تیروئید، این غده کوچک پروانهای شکل در جلوی گردن، حکم نیروگاه سوختوساز بدن شما را دارد. When this power plant experiences a drop in activity, it is as if all body systems move in heavy gear. Hypothyroidism, or hypothyroidism, is a condition in which your body does not produce enough thyroid hormone. This article is not only a diagnostic guide, but also a road map to return to an energetic life.
Starting Mechanism: Why Thyroid Fails?
The process of hypothyroidism is usually not a sudden event, but a gradual path. In most cases, the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the cells of the thyroid gland (Hashimoto's disease). In other cases, iodine deficiency, previous surgeries or even severe environmental stress can disrupt the secretion of the vital hormones T_3 and T_4.
When the level of these hormones in the blood decreases, the pituitary gland in the brain tries to make the thyroid work more by overproducing the hormone TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone). This is exactly where the blood test is used to diagnose the disease.
Recognizing the symptoms: When the body signals
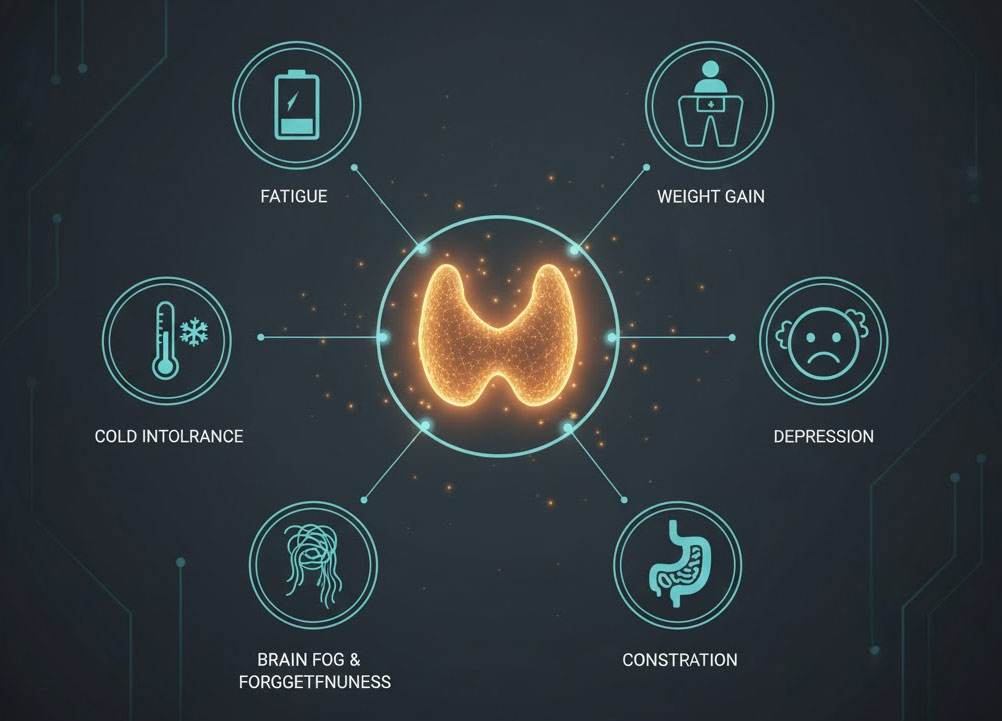
Thyroid Symptoms They are often overlooked due to their resemblance to everyday fatigue. But when you experience several of the following at the same time, your body is sending a warning message:
- Extreme and chronic fatigue: Even after 8 hours of sleep, you still feel groggy.
- Unexplained weight gain: You gain weight despite a consistent diet.
- Cold intolerance: You feel shivery when others are comfortable at room temperature.
- Skin changes and Hair: severe dryness of the skin, hair loss and thinning of the ends of the eyebrows.
- Mood and cognitive problems: brain fog (lack of concentration), forgetfulness and mild to moderate depression.
- Digestive disorders: chronic constipation due to reduced bowel movements.
Comparative-Table-of-Thyroid-Conditions
Here is a table designed to better understand the difference between normal, mild hypothyroidism, and severe hypothyroidism. Do:
| Check index | Normal status | Subclinical deficiency | Overt deficiency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH level | 0.4 to 4.0 mIU/L | High (usually 4 to 10) | Very high (above 10) | style="padding: 10px; font-weight: bold;">Free T4 level | Normal | Normal | Below normal |
| Severity Symptoms | No symptoms | Mild and transient | Severe and affecting life | ||||
| Need treatment | No | Depending on the doctor's opinion and age | Immediate treatment with medicine |
Specialized diagnosis path of hypothyroidism
If you suspect this disease, diagnosis is not possible with a physical examination alone. The endocrinologist uses the following chain for confirmation:
Blood test (thyroid panel): check the levels of TSH, Free T_4 and sometimes T_3.
Antibody test (Anti-TPO): To determine whether the disease has an autoimmune origin (Hashimoto) or not. Thyroid ultrasound: if a nodule or swelling (goiter) is observed during manual examination.
new treatment and style protocols Life
The gold standard treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement. Levothyroxine is the main drug that provides exactly the same hormone that your body does not make.
Critical points in taking the drug:
Golden time: The drug should be taken on an empty stomach, at least 30 to 60 minutes before breakfast.
Interactions: Avoid taking thyroid pills at the same time as calcium or iron supplements (at least 4 hours apart).
Brand consistency: Try to always use a specific drug brand. Do it, because changing the brand can disturb the balance of TSH. Complementary diet: although medication is necessary, but lifestyle will double the speed of recovery.
Selenium: daily consumption of two Brazil nuts (Brazil Nuts) can help convert T_4 into active T_3.
Avoid goitrogens: high consumption of raw cabbage, broccoli and soy may interfere with iodine absorption (cooking). These substances solve the problem).
Ignoring the effects of hypothyroidism
Not treating hypothyroidism doesn't just mean fatigue, this condition can lead to more serious problems.
Heart problems - increased bad cholesterol (LDL) and risk of heart failure - infertility - ovulation disorders and problems Menstruation in women.
Myxedema: An Emergency And rare, in which body functions are severely slowed down and there is a risk of coma.
More detailed analysis of symptoms, differentiation between men and women
Although many symptoms of hypothyroidism are common between both sexes, due to hormonal and physiological differences, this disease has different manifestations in some areas.
hypothyroidism in women (affecting the reproductive system):
Menstrual disorders: the most common symptom in women is a change in the regularity or intensity of menstruation. Usually, the bleeding becomes heavier (Menorrhagia) or irregular.
Fertility challenges: Hypothyroidism can make pregnancy difficult by inhibiting ovulation. Also, the risk of miscarriage in the first trimester increases if treatment is not done.
Severe premenstrual syndrome (PMS): Mood swings and physical pains before the monthly period are much more severe in affected women. Muscular):
Decreased testosterone: hypothyroidism can lead to a decrease in the level of free testosterone, which results in a decrease in sexual desire (Libido).
Erectile dysfunction: Due to the direct effect of thyroid hormones on the health of blood vessels and nerves, men may experience erectile dysfunction.
Decreased muscle mass: Men may notice that despite exercise, their muscle strength is weakened and they experience severe muscle cramps.
Sperm count: This disorder can negatively affect the quality and number of sperms and reduce male fertility.
Hidden Link Between Thyroid and Cell Metabolism Hypothyroidism
Beyond a simplistic view of "slow metabolism" is This situation is actually an energy crisis at the cellular level. Thyroid hormones are responsible for regulating the rate of oxygen consumption in all body cells. When these hormones are depleted, mitochondria (the powerhouses of cells) cannot function at high efficiency. This issue leads to the accumulation of metabolic waste materials in the tissues, which manifests itself in the form of swelling (myxedema), joint pain, and a decrease in the body's basal temperature. In fact, the body goes into "Safe Mode" to conserve vital energy only for the main organs, which causes the gradual failure of secondary functions such as hair growth and skin regeneration. It has a profound effect on the central nervous system and neurotransmitters. A decrease in thyroid hormones directly affects the reuptake of serotonin and dopamine in the brain, so many patients are initially diagnosed with depression or anxiety disorder, when the root of the problem is in their neck gland. The "brain fog" caused by this disease is not just a simple forgetfulness, but a decrease in the speed of information processing in the brain. These neurological interactions show that treating hypothyroidism is not only a physical necessity for weight loss or hair loss, but also a vital measure to maintain mental health and prevent premature dementia in old age.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hypothyroidism
- Can hypothyroidism be treated with diet alone?
no If the thyroid gland has lost the ability to produce hormones, no food can replace the vital hormones. Diet only has a supportive role and improves the quality of life. - Does hair loss stop after starting the treatment?
Yes, but you have to be patient. The hair growth cycle is long and usually 3 to 6 months after the hormone levels in the blood are regulated, hair loss will decrease and regrowth will begin. - Is hypothyroidism dangerous during pregnancy?
Yes, thyroid hormone is vital for fetal brain development. Pregnant women with this disease must be closely monitored and their drug dosage is usually increased during pregnancy. - Why do I still feel tired even though the test is normal?
This may be due to suboptimal hormone levels (even within the normal laboratory range) or lack of vitamins such as D and B_{12}, which are often associated with thyroid diseases. - Should I take medication for the rest of my life?
In most cases (especially Hashimoto's), yes. But this drug is just a substitute for a natural substance in your body, and if the correct dose is adjusted, it will not have any side effects.
Reliable scientific resources for more study of hypothyroidism
- American Thyroid Association (ATA)
- Mayo Clinic – Hypothyroidism Diagnosis & Treatment
- The Lancet – Thyroid Health Journal