جراحی میوم رحم: بررسی روشها، مزایا و عوارض احتمالی
درمان میوم رحم، برای خانمها و پزشکان یک چالش به شمار می آید. زمانی که درمانهای دارویی مؤثر نباشند یا علائم بیمار شدید و پیشرونده باشند، جراحی میوم رحم بهعنوان یک گزینه مؤثر و گاه قطعی مطرح میشود.
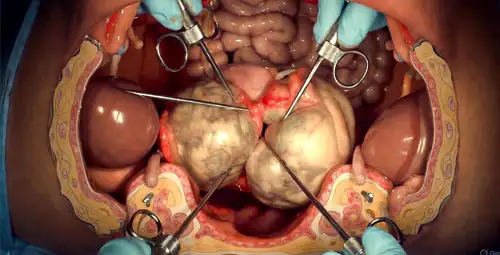
جراحی میوم رحم با هدف کاهش علائم، بهبود کیفیت زندگی و در صورت امکان حفظ عملکرد رحم انجام میگیرد. انتخاب روش جراحی به عوامل متعددی از جمله سن بیمار، شدت علائم، اندازه و محل میومها و تمایل به بارداری در آینده بستگی دارد. روشهای جراحی شامل میومکتومی با رویکردهای مختلف و هیسترکتومی بهعنوان درمان قطعی در بیماران منتخب است.
اگرچه جراحی میتواند نتایج بالینی مطلوبی ایجاد کند، اما همواره با خطرات و عوارض بالقوهای مانند خونریزی، عفونت یا چسبندگیهای لگنی همراه است. Therefore, the decision for surgery should be made based on a careful clinical evaluation and an informed conversation between the doctor and the patient. 600;">
When does a uterine myoma need surgery?
Cases in which uterine myoma surgery is recommended
In many women, uterine myomas They exist without causing special problems and do not require surgical treatment. But in some cases, the doctor diagnoses the need for surgery to treat uterine fibroids. The doctor decides to perform surgery when this disease has negative effects on the quality of life of a person. On the other hand One of the most common reasons for surgery is heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, which can lead to anemia and chronic fatigue. Persistent pelvic pain, feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen and pain during sex are also symptoms that suggest the need for surgery. In some patients, myoma leads to digestive or urinary problems.

Large or growing myomas, especially when they change the normal shape of the uterus, can also require surgery. In women who face infertility or repeated miscarriages and the role of myoma in these problems is confirmed, surgery can help improve fertility outcomes.
Controlling symptoms and improving quality of life
One of the most important goals of uterine myoma surgical treatment is to reduce or eliminate symptoms that affect the patient's daily life. they give Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding is the most common clinical symptom of myoma, which can lead to anemia, weakness, and reduced ability to perform daily activities. Surgery to remove the myoma or, in certain cases, to remove the uterus, can effectively control this type of bleeding. Also, chronic pelvic pain, feeling of pressure in the abdominal area, and pain during sexual intercourse are some of the symptoms that are significantly reduced in many patients after surgical treatment. The improvement of these symptoms plays an important role in increasing the quality of life, mental health and the patient's overall satisfaction with the treatment process.
Preserving or improving fertility
In women who desire pregnancy, one of the main goals of uterine myoma surgery is to preserve the structure and normal function of the uterus. Some myomas, especially submucosal myomas or those that cause changes in the shape of the uterine cavity, can be associated with impaired implantation or an increased risk of miscarriage. In this situation, targeted removal of fibroids can increase the chance of natural pregnancy. Choosing the right surgical method, such as myomectomy, allows the doctor to remove the problematic lumps while doing minimal damage to the healthy tissue of the uterus. Although surgery does not always guarantee a successful pregnancy, in many cases it can provide more suitable anatomical conditions for fertility and improve pregnancy outcomes.
Prevention of long-term complications of myoma
Surgical treatment of uterine myoma is also performed with the aim of preventing long-term complications. Untreated myomas may gradually enlarge and lead to worsening symptoms, increased pain and pressure on nearby organs. In some patients, the continuous growth of myomas can cause bladder or bowel dysfunction and even significant changes in the shape and size of the uterus. In addition, continued heavy bleeding can lead to chronic anemia and its complications. Surgical intervention at the right time can prevent the development of these problems and reduce the need for more complex treatment procedures in the future. In general, the ultimate goal of surgery is to create a balance between controlling symptoms, maintaining long-term health, and choosing an approach that fits the individual conditions of each patient. According to the patient's conditions and treatment goals, he can choose one of the appropriate options for surgery and treatment of the patient.
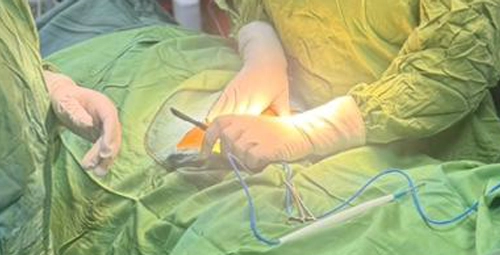
Myomectomy
Myomectomy is a procedure in which myomas are removed without removing the uterus, and it is usually performed for women who want to preserve the uterus or pregnancy in the future. Choosing the type of myomectomy depends on the size, number and location of myomas, and its main goal is to reduce symptoms while maintaining the normal structure of the uterus.
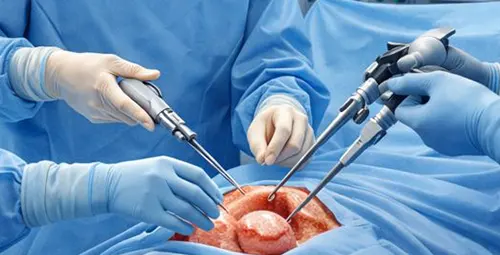
Abdominal myomectomy (open surgery)
In this method, a surgical incision is made on the abdominal wall to provide direct access to the uterus. Abdominal myomectomy is usually used in cases where myomas are very large, multiple, or deep in the uterine wall. This method allows for better control of bleeding and more accurate repair of uterine tissue, but compared to minimally invasive methods, it is associated with more pain after the operation, longer hospitalization and longer recovery period. Uterine artery and focused ultrasound are other methods that can treat fibroids without opening the abdomen. One of these methods is removing the myoma from inside the uterus using a special tool through the vagina. There are also some guided imaging techniques where the doctor can target and treat the myoma with the help of precise images. These methods are usually suitable for myomas that are inside the uterine cavity or are small to moderate in size and can reduce bleeding and other symptoms such as pelvic pain. The main advantage of these methods is short recovery period, preserving the uterus and reducing the need for open surgery.
Hysteroscopic myomectomy
In hysteroscopic myomectomy, the doctor inserts the surgical instrument through the vagina. The cervix is then removed and the myomas are removed. This method is mainly used for submucosal myomas and is performed without external incision. Hysteroscopic myomectomy is usually associated with a very short recovery period and has a positive effect on reducing abnormal bleeding and improving fertility, but it can only be used for certain types of myomas. The definitive treatment of uterine myoma is known. This procedure is usually recommended for women who have severe symptoms, have not responded to other treatments, and do not want to become pregnant in the future. The type of hysterectomy and its method are chosen based on the patient's condition.
Full hysterectomy
In full hysterectomy, the uterus is completely removed and the cervix is also removed. This method completely eliminates the possibility of myoma returning and uterine bleeding, and is one of the most common types of hysterectomy in the treatment of symptomatic myomas.
Subtotal hysterectomy
In subtotal hysterectomy, the body of the uterus is removed, but the opening is removed. The uterus is preserved. In some patients, this method is associated with a shorter recovery period and reduction of some complications, but there is a possibility of mild residual bleeding and its choice requires careful consideration.
For comprehensive explanations What is hysterectomy?
Comparison of different uterine myoma surgery methods
Invasiveness level
Uterine myoma surgery methods have significant differences in terms of their invasiveness. Open surgery, whether in the form of abdominal myomectomy or open hysterectomy, is considered the most invasive method and requires a large abdominal incision. In contrast, minimally invasive procedures such as laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are performed with small or no external incisions and cause less damage to the surrounding tissues. The selection of the invasiveness of surgery is usually based on the size, number and location of myomas.
Recovery period and time to return to activity
The recovery period is different in different surgical methods. In open surgery, the patient usually needs a few weeks to fully recover and return to daily activities. But laparoscopic myomectomy and hysterectomy are often associated with a shorter hospitalization and a faster return to work and normal life.
In the hysteroscopic method, many patients will be able to resume normal activities within a few days.
Effect on fertility and performance Uterus
Myomectomy, as a procedure that preserves the uterus, has the greatest role in preserving or improving fertility. This method is considered a preferred option especially for women who intend to get pregnant. On the other hand, hysterectomy eliminates the possibility of pregnancy by completely removing the uterus and is only suitable for patients who do not wish to preserve fertility. The choice of surgical method should be done considering the patient's fertility goals.
Possibility of myoma recurrence
There is a possibility of myoma returning after myomectomy, because the uterus is preserved and the possibility of new myoma growth remains. This is more likely in younger patients and people with multiple myomas. On the other hand, hysterectomy is considered definitive treatment and completely eliminates the risk of recurrence of myoma.
Benefits and complications of uterine myoma surgery
Benefits of uterine myoma surgery treatment
Surgical treatment of uterine myoma in many patients leads to a significant reduction or complete resolution of symptoms. Heavy menstrual bleeding, chronic pelvic pain, and a feeling of pressure in the abdomen are among the most common problems that improve significantly after surgery.
In cases where hysterectomy is performed, surgery is considered a definitive treatment and the possibility of myoma returning is completely eliminated. In some cases, myoma leads to a change in the shape of the uterine cavity. This problem can create obstacles for pregnancy. Surgery can solve this problem and increase the chances of pregnancy.
Short-term and long-term side effects of uterine myoma surgery
Like any other surgical intervention, uterine myoma surgical treatment is also associated with possible risks and complications. Short-term complications can include postoperative pain, bleeding, infection, and reactions to anesthesia, which are often manageable with proper care. In the long term, some patients may experience pelvic adhesions, dysfunction of adjacent organs, or, in rare cases, effects on reproductive function. The severity and incidence of these complications depends on the type of surgery and the individual conditions of the patient.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all uterine myomas require surgery?
What is the main difference between myomectomy and hysterectomy?
How long is the recovery period after uterine myoma surgery?
Is it possible for myomas to come back after surgery?
What effect does uterine myoma surgery have on fertility?
Summary
Surgical treatment of uterine myoma is one of the most effective treatment options for women who have severe, stable symptoms or are resistant to non-surgical treatments. Choosing the right surgical method depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, the size and location of myomas, the age of the patient, and the desire to preserve fertility. Methods such as myomectomy provide the possibility of preserving the uterus and can help improve quality of life and fertility outcomes in selected patients, while hysterectomy plays an important role as a definitive treatment in women who do not intend to become pregnant.
Despite significant benefits, uterine myoma surgery is always associated with possible risks and complications, and the decision to perform it should be based on a careful evaluation of clinical conditions and discussion. Consciously between the doctor and the patient. Choosing the right time for surgery and the right method can play a decisive role in reducing complications and achieving the best treatment results. Finally, a person-centered approach based on scientific evidence is the key to success in the surgical treatment of uterine myoma and maintaining the patient's long-term health. target="_blank" rel="noopener nofollow">
ACOG Practice Bulletin – Management of Symptomatic Uterine Leiomyomas Leiomyomas
class="elementor-column elementor-col-100 elementor-top-column elementor-element elementor-element-cb45c68" data-id="cb45c68" data-element_type="column">
Comparison of vaginal tightening methods: surgical and non-surgical With the passage of time or after childbirth, the walls of the vagina relax and the muscles...