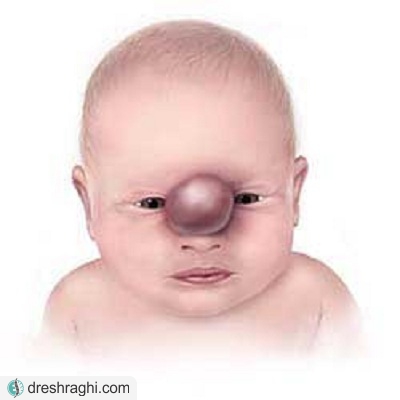
انسفالوسل (Encephaloceles) به نوعی نقص نادر لوله عصبی گفته میشود که تحت عنوان بیرون زدگی کیسه مانند مغز و غشای پوشاننده آن از جمجمه توصیف میگردد. این نقص مادرزادی به علت عدم بسته شدن کامل لوله عصبی در دوران رشد جنینی رخ میدهد. در نتیجه قسمت فوقانی جمجمه، یا فضای بین بینی و پیشانی، یا پشت جمجمه بسته نمیشود. در صورتی که این عارضه در پشت جمجمه ایجاد شود میتوان گفت که با مشکلات نورولوژیکی ارتباط دارد.
معمولاً انسفالوسل یک نوع ناهنجاری است که فوراً پس از تولد تشخیص داده میشود اما گاهی اوقات انسفالوسل کوچک در ناحیه بینی و پیشانی قابل تشخیص نخواهد بود.
انواع
میتوان این اختلال را بر اساس محل تشکیل آن به چند دسته تقسیم کرد:
انسفالوسل پیشانی
در این انسفالوسل قسمت فوقانی جمجمه درگیر شده است که بخش زیادی از مغز از طریق قسمت جلوی جمجمه بیرون میزند. به این وضعیت انسفالوسل پیشانی گفته میشود و نادرترین نوع این عارضه محسوب میگردد.
انسفالوسل آترتیک
در این نوع انسفالوسل، بخش میانی ناحیه خلفی جمجمه و استخوان آهیانه درگیر میشود. که بخش زیادی از مغز از طریق این قسمت بیرون میزند. استخوان آهیانه به استخوانهای جمجمه انسان گفته میشود که اتصال آنها به هم باعث میشود که اطراف و قسمت فوقانی جمجمه تشکیل شود قسمت مرکزی این ناحیه سطح خارجی این استخوان ها، توسط یک بخش مهم که برآمدگی آهیانه نام دارد تشکیل شده است.
انسفالوسل پس سری
این اختلال جنینی توسط ضایعات بزرگ اما نادر نشان داده میشود. مغز از طریق سمت پشت سر که شامل قسمت پشت و پایین جمجمه و استخوان اهیانه بیرون میزند. این نوع ضایعات میتوانند به صورت یک تورم کوچک یا تودههای بزرگ خود را نشان دهند. گاهی اوقات قطر این ضایعات بیش از ۲۰ سانتیمتر است. در برخی موارد اندازه این ضایعات حتی بیشتر از اندازه طبیعی مغز است. Usually, this complication presents a great surgical challenge. Usually, this disorder is related to other types of neurological disorders and it is called occipital encephalocele.
Nasal encephalocele
This complication is observed in the distance between the nose and the telmoid sinus of two of the four paranasal sinuses of the telmoid bone, this bone in the skull will separate the nasal cavity from the brain.
Encephalocele of the nose and eye
In this The complication of a lump-like protrusion is seen in the space between the nose and the eye - the eye socket that places the eye inside the skull.
Encephalocele of the meninges of the brain and its membranes
The spinal cord is formed in the meninges of the brain naturally, but in this condition, the meninges of the brain and spinal cord protrude from the open part of the skull or vertebral column. In this complication, the protruding part contains cerebrospinal fluid, and no nerve tissue can be seen in it.
Encephalocele of the brain and meninges and its membranes
This complication is defined as the protrusion of a mass such as the tissues of the brain and meninges through a defect created in the skull. A child will be affected by this condition every 1,000 births. Occipital encephalocele is more common in Europe and North America, while frontal encephalocele is more common in Africa, Russia, South Africa, and Malaysia. As we mentioned in the above sections, the defects of the neural tube and their failure to close completely during the fetal period cause the protrusion of mass like meninges. These congenital disorders may occur due to genetic problems. This complication is more common in families with a history of spina bifida and anencephaly, these two complications are among severe neurological disorders. Exposure of the mother to some environmental substances before and during pregnancy can provide the basis for the occurrence of neural tube defects during the fetal period. Some of these are:
- Teratogens: These compounds cause birth defects by interfering with the development of the fetus.
- Trypan blue: a very important substance that is used to dye dead tissues or make cells blue.
Symptoms
This condition is usually associated with skull and facial abnormalities, which causes numerous deformities in the development of head and facial bones. A variety of brain malformations can occur in this type of neural tube defect. Some of the general symptoms that are seen in sick people are:
- Spastic paralysis: It is the most severe type of cerebral palsy that completely affects all 4 lobes and the upper body of the patient. The muscles of these patients, which are responsible for controlling the mouth and tongue, have problems, and the patient will be disabled in terms of speaking and mental performance. Ataxia: In this condition, patients suffer from incoordination and imbalance due to the inability of the brain to regulate body posture and arm and leg movements. Incoordination of muscles occurs due to a defect in the cerebellum, which is located at the back of the brain. Microcephaly: a disorder. It is rare in this condition due to insufficient brain development, the patient's head size is smaller than normal. Hydrocephalus: In hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid is abnormally formed in the cerebral cortex. The accumulation of fluid causes a lot of pressure to be applied to the brain and as a result it is damaged. Seizures: People suffering from seizures frequently experience epileptic attacks, which occur due to the sudden onset of discharge of electrical charge in the brain. Vision disorders: Vision problems or loss of vision in various degrees in people with encephalocele of the nose and eyes.
- Delayed development: In this condition, the child cannot achieve sufficient growth like other children of the same age.
- Mental retardation: IQ, mental ability, and learning in children with this condition are below the average level.
Diagnosis
Visible malformations indicate a serious disorder that is easily diagnosed after the baby is born. Sometimes it can be difficult to diagnose this condition in people who have small defects such as defects in the forehead or eyes. In addition to these abnormalities, the doctor can detect some types of severe mental and brain retardation in affected people. Radiology, CT scan and MRI can help the doctor to diagnose small lesions in the nose area. Cerebrospinal fluid examination in cases where the person has protrusion of the brain membranes or protrusion of the brain and If the meninges and its membranes are affected, the cerebrospinal fluid can be evaluated by inserting a small needle into the spinal canal. This test is performed with the aim that the doctor can diagnose the cause of increased pressure in the brain that causes hydrocephalus. This test can help diagnose other neurological abnormalities.
Treatment
Usually surgery is necessary for people with encephalocele. Brain surgery is usually performed between birth and 6 months of age based on size, location of lesions, associated complications, and presence of skin over protruding lesions. If the lesions are covered by skin, the doctor will postpone the surgery for a few months, but if there is no skin on this area, it will be necessary to perform the surgery shortly after birth. The need for further treatment depends on the symptoms that appear in each patient. Craniofacial abnormalities and other skull disorders are treated with surgery. The doctor treats hydrocephalus by installing a shunt inside the patient's brain. The shunt causes excess cerebrospinal fluid to drain from the brain.
Surgery
This surgery is used to return the protruding contents back into the skull. The surgeon cuts a part of the skull so that they can have good access to the brain. The surgeon then makes an incision in the dura mater, the tough outer covering of the brain. In the next step, the surgeon returns the protruding parts of the brain, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid to the brain and separates the protrusion around it. Then the dura is closed and the skull is repaired with the help of removed tissue or artificial tissue. Encephalocele correction surgery can be performed even in severe cases without causing more functional disability.
Minimally invasive surgery
If this condition has occurred at the base of the skull, sinuses, or in the clivus area, this problem can be completely treated through the nose. This minimally invasive surgery will be performed with the help of a device called an endoscope (a small camera enters the body through the nose) and without making any cuts on the face or skin. After the surgery, the child will be hospitalized for two to five days, then he will be discharged. The doctor teaches the child's parents how to take care of the suture and other necessary points after the surgery. The child's sleep and feeding may be disturbed for 4 to 6 weeks after the surgery, but it should gradually return to normal conditions. The doctor prescribes acetaminophen and ibuprofen to control the child's pain, and if necessary, asks the child's parents to give their child narcotic drugs as a supplement.
Prognosis
In a large number of patients with encephalocele, prognosis after surgery depends on factors such as the following:
- Place of protrusion
- Type of brain tissue involved in this complication.
Pink If the surgery is successful, these patients will grow and grow up without any problems. If the child has neurological and developmental problems, the doctor should focus on reducing these abnormalities. If a large part of the extracted volume contains cerebrospinal fluid, there is a possibility of complete recovery. On the other hand, if a large part of the brain tissue is involved in this complication, there will be very few complications.
Prevention
Although it is not possible to completely prevent the occurrence of this complication, following some points can reduce the possibility of this disorder. Taking folic acid in the first few weeks of pregnancy can prevent neural tube defects. Steel is one of the most essential compounds in the synthesis and regulation of new cells required for the synthesis of RNA and DNA, which plays a very important role in the synthesis and methylation of nucleic acid. Naturally, doctors recommend pregnant women to get 400 micrograms of folic acid daily. Pregnant women should avoid smoking and alcohol so that the fetus can grow well. Screening during pregnancy is very important for timely diagnosis of some disorders.