Table of Contents
Listen to the summary of this article in this podcast:
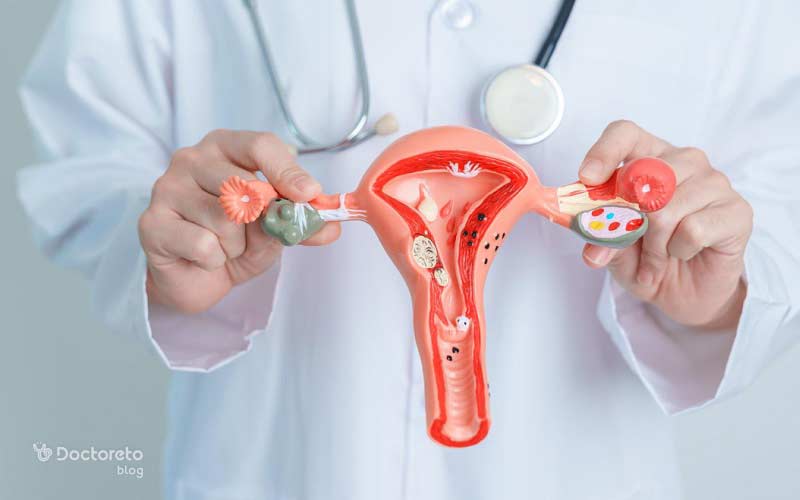
Fibroids in pregnancy In simple terms, they are usually benign muscular masses that grow from the wall of the uterus and may be present before pregnancy or seen in pregnancy ultrasound. Some infected people do not have any symptoms and find out about it by accident. If you have had heavy periods, pelvic pain, pressure, or a history of miscarriage, it is better to visit before or early in pregnancy. But what is the treatment of uterine fibroids in pregnancy and what are the side effects? In the continuation of this article from your doctor, we will examine the important points.
What is uterine fibroid in pregnancy?
Uterine fibroid disease These are usually benign masses that are made of uterine muscle tissue and are also called myoma or leiomyoma. Uterine fibroids in pregnancy usually already exist and are seen in the first ultrasounds because many people do not have clear symptoms before pregnancy.
In pregnancy, due to hormonal changes and blood supply, some fibroids may change in size or cause pain, but in many cases, pregnancy continues without serious problems. The important point is that the location of the fibroid in relation to the placenta and cervix is more important than the name of the fibroid because it can affect the pain, the condition of the fetus and the decision to give birth.
| Symptoms of uterine fibroids and pregnancy | Causes and factors related to the development of fibroids |
|---|---|
| Usually asymptomatic at first | Exact cause unknown |
| Pain or cramps in the pelvis and lower abdomen | Genetic background and history Familial |
| Sudden severe abdominal pain | Dependence on estrogen and progesterone |
| Local sensitivity of the abdomen | Older age at childbearing age |
| Feeling of pressure or heaviness in the pelvis | Obesity or overweight |
| Urine frequency | Onset Menstruation at a young age |
| Vaginal spotting or bleeding | More menstrual cycles throughout life |
| Feeling that the abdomen is bigger than expected | Local growth factors in the uterine tissue |
| Back pain or flank pain | Hormonal changes and hormone receptors in Fibroids |
| Fatigue due to bleeding and anemia | Lifestyle and metabolic factors (such as insulin resistance) |
Types of uterine fibroids in pregnancy
The types of fibroids are usually classified based on their location relative to the uterine wall and cavity, which affects the effect of fibroids on pregnancy. Some fibroids are inside the thickness of the wall, some grow under the inner lining of the uterus, and some protrude outside the uterus.
During pregnancy, this category helps to understand how likely you are to have pain, bleeding, or a change in the course of labor. Also, basal fibroids or fibroids near the cervix can cause more pain or difficulty in childbirth.
Types of uterine fibroids in pregnancy include:
- Intramural
- Submucosal
- Sub serosal
- peduncle or base
- Cervical
1. Intramural fibroid in pregnancy
Intramural fibroid grows inside the muscular wall of the uterus during pregnancy and is the most common type of fibroid. If it is small, it may not cause any symptoms, but when it gets bigger, it can cause pelvic pressure, pain and sometimes change the shape of the uterine cavity. In pregnancy, its location relative to the placenta is important and may be associated with premature contractions or pain due to degeneration.
transmural fibroid in pregnancy
Transmural fibroid is a less common term in pregnancy and usually refers to a mass that involves a large part of the thickness of the uterine wall and extends from the inner to the outer layers. When such a fibroid is large, it can change the shape of the uterus and cause pressure or pain.
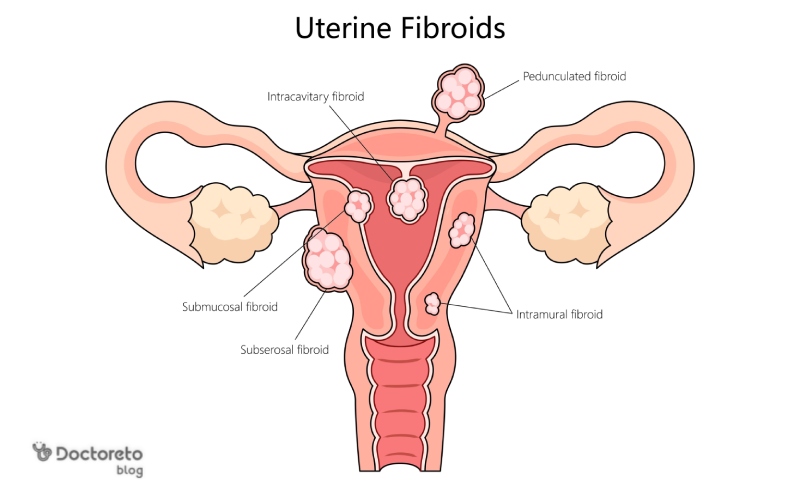
2. Pregnancy with submucosal fibroid
Pregnancy with submucosal fibroid means a fibroid that grows under the inner lining of the uterus and can change the shape of the uterine cavity. This type is more associated with bleeding and fertility problems than other types because it affects the implantation site. In pregnancy, the location and distance from the placenta is important and needs to be checked. If there is anterior fibroid in pregnancy, it sometimes affects the cesarean section or abdominal pain and should be included in the birth plan.
3. Subserosal fibroma in pregnancy
Subserosal fibroid and pregnancy usually means a lump that grows under the outer layer of the uterus and protrudes outward. This type can cause a feeling of pressure, pelvic heaviness or pain due to stretching, but it usually affects bleeding less than the submucosal type.
ectopic-uterine fibroid in pregnancy
Extrauterine fibroid in pregnancy is a term for fibroids that are located on the outer surface of the uterus and grow towards the abdominal cavity. These masses still originate from the uterine tissue but are not inside the uterine cavity. In many cases, it does not affect implantation. If they are big, they can put pressure on the bladder or intestine and cause pain.
4. Pedunculate fibroma (peduncle) in pregnancyPedunculate or pedunculated fibroid in pregnancy is a mass that is connected to the uterus with a stem and can grow inside or outside the uterus. The problem with this type is the possibility of the stem twisting and causing sudden severe pain, which is sometimes accompanied by nausea and abdominal tenderness.
5. Cervical fibroid in pregnancy
Cervical fibroids are located in or near the cervix during pregnancy and can be accompanied by a feeling of pelvic pressure, pain during intercourse, or urinary problems. During pregnancy, if it is large, it may narrow the exit path and affect the choice of delivery method. It also sometimes makes the examination more difficult and requires more careful care.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids in pregnancy
The signs of uterine fibroids in pregnancy are not always clear and some women do not have any symptoms. When the symptom occurs, it is mostly related to the size and location of the fibroid and blood supply changes in pregnancy, and pain in the abdomen or pelvis, feeling of pressure and bloating, frequent urination or constipation can occur. Sometimes spotting or light bleeding is also seen, but any bleeding during pregnancy should be checked.
Common symptoms of uterine fibroids and pregnancy usually include the following:
- Abdominal and pelvic pain or cramps
- Feeling of pelvic pressure or heaviness in the lower abdomen
- Urine frequency or difficulty in urination Constipation or flatulence Vaginal spotting or bleeding
- Sudden severe pain in some cases, especially in large or basal fibroids
Fibroid symptoms in the first trimester of pregnancy
In the first trimester, many people are newly acquainted with the presence of fibroids in pregnancy because the initial ultrasound is done. Some fibroids, especially if they are close to the uterine cavity, can slightly increase the risk of early pregnancy problems, but this depends on the location and size of the fibroid.
Fibroid symptoms in the second and third trimester of pregnancy
In the second and third trimesters, the feeling of pain is more prominent because the fibroid may undergo changes in blood supply and degeneration. A feeling of pressure on the bladder or bowel, an enlarged abdomen more than expected, or shooting pains in the pelvis may also be seen. If the fibroid is large, it sometimes changes the position of the fetus and increases the possibility of breech or the need for cesarean section. Also, in some people, premature contractions or symptoms of the threat of premature labor are raised, which must be checked.
Uterine fibroid symptoms during childbirth
Uterine fibroids may increase the risk of needing a cesarean section, especially if they are large or located in the lower part of the uterus; However, many women with fibroids have successful vaginal deliveries. Fibroids can increase the likelihood of cesarean section; The amount of increase depends on the size and location of the fibroid and the delivery conditions, and if the fibroid blocks the delivery path, a cesarean section may be necessary.
uterine fibroid symptoms after delivery
After giving birth, many fibroids shrink as the uterus contracts and the pain decreases, but not all are the same. In some people, postpartum bleeding may be heavier or longer because fibroids can affect the contraction of the uterus. If you have severe pain, fever, foul-smelling discharge, or excessive bleeding, you should be evaluated quickly.
signs of pregnancy with large fibroids
Large fibroid in pregnancy shows itself more with pressure symptoms than with bleeding. You may experience pelvic heaviness, frequent urination, constipation, flank pain, or pain that worsens when you change position. In some cases, sudden severe pain occurs due to degeneration or twisting of the fibroid base and requires immediate investigation.
Experiences of pregnancy with fibroids
In the experiences of pregnant mothers and those who became pregnant with fibroids, many mothers say that they found out about the presence of fibroids during pregnancy in ultrasound and their concern was about the pain and enlargement of the mass. Some people have reported hip and back pain in the middle weeks and have been advised by the doctor to rest, drink liquids and take painkillers. In some accounts, the fibroid has grown in size and progressed with examination. In pregnancy experiences with subserosal fibroid, worry about pressure on the fetus is common, but many have calmed down with the doctor's examination and explanation.

The cause of uterine fibroids in pregnancy
Two hormones called estrogen and progesterone cause the lining of the uterus to thicken every menstrual cycle to prepare for pregnancy. These hormones also seem to contribute to the growth of fibroids. Fibroids contain more cells that bind to estrogen and progesterone than normal uterine muscle cells.
Some of the things that can be risk factors for fibroids in pregnancy are:
- Genetic and family background
- estrogen and progesterone hormones
- Overweight, older age and some underlying factors
Diagnosis of fibroids in pregnancy
Diagnosis of having fibroids in pregnancy is usually done with ultrasound to show the number, size and location of fibroids next to the placenta and gestational sac. Sometimes, in the pelvic examination before pregnancy, the irregular enlargement of the uterus raises doubts, but imaging should be done to confirm. If there is severe pain or rapid growth, the doctor may repeat follow-up ultrasounds sooner.
uterine fibroid ultrasound in pregnancy
Uterine fibroid ultrasound in pregnancy is considered as a standard imaging test to confirm the presence of fibroids. Because it allows the doctor to distinguish fibroids from other conditions such as adenomyosis, polyps, ovarian tumors and pregnant uterus. However, not all fibroids may be visible on ultrasound.
Fibroid treatment in pregnancy
Fibroid treatment usually relies on monitoring and controlling symptoms. In periodic ultrasounds, the size and location of the fibroid and its effect on the placenta and fetal growth are checked. Some women only receive supportive care, and sometimes the fibroid shrinks during pregnancy or after delivery.To treat pain and shrink fibroids in pregnancy, rest, fluids and painkillers allowed by the doctor's opinion help. Surgery is usually postponed until after delivery unless there is a severe complication. Pregnancy and breastfeeding may have a protective effect for the occurrence of fibroids in pregnancy and the following years, and the choice of treatment for uterine fibroids and pregnancy depends on the symptoms and location.
Fibroid pain treatment in pregnancy
Fibroid pain in pregnancy is usually controlled by rest, staying hydrated, and approved painkillers, and many cases do not require aggressive action. Acetaminophen is usually considered as the first line option for pain and fever in pregnancy, and the dose and individual conditions should be observed regarding its use.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be suggested only in some conditions and usually for a short period of time. Do not take any pain reliever arbitrarily, especially if you have a history of underlying disease.
complications of fibroids in pregnancy
Regarding what are the complications of uterine fibroids it should be said that the complications of uterine fibroids depend on the size, number and location of uterine fibroids, and in many pregnancies no serious problems arise. However, fibroids can increase the risk of severe pain from altered blood supply, preterm labor, abnormal fetal position, and the need for cesarean section. If the fibroid is close to the placenta, sometimes there are concerns such as premature separation of the placenta or bleeding.
The growth of fibroids in pregnancy may increase the risk of other complications during pregnancy and delivery. These complications include the following:
- Fetal growth restriction
- Separation of the placenta
- Premature birth
- Abortion
English text:
quoted from nhs.uk
Translation Most women do not experience any symptoms of fibroids, but they can cause significant problems in rare cases.
Persian translation:
Most women do not experience any symptoms of fibroids, but in rare cases they can cause significant problems.
Is uterine fibroids dangerous in pregnancy?
Often, fibroids are benign and the risk of being cancerous is very low, but in pregnancy, the main issue is not cancer, it is the issue of pregnancy complications. Whether or not it's dangerous depends mostly on how big the fibroid is, where it's located, whether it's near the placenta, and whether it's causing severe pain or bleeding. If you have warning signs such as sudden severe pain, bleeding, fever, dizziness or decreased fetal movement, you should be checked immediately.
Is subserosal fibroid dangerous in pregnancy?
Subserosal fibroid in pregnancy Because it grows outward, it has less direct effect on the uterine cavity and implantation in many people. However, if it is large, it can cause pain and pressure or affect the condition of the fetus and the decision to give birth.
risks of pregnancy with large fibroids
Large fibroids can cause the fetus to develop improperly or to be in an abnormal position (such as breech position), which often leads to a cesarean section. Also, the risk of premature separation of the placenta is higher in these cases, which is considered a medical emergency. In some cases, these masses challenge the blood supply to the fetus and cause severe abdominal pain for the mother.
Fibroid bleeding in pregnancy
Fibroid degeneration is more often associated with acute abdominal pain. Any bleeding in pregnancy should be investigated for more common causes such as placental problems or threatened miscarriage. Management of this condition usually includes rest, staying hydrated, and pain management under the supervision of a specialist.
Does uterine fibroids cause premature birth?
Uterine fibroids, especially large or multiple types, can increase the risk of premature delivery by occupying the uterine space and causing muscle irritation. Also, if the fibroid restricts the growth space of the fetus, the possibility of premature rupture of the water sac increases. However, many women successfully complete their pregnancy despite having fibroids.
prevention of fibroids and pregnancy
Currently, there is no definitive method to prevent fibroid and pregnancy because its exact cause is not completely known. However, a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of some underlying factors and help control symptoms. If you are planning to become pregnant and have a family history of heavy bleeding or pelvic pain, it is best to be evaluated before the procedure so that treatment or monitoring can be decided if fibroids are present.
Weight management, regular physical activity and follow-up treatment of anemia in case of severe bleeding are practical and safe steps. It is important that medicinal or herbal self-treatment is not done during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Fibroids in pregnancy In many cases, only follow-up is required, and ignoring the warning signs can be dangerous. If you have fibroids, you can safely continue most pregnancies with ultrasound and following the doctor's recommendations. It is important to know that mild and occasional pain usually gets better with rest, but sudden severe pain, vaginal bleeding, fever, dizziness, decreased fetal movement, or regular contractions should be investigated quickly. Get help from a gynecologist to choose the right delivery route and postpartum care.
Your doctor takes care of your health!