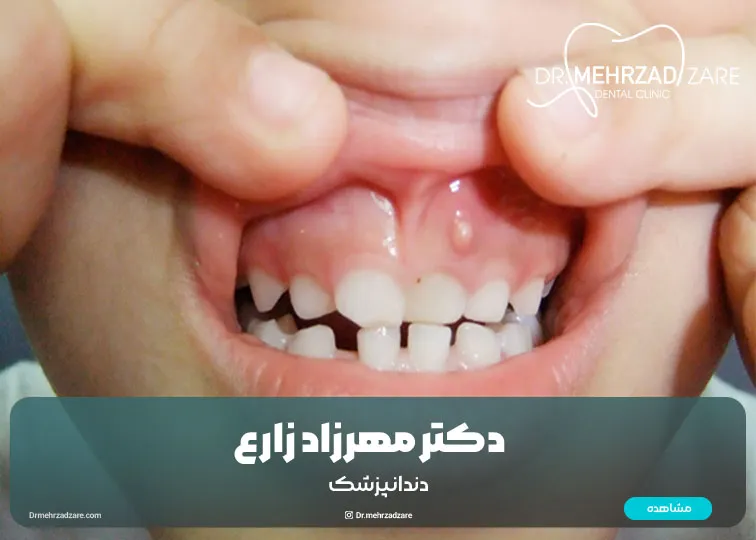
Gum cyst in children is one of the most common oral and dental problems in infancy and early childhood. Many parents are worried when they see a small or white bump on their child's gums and think that this is a serious problem; But in most cases, these cysts are benign, temporary and painless. However, accurate recognition of gum cysts in children helps parents to make the right decision and visit the dentist at the right time. From definitions and symptoms to treatment methods, prevention and misconceptions that confuse parents.
Definition of gum cyst in children
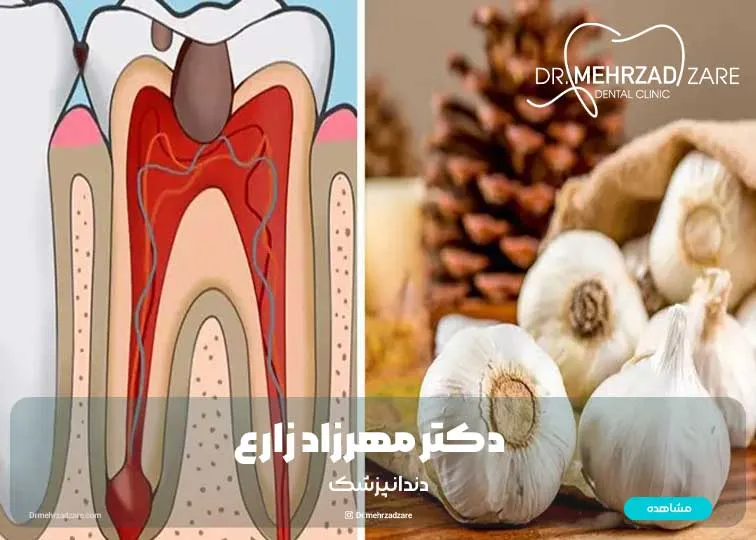
A gum cyst in children is a small cavity filled with liquid that develops on the gum or sometimes in the area of tooth growth. These cysts are usually:
-
They are small in size
-
They are white or yellowish
-
They don't cause much pain
-
They often disappear by themselves
The two most common types of gum cysts include Epstein pearls and Bohn's nodules. Both types are completely safe and are usually absorbed within a few weeks or months.
Some children also experience Eruption Cyst during the eruption of milk teeth, which is a blue or purple bump on the gums, and in most cases it resolves without special intervention.
The causes of gum cysts in children
Next, we explain the most important causes of gum cysts in children:
1. Remaining tissue remnants during tooth formation
When the teeth grow, part of tissue cells remain in the gum. These cells gather and form a small cyst.
2. Eruption of milk teeth
Sometimes a growth cyst is formed when the tooth pushes to leave the gum. This cyst usually disappears when the tooth comes out.
3. Impact or irritation of the gums
Chewing on hard objects, falling or hitting the mouth sometimes causes small cysts in the gums.
4. Genetic reasons
In some children, a family pattern can be seen, and the probability of gum cysts is higher.
5. Accumulation of keratin cells
In Epstein's cysts, the accumulation of keratin on the gum surface causes white dots.
Gum cyst symptoms in children
Symptoms of this problem are usually mild and include:
-
One or more white, yellow or blue bumps on the gums
-
Being painless or causing very little pain
-
No inflammation or bleeding
-
Mild difficulty sucking or eating (very rare)
-
Appearance in infants or teething children
If a child has severe pain or a fever, there is usually another cause and needs to be investigated.
Gum cyst prevention methods in children
Although many cysts form spontaneously and cannot be prevented, following a few tips will reduce the chance of gum problems:
1. Observance of oral hygiene from infancy
-
Cleaning the gums with sterile gauze
-
Using a soft toothbrush after the eruption of the first tooth
-
preventing the accumulation of milk or food in the mouth

2. Preventing trauma to the gums
Do not allow the child to chew hard objects or put small toys in the mouth.
3. Strengthening the child's immune system
A healthy diet, vitamins and enough sleep help oral health.
4. Knowing the condition of the child's mouth allows early detection of possible problems.
Gum cyst treatment in children
In many cases, gum cysts in children do not require complex treatment; But some conditions make a more detailed investigation necessary.
1. Home remedies and care
-
Keeping the mouth clean
-
very gentle gum massage
-
Avoid squeezing or bursting the cyst
-
Using a soft pacifier
These measures help reduce inflammation and prevent infection.
2. Professional treatment by a dentist
If the cyst causes pain, swelling or difficulty feeding the child, the dentist uses safe and quick methods:
a) Vegetative cyst drainage
In this method, the dentist uses a delicate tool to open the surface of the cyst so that the liquid inside is removed.
b) conservative treatments
In most children, the doctor only checks the growth process of the tooth and gives time for the cyst to absorb itself.
c) Check for infection
If the cyst is accompanied by redness or fever, the doctor will prescribe the appropriate medicine.
3. Alternative and complementary treatments
These methods are usually used as an aid and not a substitute for specialized treatment:
a) mild cold compress
help to reduce swelling and restlessness of the child.
b) Massage with teething gel
Note: these gels should be suitable for the child's age.
c) Using soft teething toys
Silicone tools cause gentle irritation of the gums and reduce pain.
suitable exercises to reduce gum discomfort
Although the child cannot perform complex exercises, some simple exercises will help reduce gum pressure:
1. Circular gum massage
Parents gently massage the gums with a clean finger.
2. Gentle pressure with a soft toy
This will improve blood circulation in the gums.
3. Cold pacifier sucking practice
Cooled pacifier soothes the gums.
When should you see a doctor?
If any of the following are seen, immediate referral is required:
-
Bleeding or infection
-
fever or extreme restlessness
-
whose durability is more than a few months
-
What is abnormal growth or rapid growth
-
Difficulty eating or sucking
Conclusion
Gingival cyst in children is usually a benign and controllable problem. Knowing the symptoms, causes and prevention methods gives parents peace of mind. In most cases, the treatment is simple and painless, and the child returns to normal after a short period of time. In compliance with health Mouth and regular visits to the dentist can prevent most oral and dental problems in children.
Ten frequently asked questions about gum cysts in children
1. Is a gum cyst dangerous?
Usually no and in most children it resolves by itself.
2. Does a gum cyst hurt?
In most cases, it is painless.
3. How long does the cyst stay on the gum?
From a few weeks to a few months.
4. Is it necessary to open the cyst?
No, there is a risk of infection.
5. Does a cyst affect the growth of teeth?
No, most cysts go away after the teeth erupt.
6. Is home treatment enough?
In mild cases, yes, but severe symptoms require a doctor.
7. Are gum cysts mistaken for cancer?
No, these cysts are completely benign.
8. Does trauma to the gums cause cysts?
In some children, yes.
9. What is the best way to reduce pain?
gentle massage and use of soft dental appliances.
10. Are babies more likely to develop gum cysts?
Yes, because of rapid tissue growth.
Ten misconceptions about gum cysts in children
1. "Gum cyst is always dangerous."
2. "These cysts must be operated."
3. "Cyst is a sign of serious diseases."
4. "Cyst causes tooth growth to stop."
5. "Pressing the cyst helps the treatment."
6. "Anesthetic gels are suitable for all babies."
7. "Teething toys are dangerous."
8. "Gum cyst is only seen in babies."
9. "Every bump on the gum is a cyst."
10. "Home remedies are always enough."
Keeping the mouth clean
very gentle gum massage
Avoid squeezing or bursting the cyst
Using a soft pacifier
Bleeding or infection
fever or extreme restlessness
whose durability is more than a few months
What is abnormal growth or rapid growth
Difficulty eating or sucking
Usually no and in most children it resolves by itself.
In most cases, it is painless.
From a few weeks to a few months.
No, there is a risk of infection.
No, most cysts go away after the teeth erupt.
In mild cases, yes, but severe symptoms require a doctor.
No, these cysts are completely benign.
In some children, yes.
gentle massage and use of soft dental appliances.
Yes, because of rapid tissue growth.
2. "These cysts must be operated."
3. "Cyst is a sign of serious diseases."
4. "Cyst causes tooth growth to stop."
5. "Pressing the cyst helps the treatment."
6. "Anesthetic gels are suitable for all babies."
7. "Teething toys are dangerous."
8. "Gum cyst is only seen in babies."
9. "Every bump on the gum is a cyst."
10. "Home remedies are always enough."