Table of contents
- What is ultrasound ultrasound?
- What is the use of ultrasound?
- What problems does ultrasound detect?
- What is the price of ultrasound?
- Interpretation of ultrasound test
- Types of ultrasound: several types of ultrasound Do we have it?
- Pregnancy ultrasound and pregnancy ultrasound table
- How is ultrasound performed?
- Preparation before ultrasound
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound?
- Conclusion and guide to see a doctor
Listen to the summary of this article in this podcast:
Sonography or ultrasound is a safe and accurate medical imaging test that creates images of the inside of the body using sound waves. This test is most widely used in examining fetal growth during pregnancy and is also used to identify problems such as the presence of gall and kidney stones, blood clots and cancer. Considering that the radiologist performs the ultrasound and sends the report to the doctor, visit the radiologist to perform the ultrasound after the prescription of the general practitioner or gynecologist. You can find out about the appointment times of the specialist doctor you want on the online appointment site of your doctor and register it or receive expert advice online and over the phone.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound (also called sonography or ultrasonography) is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging test. In this method, high-frequency sound waves are used to create images (sonograms) or live videos of internal organs or other tissues such as blood vessels. The images obtained from ultrasound help doctors to see the details of the soft tissues inside the body without any incision.
Television examination or ultrasound machine directs high-frequency sound waves to the internal structures of the body for examination. The reflected sounds or echoes are recorded to create an image that can be seen on the monitor. Finally, sound waves are emitted and received from a small handheld probe.
What is an ultrasound device?
The ultrasound device works like sonar technology, which uses sound waves to detect objects under the surface of the ocean. These sound waves are emitted from a device called an ultrasound probe. The ultrasound technician uses a special gel on the part of the body that he wants to examine. Then he places the probe on the desired part.
Actually, the ultrasound machine emits sound waves from a probe that is placed on the body by the ultrasound technician. After hitting the internal tissues of the body, these waves are reflected and processed to produce images.
What is the difference between ultrasound and ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a type of medical technology that uses high-frequency sound waves for imaging. This technology is usually used in ultrasound. In fact, ultrasound means the production and use of sound waves, while sonography refers to imaging using these waves.

What is the use of ultrasound?
Doctors usually use ultrasound to check the health and growth of the fetus during pregnancy. Of course, in addition to examining the state of pregnancy and the fetus, ultrasound is also used to identify many medical problems, including heart diseases, uterine and ovarian abnormalities, digestive problems, liver and kidney disorders, lymph node problems, vascular diseases, and the examination of tumors and cysts. In general, the use of ultrasound includes the following:
- Breast examination
- Digestive system (liver, pancreas, spleen or gall bladder)
- urinary system (such as kidneys or bladder)
- Heart and blood vessels
- Examination of testicles
- Female reproductive system (ovaries or uterus)
- Thyroid checkup
- Brain, pelvic bone or spine (in infants)
Among the other applications of ultrasound, the following can be mentioned:
- Diagnosis, treatment and guidance of operations such as biopsy
- Ultrasound can show whether it is a cancerous lump or a fluid-filled cyst?
- Guide a needle with anesthetic solution near the nerves
What problems does ultrasound detect?
Ultrasound can help your doctor diagnose a wide range of medical problems, including:
- Abnormal growth (tumor) such as cancer, ovarian cyst or thyroid nodule
- Blood clot Enlargement of the spleen
- Extrauterine pregnancy Gallstones
- Heart problems such as coronary artery disease or congenital heart defects
- Kidney or bladder stones
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder)
- Varicocele
How much does ultrasound cost?
The cost of ultrasound cannot be determined accurately. Because this test depends on various factors and ultrasound has a different cost in each area. In some laboratories, due to the up-to-date ultrasound equipment and the high experience of the specialist, the price of ultrasound increases. If you are covered by health insurance, you can use insurance services to reduce the cost. Usually, insurance covers about 15 to 20 percent of the cost.
| The price of ultrasound | Free price in Tomans |
|---|---|
| Thyroid or parathyroid ultrasound | 241,925 thousand Tomans |
| Pregnancy ultrasound (including age, position of the placenta, fetus and heart rate) | 364,125 thousand Tomans |
| Ultrasound of the chest | 198,230 thousand Tomans |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract (full bladder) | 291,300 thousand Tomans |
| Full ultrasound of the abdomen and Pelvis | 483,485 thousand tomans |
| NT ultrasound and anomaly of the first trimester of pregnancy | 681,350 thousand tomans |
| Ultimate ultrasound | 267,850 thousand tomans |
| Trans pregnancy ultrasound Vaginal | 582,600 thousand Tomans |
| Ultrasound search for ectopic pregnancy (EP | 238,720 thousand Tomans |
| Ultrasound of each joint | 291,300 thousand Tomans |
| Doppler ultrasound of the uterus and ovaries through Vaginal | 1,019,550 million tomans |
| Appendix ultrasound | 203,910 thousand tomans |
| Prostate ultrasound (transrectal) | 436,950 thousand tomans |
Interpretation of ultrasound test
In ultrasound, sound waves are sent to the body and after hitting different tissues, they create a reflection that returns to the device and provides an image of the tissues. The interpretation of the results is based on the shape, size, position and characteristics of the tissues. For example, in examining the organs, measurements and the presence of abnormal changes may be noticed by the doctor.
Types of ultrasound: how many types of ultrasound do we have?
There are different types of ultrasound, including transabdominal ultrasound (to examine the abdominal organs), transvaginal ultrasound (to examine the female reproductive system), echocardiography (to evaluate the condition of the heart), Doppler ultrasound (to examine blood flow), and three-dimensional or four-dimensional ultrasound. Each of these items are used for different parts of the body.| Types of ultrasound | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Transabdominal ultrasound | Examination of internal abdominal organs (such as liver, kidneys, bladder, uterus and ovaries) |
| Trans ultrasound Vaginal | Examination of the female reproductive system and examination of fertility problems, cysts and fibroids |
| Echocardiography or ultrasound of the heart | Evaluation of heart function such as narrowing of arteries and heart problems |
| Doppler ultrasound | Evaluation of blood flow |
| 3D or 4D ultrasound (3D/4D) | 3D and 4D imaging of body organs |
1. Internal ultrasound
If the internal reproductive organs or urinary system need to be examined, the technician places the ultrasound probe in the rectum in men and in the vagina in women. An endoscope may be used to evaluate part of the digestive system (for example, the esophagus, thoracic lymph nodes, or the stomach).
In this case, a lamp and a sono probe are connected to the end of the endoscope, which usually enters the patient's body through the mouth. Before performing these ultrasounds, the patient is given medication to reduce any possible pain. Internal ultrasounds are a little more difficult to perform than external scans, and there is a slight possibility of internal bleeding.
2. External ultrasound
External ultrasound technician applies a lubricating gel on the patient's skin and places a probe on the lubricated skin. The probe is moved over the part of the body that needs to be examined and provides an image of the desired part. This type of ultrasound is also used to check the heart of a patient or a fetus.
In external ultrasound, a person does not feel pain or discomfort, but only feels the ultrasound probe on his skin. Of course, during pregnancy, due to the pressure on the bladder, the patient may feel a little uncomfortable. This method can help diagnose problems related to soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, tendons, and joints. This type of ultrasound is also used to diagnose frozen shoulder, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome and other cases.
English text:
quoted from mayoclinic
"Diagnostic ultrasound, also called sonography or diagnostic medical sonography, is an imaging method that uses sound waves to produce images of structures within your body." "
3. Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound is used to evaluate internal organs such as the liver, kidneys, bladder, uterus, and ovaries. The best time to perform this ultrasound is usually early in the morning and with an empty stomach, because this method requires a better view through the abdominal tissues. In the table below, we examined the ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis:| Abdominal ultrasound | Pelvic ultrasound |
|---|---|
| Kidney, liver and gall bladder ultrasound | Bladder ultrasound |
| Spleen and pancreas examination | Uterus examination and Ovary |
| Ultrasound of the appendix | Ultrasound of the prostate |
| Ultrasound of the adrenal glands | Ultrasound of the testis (varicocele examination in men) |
| Ultrasound of the deep abdominal lymph nodes |
best time for abdomen and pelvis ultrasound
The best time to perform abdominal and pelvic ultrasound is usually early in the morning and when the stomach is empty. For abdominal ultrasound, you must fast for at least 6 hours. In a pelvic ultrasound, it may be necessary to fill the bladder to obtain clear images of the organs.
4. Ultrasound endoscopy
In this method, the doctor carefully inserts a flexible tube (called an endoscope) into the throat. This tube has an ultrasound probe at the end. This probe shows the inside and outside of the digestive or abdominal organs (such as the liver). During an ultrasound endoscopy, the doctor may take a small tissue sample for analysis in the laboratory.
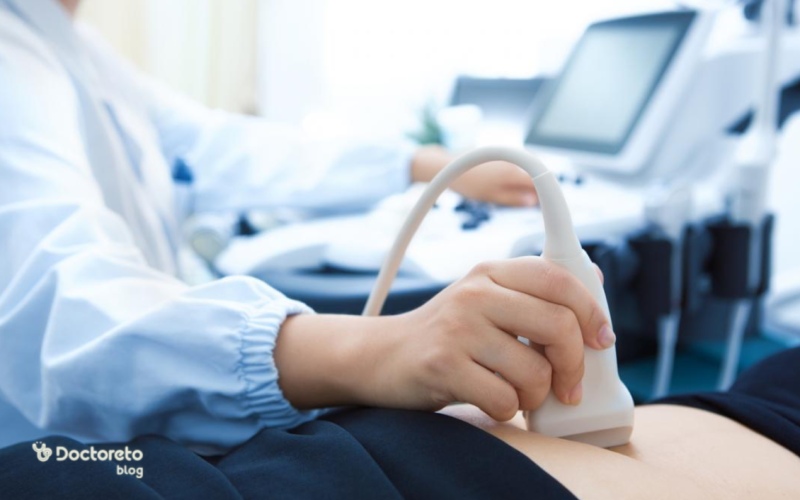

5. Echocardiography through the esophagus
During the specialized ultrasound echocardiography through the esophagus, the doctor carefully directs an endoscopic probe into the patient's throat. This probe takes pictures of the heart and adjacent blood vessels.
6. Rectal ultrasound for endometriosis
To Diagnosis of endometriosis in ultrasound the doctor places a probe in the rectum. This probe takes pictures of the rectum or other nearby tissues, such as the prostate (in men). In some cases, rectal ultrasound for endometriosis may cause pain and discomfort.
7. Vaginal ultrasound
In vaginal ultrasound, the technician places a probe in the vagina. This probe shows reproductive tissues (such as the uterus or ovaries). Sometimes vaginal ultrasound is also called pelvic ultrasound. Because the structures inside the pelvis (pelvic bones) are also evaluated in this type of ultrasound. The best time for vaginal ultrasound is after the menstrual cycle and it takes about 1 hour at most.
8. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
In contrast-enhanced ultrasound, during the ultrasound, the doctor injects the contrast material through a catheter or intravenously to the patient. These materials help provide a clearer and more accurate picture of your organs. This type of ultrasound is usually used to check the kidneys, liver and bladder.
9. What is NT ultrasound?
In NT ultrasound, the clear space behind the neck (also called nuchal translucency or NT scan) is checked to evaluate the risk of Down syndrome and some other chromosomal abnormalities as well as congenital heart problems in the baby. Obstetricians and gynecologists request this test along with blood tests in combined screening tests of the first three months of pregnancy for all pregnant women.
NT ultrasound measures the clear space in the tissue behind the baby's neck. This space is called the transparent space behind the neck. If there are some abnormalities and genetic problems in the first three months of pregnancy, more fluid accumulates in the back of the fetus's neck. This makes this clear space larger than average.NT scan should be done in the 11th to 14th week of pregnancy, because only in this period of time the lowest part of the fetal neck is still clear. The last day you can do Sono NT is the day you enter week 13 and day 6 of your pregnancy. In some testing centers, using highly specialized equipment, other genetic abnormalities may be detected during Sono NT.
NT scan is not invasive. Of course, the results are not completely certain. Diagnostic tests such as CVS or amniocentesis are necessary to confirm a positive scan result.
10. What is NB ultrasound?
NB stands for Nasal Bone. During the NT scan, doctors check the thickness of the neck fold and in the NB ultrasound, the formation of the baby's nasal bone. A thick neck crease or the absence of a nasal bone can indicate the presence of Down syndrome. NT scan is usually done at the same time as blood test. This ultrasound is in the list of tests and ultrasounds during pregnancy.
The result of the screening test shows you how likely you are to have a baby with a chromosomal disorder. For example, the chance of having a child with T21 (Down syndrome) may be 1 in 2,500. Note that the NT scan and blood are only screening tests. These tests can only tell you if a chromosomal disorder is likely. To find a definitive yes or no answer, you need to do diagnostic tests such as MaterniT21 or CVS.
11. Abnormal ultrasound
Most doctors recommend anomalous ultrasound at 20 weeks of pregnancy. This ultrasound is usually called ultrasound before the second birth. This test examines the growth of the fetus during pregnancy. This ultrasound is also called gender diagnosis ultrasound. This type of ultrasound may show the biological sex of your child.
Other ultrasounds (early or late in pregnancy) can provide a partial image of the uterus or ovaries. The gynecologist may recommend additional scans to answer questions or concerns, such as the possibility of birth defects.
Anomalous ultrasound usually takes about 30 minutes and the best time to do it is between 20 and 24 weeks of pregnancy. In general, experts say that before performing ultrasound, the bladder should be empty and drink a lot of water.In this video, Dr. Amirpasha Henrapisheh, radiologist and ultrasound specialist, talks to you about pregnancy ultrasound.
12. Fetal echocardiography
Fetal echocardiography is an imaging method to evaluate fetal heart health. This method is usually performed between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy and is useful for identifying congenital heart problems. The images created with this method include the details of the anatomy of the fetal heart.
13. What is Doppler ultrasound?
Doppler ultrasound is used to evaluate blood flow in blood vessels. This method helps to diagnose vascular disorders such as blood clots, narrowing of arteries or blood circulation abnormalities.
Doppler ultrasound can assess the function and condition of the heart valve, any abnormalities in the heart, valvular insufficiency or leakage of blood from the valves, and also show how well the heart can pump blood. Doppler sonography is also used to check the following:
- Inspection of the wall of blood vessels Check for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or aneurysm
- Fetal heart examination and heartbeat
- Fetal Doppler ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound in pregnancy
- Investigation of plaque accumulation and blood clotting
- checking the blockage or narrowing of the vessels
What is the difference between normal ultrasound and Doppler?
Conventional ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of structures inside the body, but cannot show blood flow. Doppler ultrasound works by measuring sound waves that are reflected from moving objects such as red blood cells.
14. 3D ultrasound and 4D ultrasound
Most types of ultrasound create flat or two-dimensional images. Some doctors recommend 3D or 4D ultrasound. Both of these sonos provide a life-like view of the fetus. 3D/4D ultrasound in pregnancy provides 3D and 4D imaging of the fetus and is used to observe the details of the face and body of the fetus more accurately.
15. Ultrasound of the liver
Liver ultrasound is a non-invasive test that creates images of a person's liver and blood vessels and can help diagnose various liver diseases such as fatty liver, liver cancer, and gallstones. Ultrasound of the liver is a type of ultrasound through the abdomen. It is better to fast at least 6 to 7 hours before the liver ultrasound.16. Ultrasound of kidney and urinary tract and bladder
Renal and urinary tract ultrasound (REE-nul) uses sound waves to produce images of the kidney and bladder. During the scan, an ultrasound machine sends sound waves to the kidney area and images are recorded on a computer. Black and white images show the internal structure of the kidney and related organs.
17. Breast ultrasound
Chest ultrasound is a non-invasive diagnostic test that is used to evaluate organs and structures inside the chest such as the lungs, mediastinum (a region in the chest that includes the heart, aorta, trachea, esophagus, thymus, and lymph nodes) and the pleural space (the space between the lungs).
English text:
"Clinically, gynecomastia is diagnosed by finding subareolar breast tissue of 2 cm in diameter or greater."
Persian translation:
"Clinically, gynecomastia is diagnosed by finding subareolar breast tissue of 2 cm in diameter or greater." href="https://misuse.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/error/abuse.shtml" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">ncbi
18. Testicular ultrasound
Scrotal ultrasound is an imaging method to examine the testis and other structures of the scrotum. Ultrasound is performed by moving the ultrasound transducer on the scrotum. Ultrasound images are simultaneously viewed on the monitor.
19. Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is used to evaluate the state of the thyroid gland and identify problems such as goiter or nodules. This method is non-invasive and painless and is usually done to check the size, shape and texture of the thyroid gland.
20. Stomach and intestinal ultrasound
Stomach and intestinal ultrasound is a non-invasive method used to evaluate the structures inside the abdomen. This ultrasound includes the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen and abdominal aorta.
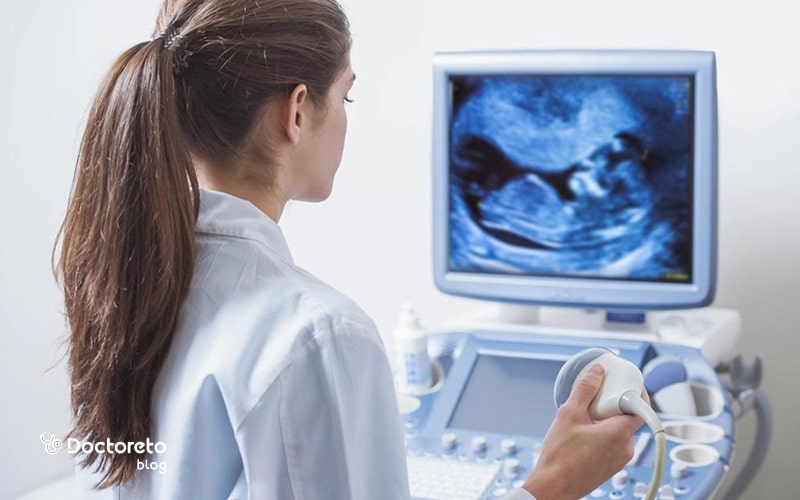
pregnancy ultrasound and pregnancy ultrasound table
Doctors use pregnancy or childbirth-related ultrasound, which is also called prenatal ultrasound, to monitor the health of the mother and fetus during pregnancy. In early pregnancy, a doctor may use an abdominal or transvaginal ultrasound as one of the pregnancy tests to check for:
- Diagnosis of pregnancy sac
- Determining the date of birth
- Fetal health status (including heart rate)
- Determining the gestational age of the fetus
- Examination of multiple births (presence of more than one embryo)
| Week of pregnancy | Type of pregnancy ultrasound | Purpose of pregnancy ultrasound |
|---|---|---|
| Week 6 to 7 | Transvaginal ultrasound | Confirmation of pregnancy and fetal heart examination |
| Week 10 12 | Transabdominal ultrasound | Fetal development examination and Down syndrome screening |
| Weeks 18 to 20 | Transabdominal ultrasound | Fetal anatomy examination |
| Weeks 28 to 32 | Transabdominal ultrasound Abdominal | Checking the condition of the fetus and amniotic fluid |
| 36 to 38 weeks | Transabdominal ultrasound | Checking the condition of the placenta and the readiness of the fetus for delivery |
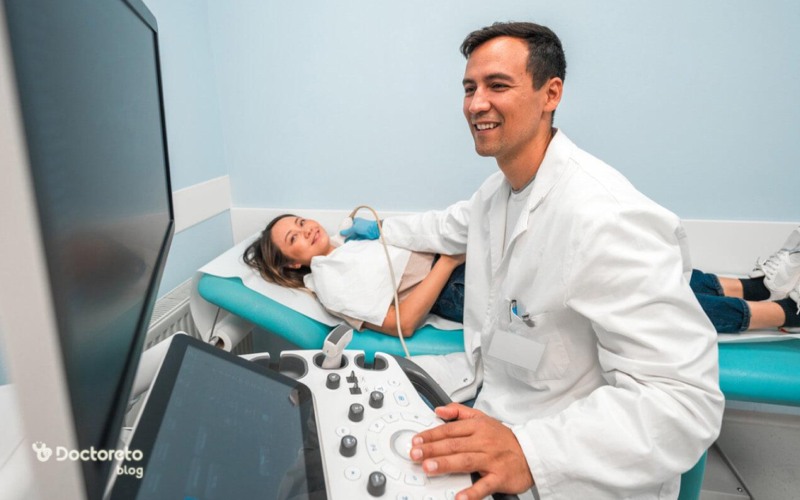
How is ultrasound performed?
For the ultrasound, the doctor may ask you to remove some of your clothes or use a special hospital gown. For the scan, you should lie on your side or back on a comfortable table. Most scans take between 20 and 60 minutes.
During the sono test, the operator or doctor performs the following steps:
- The technician applies a small amount of water-soluble gel on the skin of the desired area. This gel does not harm the skin and does not cause stains on your clothes and is easily washed.
- The technician moves a hand tool called a probe or scanner over the gel. Depending on the area that needs to be scanned, the scanner moves on the skin or inside your body (for example, during uterine examinations).
- You must stay still during the ultrasound. The technician may ask you to hold your breath for a few seconds. Being still can help create sharper images.
- In the last step of the sono technician, the gel remains on the skin.
Ultrasound can be done in a doctor's office, hospital or clinic on an outpatient basis. Ultrasound is usually not painful and is not associated with any noise.
preparation before ultrasound
Some specific factors (such as a full bladder or stomach) can cause sono images to have more or less detail. In most cases, no special preparation is needed for ultrasound, but depending on the type of ultrasound, the doctor may ask you to:
- Avoid bathing before scanning.
- Drink a certain amount of water just before the scan.
- Avoid eating or drinking several hours before the ultrasound.
- When examining the liver or gallbladder, you may need to fast or not eat anything for a few hours before the operation.
- For scanning during pregnancy (especially in early pregnancy), the patient should drink some water and not urinate before the test. When the bladder is full, the scan produces a better image of the uterus.
When is the best time to do an ultrasound?
You can go to the ultrasound center at any time of the day and do this test. Some abdominal ultrasounds, such as liver ultrasounds, need to be done on an empty stomach. In this case, it is necessary not to eat anything from 12 o'clock in the night before Suno.
Uterine sonography can be performed on any day of the menstrual cycle. If you need a uterine ultrasound to check for cysts or polyps, it is better to do it after menstruation, that is, between days 5 and 11 of menstruation. Because in these days, uterine polyps are well seen.How many glasses of water should we drink before ultrasound?
For abdominal ultrasounds, the bladder must be full. Typically, the patient is asked to drink 3 to 5 glasses of water 1 to 2 hours before the ultrasound so that the bladder is completely full and a more accurate imaging can be performed.
Does one have to fast for ultrasound?
In most cases, the ultrasound does not require fasting, unless the ultrasound of the abdomen or liver is to be performed. In such cases, it is better for the patient to be fasting to increase the accuracy of the results.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a non-invasive method, which means that there is no need to cut or insert any foreign object into the body. Also, this procedure is painless and does not cause any special side effects. The advantages of ultrasound include high safety and no use of ionized radiation, which differentiates it from methods such as CT scan and radiology.
However, ultrasound is more effective for examining soft tissues and less useful for examining bones or very hard organs. Also, this method is less accurate in examining some deeper body structures such as lungs or brain.
| Advantages of ultrasound | Complications of ultrasound |
|---|---|
| Painless and non-invasive | The quality of the results largely depends on the mastery of the specialist |
| Reasonable price | Possibility of sensitivity to the gel used in Ultrasound |
| No use of dangerous radiation | False results in some cases |
| Safe for pregnant women | Limitations of imaging in some body tissues (such as the brain) |
| Ease of use |
Does ultrasound hurt?
Ultrasound is usually painless. Of course, sometimes during the ultrasound, pressure is applied on the body, which may be a little uncomfortable, but most of the time, the person does not feel any pain.
Conclusion and guide to see a doctor
Most specialists recognize ultrasound as an accurate and safe imaging test. This test is usually painless and is used to diagnose or obtain information about a wide range of medical conditions. Because the operator's skill affects the accuracy of the results, make sure you have the ultrasound performed by an experienced sonography specialist. On the online appointment site of your doctor, you can find out about the appointment times of the specialist doctor you are interested in and register it, or receive expert advice online and over the phone.
Your doctor takes care of your health!