The cause of back pain in children
Children's back pain can have many reasons and if neglected, it can cause serious consequences for their physical and even mental health. In some cases, this pain extends to the hip area and manifests as back and hip pain which may indicate neurological involvement or structural problems. Knowing the common causes, accompanying symptoms and treatment methods plays an important role in preventing long-term injuries. Next, we will examine factors such as carrying a heavy backpack, improper body posture, sports injuries, congenital problems, and infections.
- Carrying a heavy backpack: using backpacks full of books and heavy items is one of the most common causes of back pain in children. The high weight of these backpacks puts pressure on the spine and causes pain in the lower back, especially if the child carries it unbalanced.
- Incorrect body position: sitting or standing incorrectly for a long time can lead to pressure on the back muscles and changes in the natural curvature of the spine. Children are often in a bad position when using electronic devices, which is one of the main causes of chronic pain.
- Sports injuries: heavy sports activities or injuries caused by games and sports can lead to muscle strain and pain in the lower back. Failure to properly warm up or incorrect use of sports equipment increases this risk.
- Congenital problems: Some children are born with structural problems such as scoliosis (abnormal curvature of the spine) or intervertebral disc problems that can cause back pain. These problems are usually identified during medical examinations or with imaging.
- Infection or inflammation: conditions such as bone infection (osteomyelitis) or joint inflammation (arthritis) can lead to severe pain and limited movement in children. These problems require immediate medical intervention.
Symptoms of back pain in children
The symptoms of back pain in children are increasing and it has become a serious concern in the field of public health. Recent studies show that the prevalence of back pain in children and adolescents ranges from 30% to 70%, and this rate increases with age. In a study in England, 24% of children aged 11 to 14 had experienced back pain in the past month, with more girls (29%) than boys (19%).
Common symptoms include constant or intermittent pain in the lower back, decreased mobility, and in more severe cases, numbness or weakness in the legs. Risk factors include poor posture, prolonged cell phone or computer use, and obesity. Considering that only 12% to 20% of children with back pain go to the doctor, the importance of awareness of parents and teachers in early diagnosis and prevention of long-term complications of this problem increases; Because if neglected, some of these pains can lead to more serious problems such as lumbar disc at an older age, and getting to know the newest lumbar disc treatment method can play an important role in choosing an effective and timely treatment path.
| symptoms of back pain | Description |
| Persistent or intermittent pain | Pain may occur continuously or intermittently and its intensity varies throughout the day. |
| Feeling cramping | Children may experience stiffness or spasms in the back muscles that restrict movement. |
| Reduce range of motion | Pain or stiffness can reduce the ability to freely move the back. |
| Trouble sleeping | Night pain can prevent a child from sleeping comfortably and cause fatigue the next day. |
| Numbness or weakness in the legs | This symptom may indicate pressure on the nerves and needs immediate investigation. |
| Increased pain when sitting | Sitting for long periods of time, especially in the wrong positions, can aggravate the pain. |
| Pain when bending or lifting objects | Activities such as bending over or lifting heavy objects may increase the pain. |
| Walking disorder | Muscle pain or weakness can disrupt the balance and normal movement of the child. |
| Change in body position | The child may change their position in an effort to reduce pain. |
| Swelling or redness in the lower back | Swelling or redness can be a sign of serious injury or infection in the back area. |
Complications of child's back pain
Back pain in children can cause limitations in daily activities. A child suffering from this problem may have difficulty doing sports, playing or even participating in school activities. In addition to physical weakness, these limitations can also lead to a decrease in the child's self-confidence. In cases where this pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by neurological symptoms, the possibility of dangerous back pain is raised, which requires immediate medical attention.
Weakness in mobility and inactivity can lead to muscle fatigue and weakening, and over time, affect the child's balance and movement coordination. Decreasing physical activity disrupts the normal growth of bones and muscles and ultimately endangers the overall health of the child's body. To prevent these complications, it is very important to accurately identify the cause of back pain and perform appropriate exercises such as physical therapy.
Permanent changes in the spine
Long-term back pain in children may lead to permanent changes in the spine. Conditions such as scoliosis (lateral deviation of the spine) or kyphosis (abnormal protrusion of the back) can be caused by constant pressure on the spine. These problems not only increase pain, but also negatively affect the physical condition and appearance of the child. A misaligned spine can also impair the functioning of internal organs, such as the lungs and digestive system. In more severe cases, these changes may require complex medical interventions or lumbar disc surgery.
Psychological effects
Children who suffer from back pain often face psychological problems. Constant pain can make the child feel helpless and unable to perform daily activities. This state may lead to anxiety, depression and even social isolation. Reducing participation in group activities and peer games can also affect a child's self-esteem. These mental problems sometimes have long-term effects on the child's social relationships and academic performance.
Developmental problems and delayed puberty
Children's back pain may affect their physical development. Continuous pain and movement restrictions reduce physical activity and thus impair the strengthening of muscles and bones. In severe cases, this condition can lead to more serious developmental problems such as short stature or general weakness; In addition, back pain may affect the body's hormonal processes and delay the child's puberty.
This problem is especially observed in children who leave sports activities. Timely medical care and providing appropriate exercise programs play an important role in preventing these complications.
Dependence on drug treatments
One of the possible side effects of children's back pain is the long-term use of painkillers. These drugs, although they may reduce pain; But in the long run, they can cause side effects such as digestive problems, weak immune system or drug dependence. Continuous use of these drugs can negatively affect the overall health of the child and create unhealthy habits. Instead of relying on painkillers, alternative treatments such as physiotherapy, stretching exercises and using non-pharmacological methods are more effective options.
These methods not only reduce pain, but also prevent physical and mental problems caused by drug use.
Risk of other diseases
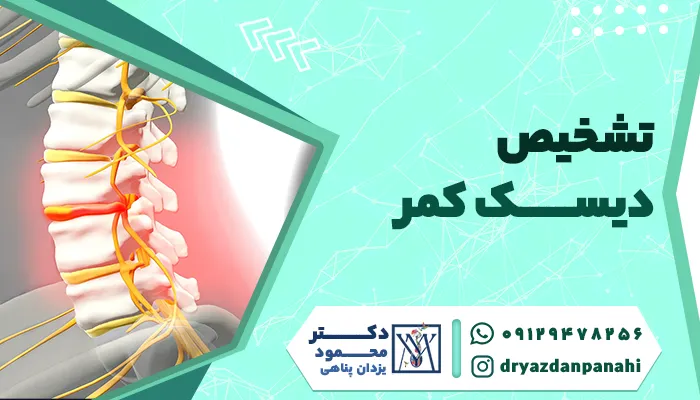
Long-term back pain in children can lead to other diseases such as lumbar disc, early arthritis, or even spinal canal stenosis. These problems are usually caused by constant pressure on the spine or lack of proper treatment. Diseases related to back pain can severely limit a child's mobility and even require more complex treatments such as surgery. Timely diagnosis and treatment of children's back pain using methods such as physiotherapy and muscle strengthening can prevent the development of these diseases.
Sleep problems and insufficient rest
Back pain can directly affect the quality of children's sleep. Persistent or sudden pain during the night may wake the child up or disrupt his sleep cycle. Insufficient sleep can cause other complications such as chronic fatigue, weak immune system, decreased concentration and academic problems; Also, lack of sleep may affect the child's behavior and cause irritability or decreased motivation. To improve the child's sleep, it is recommended to use suitable mattresses, adjust the sleeping position, and if necessary, see a doctor.
Diagnosis of children's back pain
Diagnosis of children's back pain requires careful and specialized examination, because its causes can vary from simple muscle problems to serious spine diseases. In the following, we introduce the most important methods of diagnosing this problem:
- Detailed physical examination; The doctor makes an initial assessment of the child's back condition by examining how to stand, walk, the flexibility of the spine and the presence of pain in certain areas.
- Medical history review; Information such as the time of onset of pain, its intensity, presence of fever, history of injury or underlying diseases will help the doctor to identify the exact cause of the pain.
- X-ray imaging (X-Ray); It is used to check the bone structure of the spine, identify fractures, deviations or congenital problems.
- MRI (MRI); This precise imaging method is very effective for viewing soft tissues such as discs, spinal cord and muscles, especially in cases where there is a possibility of disc herniation or infection.
- bone scan or laboratory tests; In suspected cases of infection or inflammatory diseases, the doctor may prescribe a bone scan or blood test for a more detailed investigation.
These methods, along with medical experience and expertise such as Dr. Mahmoud Yazdan Panahi, enable faster diagnosis and choosing the best treatment path for the child.
Dr. James G. Wright, pediatric orthopedic specialist from Harvard University, says about the diagnosis of back pain in children:
"The accurate diagnosis of back pain in children is an important challenge, because the causes of this pain can range from simple muscle problems to complex spinal diseases. The use of accurate examinations and appropriate imaging is the key to determining the real cause and choosing an effective treatment."
The cause of fever and back pain in children
Fever with back pain in children can be a sign of a problem beyond simple muscle pain and usually requires medical attention. This combination of symptoms is sometimes caused by the involvement of the body's immune system against an internal factor and may indicate the presence of inflammatory, infectious processes or even hidden disorders in the internal organs. In such a situation, the child's body reacts to the underlying factor by increasing the temperature, and back pain appears as one of the consequences of this conflict.
The importance of this condition is that its severity, persistence or accompanying symptoms such as lethargy, loss of appetite or movement restriction can be important clues for early diagnosis and prevent more serious complications in the future.
The cause of back pain in 7-year-old children
Back pain in 7-year-old children is usually caused by the body being in a situation that is not compatible with their developing muscle strength and structure. At this age, the bones and muscles are not yet fully developed, and any continuous pressure, incorrect movement pattern or age-disproportionate activity can cause back pain. On the other hand, some hidden factors such as developmental disorders, underlying diseases or problems that the child is not able to accurately express can be behind this pain. For this reason, back pain in this age group should not be taken lightly, and it is very important to pay attention to the continuation of the pain, change in the child's behavior or reduced mobility, because early diagnosis will play an important role in preventing more serious problems in the future.Treatment of child's back pain
Physiotherapy is one of the most effective methods of treating children's back pain. This method strengthens the back muscles and reduces the pressure on the spine by using stretching and strengthening exercises. Physiotherapists design programs according to the age, physical condition and severity of the child's problem. These exercises can improve flexibility and balance and prevent the recurrence of pain; In addition to exercises, physical therapy may include the use of devices such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Regular physical therapy sessions and child and parent cooperation in following up home exercises improve the treatment results. Consultation with a specialist doctor is necessary for referral to an experienced physiotherapist, because incorrect treatment may cause more problems; Especially in cases where the back pain has a more serious root and can lead to disc conflicts in the future, getting to know the newest method of back disc treatment with less pain and recovery time will help parents to choose the right treatment path more informed and timely if needed.
Correct body posture
Incorrect body position is one of the common causes of children's back pain, which can be corrected to help improve the problem. Correct sitting or standing, especially when using school desks and chairs or when doing homework, plays a key role in reducing pressure on the spine; In addition, it is very important to carry the backpack correctly, with a balanced weight and using both straps. Teaching children proper movement techniques, such as lifting heavy objects using the knees instead of bending the back, can also be effective.
These simple changes can prevent more serious problems in the future. Parents and teachers can play an important role in monitoring children's body condition. Consultation with a physiotherapist or orthopedic specialist can provide practical guidance to improve posture.
Painkillers
Using painkillers is one of the common ways to reduce severe pain in children. These medications usually include mild pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, which can reduce inflammation and provide immediate relief. However, the drug should be taken under the supervision of a doctor to avoid possible side effects such as digestive problems or drug allergies. Long-term use of painkillers is not recommended, because it can lead to dependence or decrease the effect of the drug.
Doctors usually prescribe pain medications as part of combination therapy, along with methods such as physical therapy or posture correction. The main purpose of prescribing these drugs is to reduce children's back pain and create conditions for performing exercises and therapeutic activities.
Adequate rest
Rest is one of the most effective ways to reduce back pain caused by muscle strain in children. This method, especially in cases where back pain in children is caused by heavy activities or sports, can help reduce inflammation and accelerate recovery; However, rest should be done in moderation, as prolonged rest can weaken the muscles and increase the problem. Combining short-term rest with light activities and stretching exercises can bring better results.
Using the right mattress and adjusting the child's sleeping position is important to reduce pressure on the back. Parents should take care that the child's rest does not mean complete immobility and gradually encourage him to do daily activities. If the pain does not improve, it is recommended to see a doctor.
Home treatment of children's back pain
For many children with mild to moderate back pain, home remedies can play an effective role in reducing pain and improving the condition. These solutions are usually simple, safe and do not require complex drugs and can help maintain the child's comfort and mobility. Below are some useful home methods for managing children's back pain:
- relative rest and reduction of heavy activities; Give the child time to avoid activities that aggravate the pain but not be completely immobile to prevent muscle weakness.
- Using hot and cold compresses; In the first 24 hours after the onset of pain, using a cold compress can reduce inflammation and swelling; After that, a warm compress helps to improve blood flow and reduce muscle cramps.
- gentle stretching exercises; Performing light and soft stretching exercises, under the supervision of parents or a specialist, can help increase flexibility and reduce muscle cramps.
- Attention to the correct sitting and sleeping position; Proper adjustment of the child's body position when sitting and sleeping reduces the pressure on the spine and helps to improve the pain.
- Maintaining a proper weight; A healthy and balanced weight prevents extra pressure on the back and helps the health of the child's spine.
Children's back pain and its step-by-step review
Children's back pain is a common problem that needs to be examined step by step and carefully. Initially, diagnosis of the cause of children's back pain is done through clinical examination and the use of imaging methods such as X-ray or MRI. Then, treatment is determined based on the cause of the pain, which can include posture correction, physical therapy, or, in certain cases, the use of pain medications. In cases where the pain is caused by more serious problems such as lumbar disc, it is necessary to visit a lumbar disc surgeon.
Experienced surgeons can provide effective solutions to treat these problems and, if necessary, perform surgical interventions. Paying attention to the treatment of children's back pain at the right time can prevent the development of problems and improve the quality of life of the child. Finally, continuous monitoring and treatment follow-up is the key to success in managing this problem.