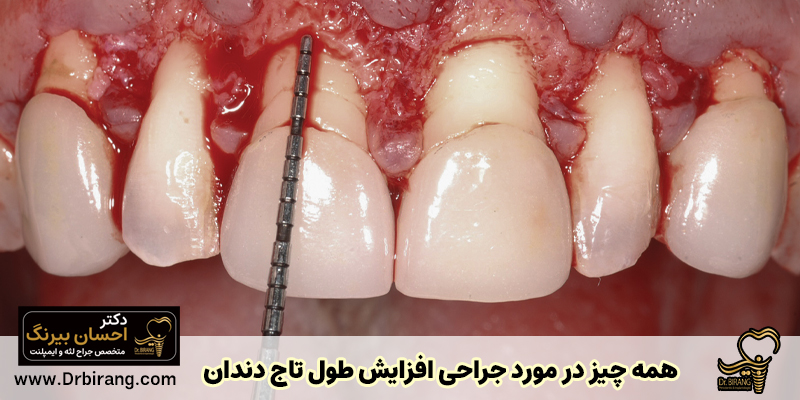
One of the common concerns among dental clients is to see an abnormal lump or lump on the gums. This bump, which is commonly called gum extra meat, may appear in different situations such as after surgery, tooth extraction, or even without any specific reason. If you have faced such a situation, you must have many questions in your mind; What is the cause of this condition, is it dangerous and how should it be treated? In this article from the website of Dr. Ehsan Birang, the best gum surgeon in Tehran, we answer all these questions.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is extra gum tissue and why is it created?
- 2 The main causes of creation Excess gum tissue
- 3 Review of special conditions: excess gum tissue in different situations
- 4 Is excess gum dangerous and why should it be treated?
- 5 Treatment of excess gum
- 6 Home remedies for extra gum tissue
- 7 Specialized treatments and surgery for extra gum tissue
What is extra gum tissue and why is it created?
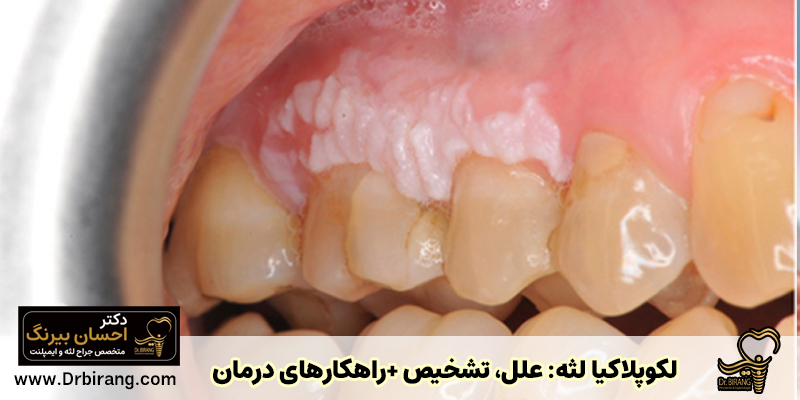
In general, gum extra meat or gum hyperplasia is called excessive and abnormal growth of gum tissue. This complication is an unusual bump or lump that can appear anywhere in the mouth. This situation is different from extra gum (Gummy Smile); Extra gingiva is a natural condition in which a large part of the gum is visible when smiling and is usually not related to inflammation or disease. This distinction is very important and will help you diagnose the problem correctly.
The main causes of excess gum tissue
This complication can be caused by various reasons, the most important of which are:
- Chronic inflammation: The most common cause is long-term inflammation due to the accumulation of dental plaque and tartar. If oral hygiene is not followed properly, bacteria accumulate in the gum line and cause inflammation and swelling, which can eventually lead to bumps on the gums.
- Hormonal factors: Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy or menopause can make the gums more sensitive and provide the basis for their excessive growth. For this reason, some women face this problem during pregnancy.
- Use of certain drugs: Drugs such as phenytoin (for the treatment of seizures), cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant drug) and some calcium channel blockers (for blood pressure) can cause gum tissue growth as a side effect.
- Trauma or impact: Physical damage to the gums, such as scratching or brushing incorrectly, can irritate the tissue and cause extragingival flesh.
- Genetic factors: In some rare cases, hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a genetic disease that causes the gums to become excessively enlarged, usually occurring in childhood.
- Systemic diseases: Some diseases such as leukemia (blood cancer) or diabetes can also cause gum hyperplasia.
Examination of special conditions: excess gingival flesh in different situations
In many cases, excess gum tissue is associated with certain conditions that we will discuss below:
Extra gum tissue after tooth extraction
Observation of extra gum tissue after tooth extraction is also caused by natural tissue repair in the empty tooth cavity. The body tries to create new tissue to fill the place of the extracted tooth, and this process is sometimes accompanied by excessive growth of granulation tissue.
Gingival extra meat in orthodontics
Fixed orthodontic treatments can cause plaque and bacteria to build up around brackets and wires. This accumulation of plaque and improper dental hygiene can lead to inflammation and eventually overgrowth of gum tissue.
Extra gum tissue in children
In addition to inflammatory factors, the use of certain drugs (such as phenytoin) or hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) can be the main causes of excess gingival flesh in children.
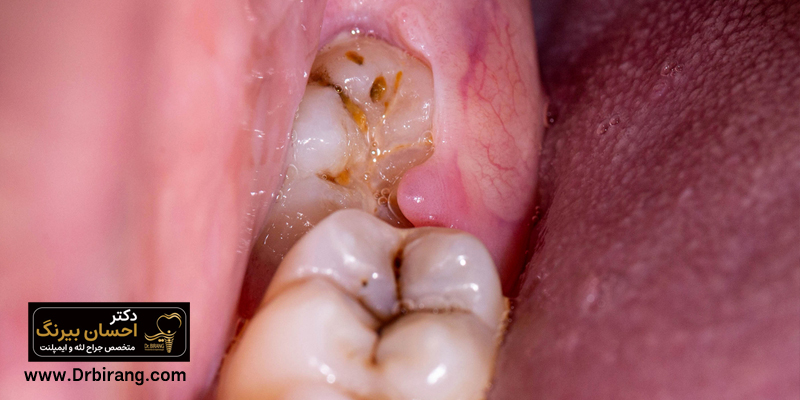
Excess gum tissue around wisdom teeth and broken teeth
The location of the wisdom tooth at the end of the mouth makes it difficult to clean, and this causes the accumulation of plaque and inflammation. Also, a broken tooth can damage the gums with its sharp edges and cause the growth of extra tissue for repair. In these cases, treating the damaged tooth (pulling or repairing) is the first step.
Excess gingival tissue caused by artificial teeth (opolism fissuretum)
This condition is common in people who use dentures and is caused by the constant irritation of the gums by dentures that are loose or ill-fitting. Although these masses are usually benign, they can cause discomfort and health problems.
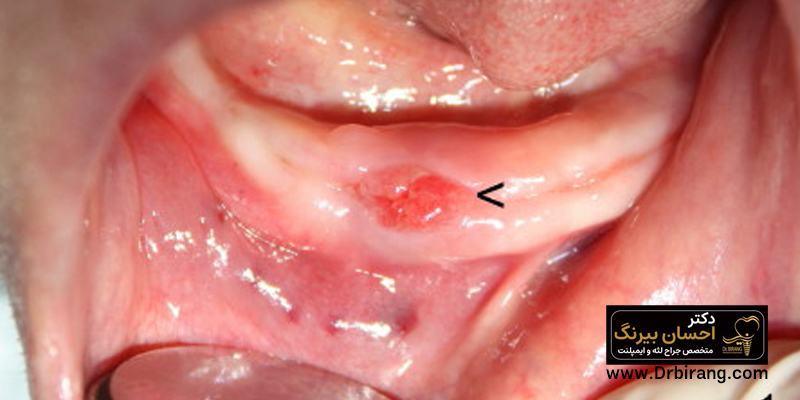
Learn more: Gum Ulcers from Dentures: The Complete Guide to Causes, Treatment and Prevention
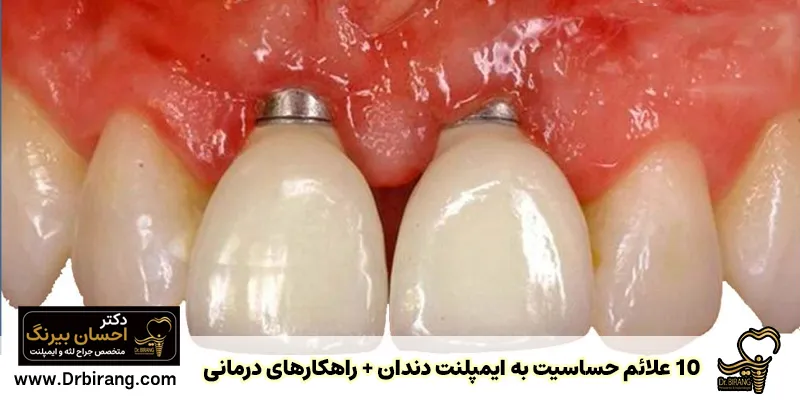
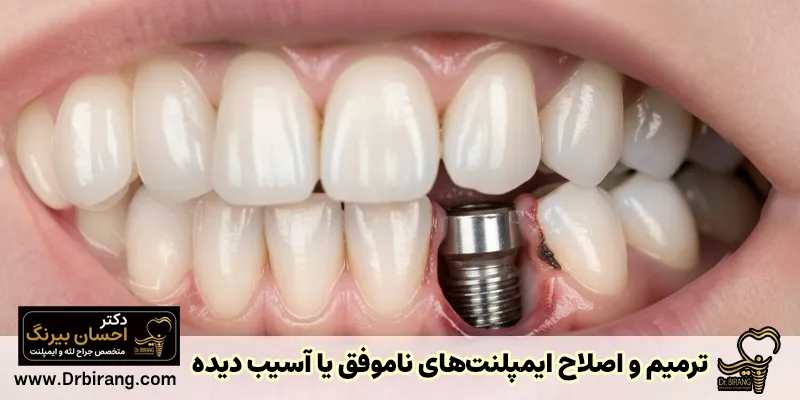
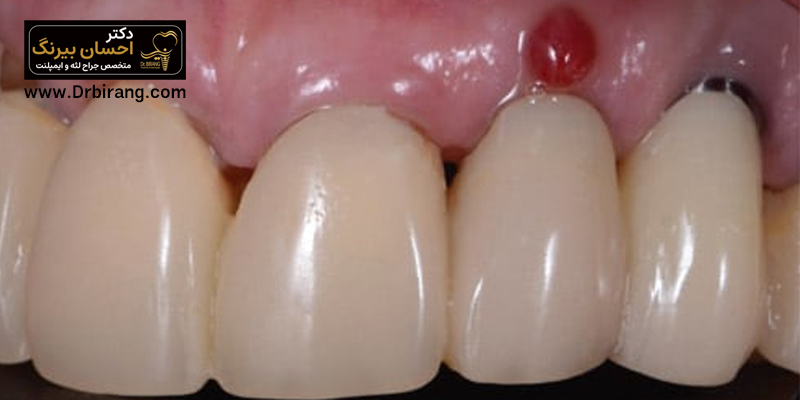
Extra gum tissue after implant
Observation of extra gum tissue after implant can be caused by the body's reaction to a foreign object or an infection. If the dental prosthesis is not placed correctly on the implant or oral hygiene is not followed well after surgery, plaque and bacteria accumulate and cause inflammation and growth of extra tissue around the implant. This condition, which is called peri-implantitis, is very serious and must be checked by a dentist.
Is excess gum dangerous and why should it be treated?
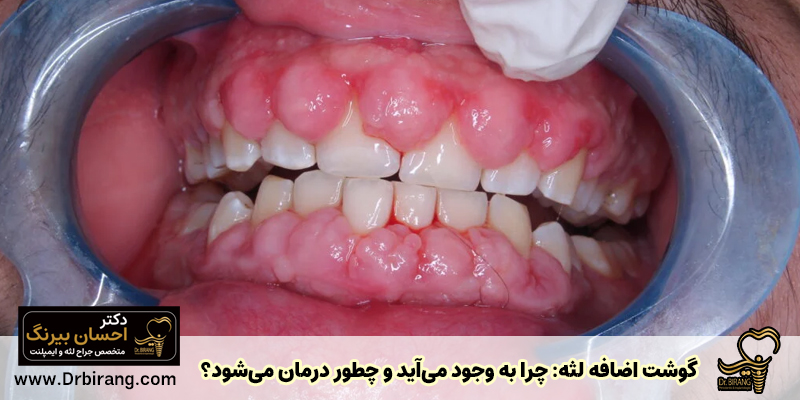
Although in many cases, extra gum tissue is a benign complication, it cannot be ignored. These bumps can cause the following problems:
- Accumulation of plaque and bacteria: The growth of gum tissue makes it more difficult to care for the teeth and leads to the accumulation of plaque and bacteria around the teeth, which itself can cause inflammation and bad breath.
- Disturbance in chewing and speaking: In severe cases, extra gum tissue may cover the surface of the teeth and make it difficult to chew or speak.
- Appearance beauty: These ridges can affect the appearance of the smile.
Treatment of extra gum tissue
The treatment of this complication depends on its main cause. If the cause is inflammation and poor oral hygiene, the first step is professional teeth cleaning and proper hygiene education. By removing the plaque and mass, the inflammation subsides and in many cases, the gum tissue returns to its normal state.
If the cause is the use of medication, the dentist, in consultation with the general practitioner, may suggest changing the dosage of the medication or prescribing an alternative medication.
In most cases, extra gum tissue is a benign, non-cancerous condition. However, it should be examined by a dentist to determine its root cause. If this complication is due to infection or inflammation, not treating it can lead to more serious problems such as tooth loss.
No, you should never try to forcefully remove this bump with dental floss or a toothbrush. This can cause damage to the gum tissue, bleeding and even infection. The best way is to observe oral and dental hygiene and see a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment.


 Learn more:
Learn more: