آیا فکر میکنید دیسک کمر سراغ جوانها نمیآید؟ همین تصور اشتباه باعث میشود بسیاری از نشانهها جدی گرفته نشوند. علائم دیسک کمر در جواناناین روزها بیشتر از قبل دیده می شود.سبک زندگی امروز فشار زیادی به ستون فقرات وارد میکند. نشستن طولانی پشت میز، استفاده مداوم از لپتاپ و گوشی، انجام ورزشهای سنگین بدون آموزش اصولی و حتی بلند کردن اشتباه یک کیف پر از کتاب، همگی زمینه را برای بروز دردهای کمری فراهم میکنند.
آگاهی از این علائم کمک میکند هر فرد در اولین مرحله مشکل، اقدام مناسب انجام دهد؛ نه اینکه درد را به خستگی یا فعالیت زیاد نسبت دهد. Knowing the difference between a simple pain and the beginning of a disc protrusion makes the treatment path shorter and less expensive. The purpose of this article is to explain these symptoms in detail and to introduce specialized solutions, including physiotherapy, to control and treat lumbar disc at a young age.
Afq Roshan, Good Physiotherapy in Saadat Abad, Tehran, has experience in effective treatment of lumbar disc in his young patients. Many patients have recovered with the help of new devices, specialized methods and targeted therapy exercises and have been able to return to their daily activities without surgery. Call 02188686800 to get a free consultation or book an appointment.
The difference of disc protrusion and rupture; Where does the problem start?
In the spine, there is a disc between both vertebrae, which acts like a soft cushion and absorbs everyday pressure. Each disc has two parts:
- Outer layer: Annulus Fibrosus
- Jelly internal part: Nucleus Pulposus
A tough outer layer that holds the disc around and a gel-like inner part that keeps the spine soft and flexible.
When a lot of pressure, long sitting or wrong movements are applied to the back, these discs gradually change shape. In the first stage, the outer layer only stretches but does not tear. In this case, the jelly part is still in place, but the disc protrudes slightly and may put pressure on the nerve. This condition is the same as lumbar disc herniation.
If these stresses continue or if the back is injured more severely, the outer layer that holds the disc in place may tear. When this tear occurs, the gel inside the disc pushes out of the gap and impinges on the nerve. This condition is called lumbar disc rupture.
This direct contact of the gel material with the nerve causes shooting pain, numbness in the leg, muscle weakness or a burning sensation.
Actually, this is the difference between protruding and tearing:
- Protrusion: The disc is only stretched, not torn.
- Rupture: the disc wall is opened and the gelatinous substance protrudes.
Investigation of lumbar disc symptoms in youth; From mild to excruciating pain
Symptoms of lumbar disc in young people sometimes start with mild pain and gradually increase in intensity, so ignoring them can be problematic. These symptoms are not only limited to the waist and can also involve the legs, hips and even fingers.
Recognizing these symptoms helps to quickly diagnose and prevent severe injuries. In the rest of the article, we will examine some important symptoms.
sciaticaOne of the most characteristic symptoms of lumbar disc in young people is a sharp pain that starts from the lower back and continues to the hips, thighs and even the soles of the feet. This type of pain is usually felt as sharp, burning and sudden and is often aggravated by prolonged sitting or heavy bending. The cause of this pain is the pressure of the protruding or protruding disc on the nerve root.
A student who sits at the laptop after a long day and when he gets up, he feels a sharp pain from the hip to the back of the thigh. Many young people attribute such pain to fatigue or heavy exercise, when it could be a symptom of sciatica caused by a herniated disc.
This pain usually involves one side of the body and often subsides with relative rest, but becomes more severe if pressure continues. Paying attention to this sign helps the person to take specialized treatment, such as physiotherapy, in the early stages and prevent the problem from progressing.
numbness or tingling feet and fingers
Numbness or numbness in feet and fingers is another important symptom of lumbar disc. When the disc presses on the nerve roots, nerve messages are not transmitted properly and the person feels numbness, tingling, or pins and needles. This symptom often appears in the morning or after long activities and is sometimes associated with pain.
An athlete who notices that his leg is abnormally numb or weak after squatting or long running. In some cases, the numbness can affect only one toe or part of the foot. This is a warning sign, because it indicates that the nerve is under pressure and needs a specialist investigation. Early treatment with corrective exercises and physical therapy can prevent the development of nerve pressure and permanent damage.
muscular weakness in legs
Muscle weakness is one of the important symptoms of lumbar disc and many young people attribute it to fatigue or heavy exercise, but this symptom needs serious attention. When a bulging or ruptured disc puts pressure on a nerve, the muscles that are controlled by that nerve lose strength. In such a situation, a person experiences a feeling of weakness, inability, or less control over the muscles when performing normal movements.
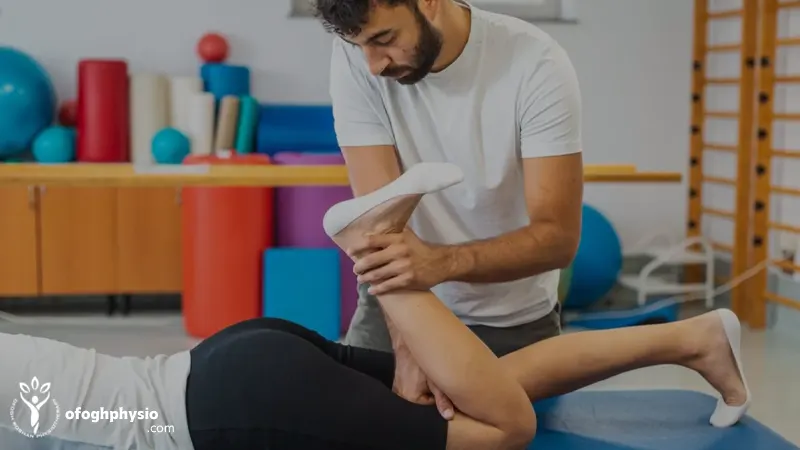

When climbing stairs, a person notices that his leg has less resistance or his ankle does not rise well. Athletes who ignore this sign may suffer from performance loss and even secondary injuries during sports training.
Physiotherapy with targeted exercises and strengthening related muscles can restore muscle strength and reduce pressure on the nerve. It is very important to identify this sign in the early stages to prevent disc progression.
pain when sitting for a long time
Prolonged sitting increases the pressure inside the disc and causes pain in many young people. When the lumbar discs are bent or compressed, the analus fibrosus is pressed, and if they are damaged or protruded, a shooting pain occurs. This pain is usually reduced by changing position or standing for a short time.An employee who sits at a desk after a long meeting feels that his back is "locked" when he gets up from the chair. Many students and people who sit in front of a computer or mobile phone for many hours experience this pain. Correct posture training and short-term stretching exercises during the day can reduce the pressure and prevent the problem from progressing.
pain with bending or carrying objects
Bending movements or lifting objects puts a lot of pressure on the disc. In an injured disc, even lifting a light object or suddenly turning the back can cause severe pain. This pain is usually short-term but it repeats with any similar movement.
A person bends down to pick up a water bottle and suddenly his back is shot. This indicates that the analus fibrosus is under pressure and the disc is subject to damage. Physiotherapy and teaching correct movements when lifting objects play an important role in preventing the progression of injury.
spasms and severe cramps of the back muscles
When a lumbar disc is injured or protrudes, the body reacts to protect the spine by tightening the muscles around the lower back. This condition is known as back muscle spasm or back muscle cramp and can limit simple movements such as bending, standing or turning. Spasm may be accompanied by severe pain and sometimes the person feels that his back is "locked".

A young man who wakes up after a long breakfast in a cafe and notices that his back is locked and he can't stand straight. Even gently stretching the back causes severe pain. This type of cramp is a sign that the disc is under pressure and requires relative rest and specialized treatment such as physical therapy to relax the muscles and support the spine.
one-sided pain in the back or buttock
Disc protrusion often affects one side of the body. For this reason, the pain is usually felt only on one side of the back, buttock or thigh and is hardly visible on the other side. This type of pain is due to the pressure of the disc on the nerves of one side of the spine.
When sitting at a desk, a person notices that the severe pain affects only the right side of their back and hip, and it gets worse when they move or bend over. This unilateral pattern helps the doctor and physiotherapist to identify the location of the damaged disc and design the treatment plan more precisely.
Feeling of heat or burning in the path of the nerve
Some people experience disc pain as a burning sensation along the nerve path, not just a sharp pain. This feeling is caused by the pressure or stimulation of the nucleus pulposus on the nerve root and can be accompanied by tingling or numbness.
A student after a long day of studying, while walking or standing, feels a thrust from the hip to the back like an electric current or fire. This type of unusual pain is often ignored, but it is an important symptom of nerve involvement and requires specialized investigation and treatment.
pain worsening with sneezing, coughing or abdominal pressure
Increasing intra-abdominal pressure, especially when sneezing, coughing or straining, can increase the pressure on the disc and nerve and cause sudden pain. This sign indicates that the disc is damaged or bulging and the pressure on the nerve root has increased.
When a young man coughs, he suddenly feels a sharp pain in his leg. Even a small pressure causes severe pain, so it is necessary for these people to avoid activities that put a lot of pressure on the disc and consult a physiotherapist.
Limitation of the range of motion of the back
People with a damaged lumbar disc usually find that they cannot bend, turn, or perform everyday activities as well without pain. This limitation is due to pain and muscle spasm, and sometimes it changes the body's natural position to reduce the pressure on the disc.
When putting on shoes or socks, a person finds it difficult to bend and has to raise the knee to be able to put on the shoes. This situation shows that the range of motion of the back is reduced and the spine bears more pressure. Limitation of range of motion is one of the classic symptoms of lumbar disc, and it improves over time with corrective exercises, physical therapy and controlled stretching.
Lumbar-disc treatment in youth with modern method of physiotherapy
Physiotherapy plays a very important role in controlling pain, improving function and preventing the progression of lumbar disc damage. Specialized exercises, controlled stretching and training of correct spinal movements reduce the pressure on the disc and protect the nerves. One of the effective methods of treating lumbar disc in youth is physical therapy, manual therapy or manual therapy. In this method, the spine and surrounding muscles are treated with precise and targeted manipulation, which results in reducing spasms, increasing range of motion, and improving blood supply.

Along with the therapy manual, the rehabilitation exercise program is designed so that the patient can perform daily movements without putting pressure on the disc. Correcting sitting, sleeping and daily activities is also an integral part of the treatment and helps to prevent recurrence.
Modern physiotherapy methods are also used to reduce pain and inflammation and improve disc function. Among these methods, we can mention electrotherapy, magnet therapy, shock wave, dry needling, traction and ultrasound. By reducing muscle spasms, stimulating blood flow, reducing inflammation and speeding up the healing process, these techniques help the patient return to daily activities faster.
By combining routine therapy, rehabilitation exercises and modern physical therapy methods, many young people can reduce pain, restore spinal flexibility and improve their quality of life without the need for surgery.
Non-surgical treatment of lumbar disc; When surgery is not the only way
Non-surgical lumbar disc treatments in young people are usually the first and most effective course of treatment, as most cases improve without the need for surgery and only with lifestyle modifications, physical therapy and inflammation control. The aim of these methods is to reduce pain, reduce pressure on the disc, restore the normal function of the spine and prevent the progression of the damage.
These types of treatments focus on the root of the problem, i.e. inflammation, muscle spasm, and central muscle weakness, and gradually improve the patient's condition and make it possible to return to daily activities. In the following, we examine each of the non-surgical treatments introduced in the table in more detail.
| Method of treatment | Description |
| Short-term rest | Reduce pressure on the disc by resting in the right position; Long rest causes muscle weakness and aggravation of pain. |
| Correcting activities | Learning to sit correctly, bend and lift objects without putting pressure on the disc; Preventing the progression of the injury. |
| Medications | Analgesics, anti-inflammatories, muscle relaxants, and neuroleptics (such as gabapentin); Use under physician supervision. |
| Local injection | Injection of corticosteroids or anti-inflammatory drugs around the nerve to reduce inflammation and pain. |
| Weight and lifestyle control | Weight reduction and regular physical activity; Reducing pressure on the spine and disc. |
Diagnosis of lumbar disc; The role of physical tests and MRI in identifying the problem
Diagnosis of lumbar disc in young people is a combination of careful clinical examination and, if necessary, the use of imaging methods. The goal of diagnosis is to determine whether the pain is actually originating from the disc or from the muscles, ligaments, and even the joints of the spine. Many back pains are similar, so correct diagnosis is very important.
In the first step, a physiotherapist or doctor performs a physical examination. This examination includes checking the range of motion, straight leg raise test (Straight Leg Raise Test) to evaluate the pressure on the sciatic nerve, checking the sense of touch, reflexes, muscle strength and the way of standing or walking. These tests help the specialist to determine which nerve is under pressure and the severity of the problem.
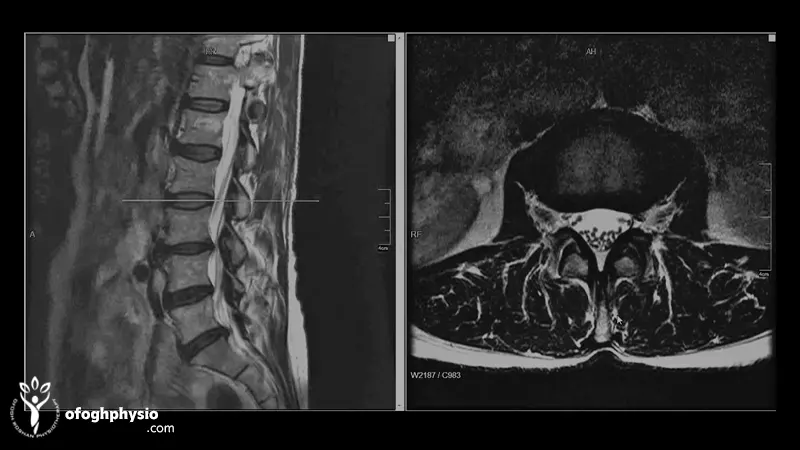
If there is a possibility of disc protrusion based on the examination, the next step is MRI imaging. MRI is the best way to see the condition of the outer layer of the disc (Annulus Fibrosus), the jelly layer inside it (Nucleus Pulposus), the amount of protrusion and whether there is pressure on the nerve roots or not. In some special cases, CT Scan or EMG is also used; EMG is used when the specialist wants to check the degree of nerve damage more precisely.
The important point is that the presence of a bulging disc on MRI does not always mean pain. Many young people have a bulging disc but do not feel any symptoms. Therefore, decision making for treatment is not done only by relying on MRI and clinical examination plays the main role.
Finally, physical therapy is recommended when the pain worsens with activity, there is numbness or tingling, or the pain pattern suggests that the nerve is being compressed. Physiotherapy, as the first, most effective, and safest treatment method, is the best option for most young people before any invasive treatment.
When does the lumbar disk need operation
Lumbar disc surgery is usually recommended when non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medication, activity modification, and injections fail to control symptoms for at least 6 to 8 weeks. The most important criterion for surgery is severe and continuous pressure on the nerve, which causes symptoms such as severe shooting pain, extensive numbness, progressive weakness of the leg muscles, or impaired control of urine and feces.In such situations, surgery acts as a life-saving way and prevents permanent nerve damage. But in most young people, the lumbar disc can be treated with basic rest and physical therapy, and there is no immediate need for surgery.
From a specialized point of view, surgery is suggested when:
- Severe sciatica pain continues for more than 6 weeks and disrupts the patient's life.
- Muscular weakness in the leg is progressing and the person becomes unstable when standing or walking.
- Severe compression of the nerve in MRI that is consistent with clinical symptoms. Cauda equina syndrome occurs; An emergency situation that is associated with incontinence, numbness of the seat area and severe pain.
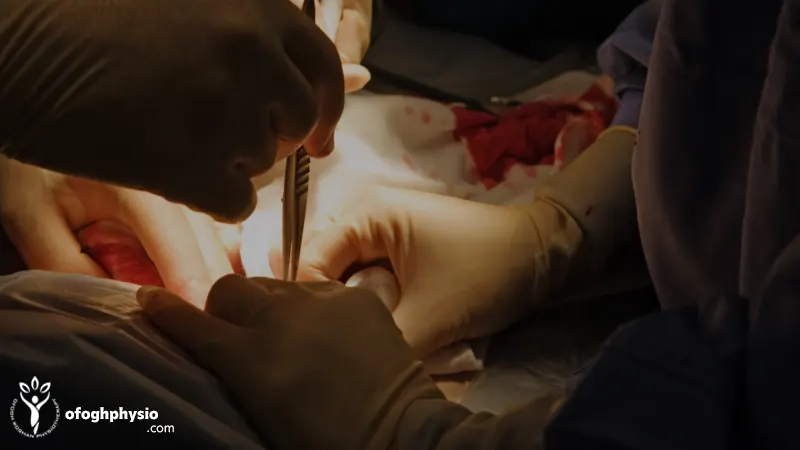
However, more than 80% of patients recover without surgery, and physical therapy plays a major role in this process. The important thing is that the cost of physiotherapy is only about 10-15% of the cost of surgery; It means that it is more reasonable from the economic point of view, and the patient stays away from the complications and risks of heavy surgery.
As a result, surgery is a last resort, not a first step. In most cases, the right choice is to start specialized physiotherapy treatments and regular follow-up.
complications of lumbar disc operation in youth; What you should know before making a decision
Although lumbar disc surgery can be life-saving in certain cases, it is not always without risk, especially for young people who have more active spines, greater mobility needs and long-term recovery expectations. One of the most important points is that the surgery only removes part of the damaged disc, and the main problem, which is muscle weakness, wrong movements and repeated pressures, is still there; Therefore, there is a possibility of return of pain or protrusion again.
The most important possible complications of lumbar disc surgery include the following:
- Recurrence of the disc (Re-herniation): It is one of the most common complications, and the same disc or adjacent discs may be damaged, especially if the person does not modify his lifestyle after the operation. Adhesion and inflammation around the nerve: after surgery, scar tissue may form and cause chronic or excruciating pain.
- Infection or bleeding: although it is rare, it is still one of the risks of surgery.
- Muscle weakness or long-term numbness: If the nerve has been under pressure for a long time, it may not fully return to normal even after surgery.
- Limitation of activity for weeks to months: the surgical recovery period makes the patient stay away from activities and sports, which can cause more muscle weakness.
In general, surgery can be helpful, but in young people it is usually a last resort; Because with physiotherapy, strengthening exercises and modification of movement patterns, they often recover without the need for surgery and stay away from these possible complications.
afq roshan; Therapeutic exercises and therapeutic routines for spine health
Do you think lumbar disc is only a problem for the elderly? The fact is that the lumbar disc can be seen in young people and the wrong lifestyle can aggravate this problem. Prolonged sitting, heavy exercise or improper carrying of objects puts a lot of pressure on the spine and this pressure increases the risk of injury. Lumbar disc symptoms in young people include back pain, leg cramps, numbness, muscle weakness, spasms, and limited range of motion. Not paying attention to these symptoms causes damage to progress and disrupts daily activities.
Afq Roshan, the best physiotherapy in Saadat Abad, Tehran, has treated thousands of patients with back and neck discs using modern equipment, therapeutic exercises, manual therapy and a team of experienced specialists. These methods help reduce pain, strengthen muscles, improve flexibility of the spine and quickly return to daily activities, without the need for heavy surgery and at a much lower cost.
To book an appointment or free consultation, call 02188686800 and benefit from your exclusive treatment plan. If you have any questions or doubts about the back or neck disc, be sure to raise it in the comments section; Our team will respond as soon as possible and provide practical guidance.What foods are bad for lumbar discs?
Processed foods, fried foods, fast food, and high-sugar foods increase body inflammation and aggravate disc pain. Consuming too much salt also causes water retention and more pressure on the damaged tissues.
Is lumbar disc healing?
Yes, many cases of lumbar disc herniation will improve without surgery with physical therapy, corrective exercises, and reduction of inflammation. Early treatment increases the speed of recovery.
When does lumbar disc need surgery?
When severe pain, extensive numbness or progressive weakness develop and non-surgical treatments do not respond, surgery is considered. In cases where urine or stool control is disturbed, immediate action is necessary.
What if we don't operate the lumbar disc?
In mild cases, improvement may be achieved with physical therapy and basic care. But in extreme cases, neglect can cause permanent nerve damage or severe muscle weakness.
What is good for lumbar discs?
Physiotherapy, strengthening central muscles, weight loss, lifestyle modification and avoiding heavy movements help to reduce pain. Gentle heat therapy and correct sitting also reduce the pressure on the disc.