Table of contents
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the most common complications of diabetes that gradually damages the kidneys. This disease usually occurs in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients and can lead to kidney failure. Knowing the symptoms, stages of development and its treatment methods is vital to control the disease. Medical care and lifestyle changes play an important role in reducing complications. This article from Dr. Tu examines the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Being aware of this issue can help prevent serious injuries.
What is diabetic nephropathy?
Diabetic nephropathy is a chronic kidney disease and one of the complications of diabetes, which is caused by damage to the small blood vessels of the kidney in diabetic patients. This damage reduces the kidney's ability to purify blood and remove waste materials. Diabetic nephropathy progresses gradually and in advanced stages can lead to kidney failure.
Its most common symptoms include protein in the urine and increased blood pressure. Early detection can slow down the disease process. This disease is one of the most important causes of dialysis in diabetic patients.English text:
quoted from mayoclinic
Over time, diabetes that isn't well controlled can damage blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste from the blood. This can lead to kidney damage and cause high blood pressure.
Persian translation:
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood. This can lead to kidney damage and increase blood pressure.

Steps of diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is generally divided into five stages, each stage indicating the severity of kidney damage. In the first stage, microscopic changes occur in the kidney and usually have no symptoms. The second stage is associated with a slight increase in protein excretion in the urine. In the third stage, clear proteinuria and a relative decrease in kidney function are observed, and blood pressure may increase.The fourth stage includes a severe decrease in kidney function and obvious symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, and widespread swelling. The fifth or final stage leads to complete kidney failure and requires dialysis or a kidney transplant. Knowing these steps is very important for early diagnosis and proper management of the disease.
symptoms of diabetic nephropathy
Symptoms of the complication in the early stages are often silent and may only be determined by a urine test. As the disease progresses, swelling occurs in the legs, wrists, and hands, which is caused by fluid accumulation. High blood pressure is also one of the common symptoms of kidney damage and can aggravate the condition of the disease. Excessive fatigue and daily energy loss are other symptoms associated with kidney function decline.
Change in color, unpleasant odor or increased volume of urine may indicate further kidney damage. In advanced stages, nausea, loss of appetite and sleep problems can be serious signs of diabetic nephropathy.
cause of diabetic nephropathy
The main cause of diabetic nephropathy is long-term high blood sugar, which gradually damages the small blood vessels of the kidney. This damage reduces the kidney's ability to filter blood and remove waste materials. High blood pressure also aggravates the process of damage to the kidneys and can lead to swelling and increased protein in the urine.
Genetic factors and family history play an important role in the possibility of developing nephropathy, and some people with a family history of diabetes are more at risk. Obesity, unhealthy lifestyle and smoking can increase the severity of the disease. Chronic inflammation from diabetes also contributes to gradual kidney damage. In general, a combination of high blood sugar, blood pressure, genetics and environmental factors causes diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy diagnosis methods
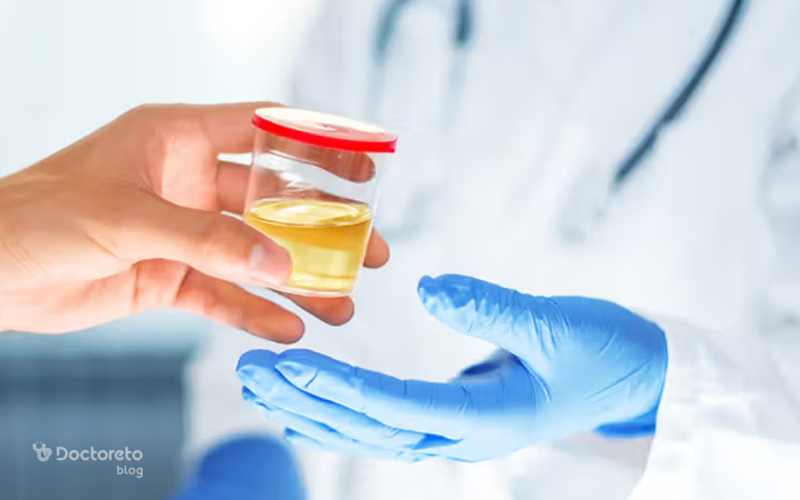
Diabetic nephropathy is usually diagnosed by urine test interpretation and checking the excretion of protein in urine. Blood tests to measure creatinine and glomerular filtration rate are also necessary. Renal ultrasound can show the structural changes of the kidney. Examining the patient's blood pressure and history of diabetes is an important part of the diagnosis. Early diagnosis allows timely treatment and prevention of disease progression. The doctor may prescribe additional tests based on the patient's condition.
diabetic nephropathy treatment
Diabetic nephropathy treatment focuses on slowing the progression of the disease and protecting kidney function. Accurate control of blood sugar and blood pressure is the first and most important step of treatment to reduce the damage to the small blood vessels of the kidney. A proper diet, including limiting excess salt and protein, helps reduce stress on the kidneys. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight also play an effective role in improving kidney function.
The use of special drugs to reduce proteinuria and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors is recommended by the doctor. Treatment should be done regularly and under the supervision of a doctor to prevent the progression of the disease. In addition to medicine, home measures such as sugar control, exercise and healthy diet complement medical treatment.
| Method of treatment | Description and goal of treatment |
|---|---|
| Precise control of blood sugar | Reducing continuous damage to kidney glomeruli and slowing down the progression of the disease |
| Controlling blood pressure | Reducing intraocular pressure Kidney and reducing proteinuria |
| ACE inhibitors | Urine protein reduction and kidney function protection |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) | ACE replacement in case of intolerance |
| Diet adjustment | Salt reduction, protein regulation and control Calories |
| Reduce salt intake | Help control blood pressure and swelling |
| Regulate protein intake | Reduce kidney metabolic load |
| Regular physical activity | Improve sugar, blood pressure and weight control |
| Stop Smoking | reducing the progression of kidney damage and heart risk |
| diuretic drugs | control of edema and fluid accumulation |
| blood lipid-lowering drugs | reducing cardiovascular risk |
| regular monitoring tests | creatinine, GFR and Urine albumin |
| Dialysis | Replacement of renal function in advanced failure |
| Kidney transplant | Final treatment in end-stage renal failure |
1. Drug for diabetic nephropathy
Common medications for diabetic nephropathy include ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers. These drugs lower blood pressure and slow kidney damage. Diuretics are also prescribed to control edema and excess fluid. If needed, drugs to lower cholesterol and control blood sugar are also taken. The doctor determines the dosage and drug combination suitable for each patient. Taking medicine regularly and adhering to medical orders is vital to maintain kidney function.2. Home treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Adhering to a healthy diet, reducing the consumption of salt and sugar, and increasing the consumption of suitable vegetables and fruits are home treatment methods. Regular physical activity helps improve blood circulation and control blood pressure. Avoiding smoking and alcohol is necessary to reduce the pressure on the kidney.
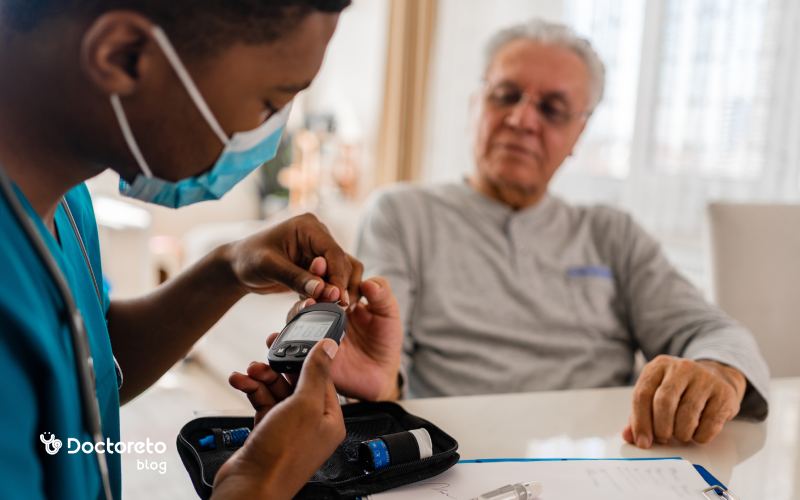
Regular blood sugar control at home with a glucometer is an important part of disease management. These home remedies are complementary to medical treatment and should not replace medicine.
English text:
You may need to avoid certain foods or have a limit on the amount of fluid you have – including water – but you'll need support from a dietitian to help you with the changes to your diet.
Persian translation:
You may need to avoid certain foods or limit the amount of fluids you drink, including water, but you will need the help of a nutritionist to make these dietary changes. noopener">diabetes
preventing the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Prevention of the progression of diabetic nephropathy requires careful control of blood sugar and blood pressure to minimize damage to the kidneys. Adhering to a healthy diet, including salt reduction and adequate protein consumption, plays an important role in reducing pressure on the kidneys. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight help improve blood circulation and kidney function. Quitting smoking and avoiding alcohol consumption are also effective factors in preventing kidney damage.
Regular follow-up of kidney condition with periodical tests allows early detection of problems. Patient education and increased awareness about the early symptoms of diabetic nephropathy can ensure the prevention of severe complications. Overall, a combination of a healthy lifestyle, disease control and medical follow-up is the best way to prevent the progression of nephropathy.
complications of diabetic nephropathy
In advanced stages, diabetic nephropathy can lead to complete kidney failure and the need for dialysis or transplantation. High blood pressure, extensive edema and nephrotic syndrome are other common complications. The risk of cardiovascular diseases is also higher in these patients. Accumulation of toxins in the body causes fatigue, nausea and loss of appetite. Decreased kidney function may disturb the balance of electrolytes and calcium. Disease control and regular medical follow-up are necessary to prevent these complications.
Conclusion
Diabetic nephropathy is one of the serious complications of diabetes that can gradually reduce kidney function. Early diagnosis and proper management, including medication, healthy lifestyle and medical follow-up, play an important role in reducing disease progression. Proper diet, exercise and control of blood pressure and sugar are an important part of prevention and treatment. Patient education and awareness also lead to better decision-making in kidney care. By following medical tips and home care, serious complications can be minimized.
Your doctor takes care of your health!