignore your symptoms. If you are not injured, but the swelling is getting worse or does not go away in a few days, it is necessary to see Dr. Homan Kokbi, orthopedic surgeon and specialist in Tehran
Correctly diagnosing the cause of swelling, choosing the right treatment and preventing future problems play an important role in knee health.