Types of therapeutic exercise
Therapeutic exercise (or therapeutic exercise) is a set of targeted physical activities that are planned according to the individual's conditions in order to improve physical performance and also play a therapeutic and rehabilitation role.
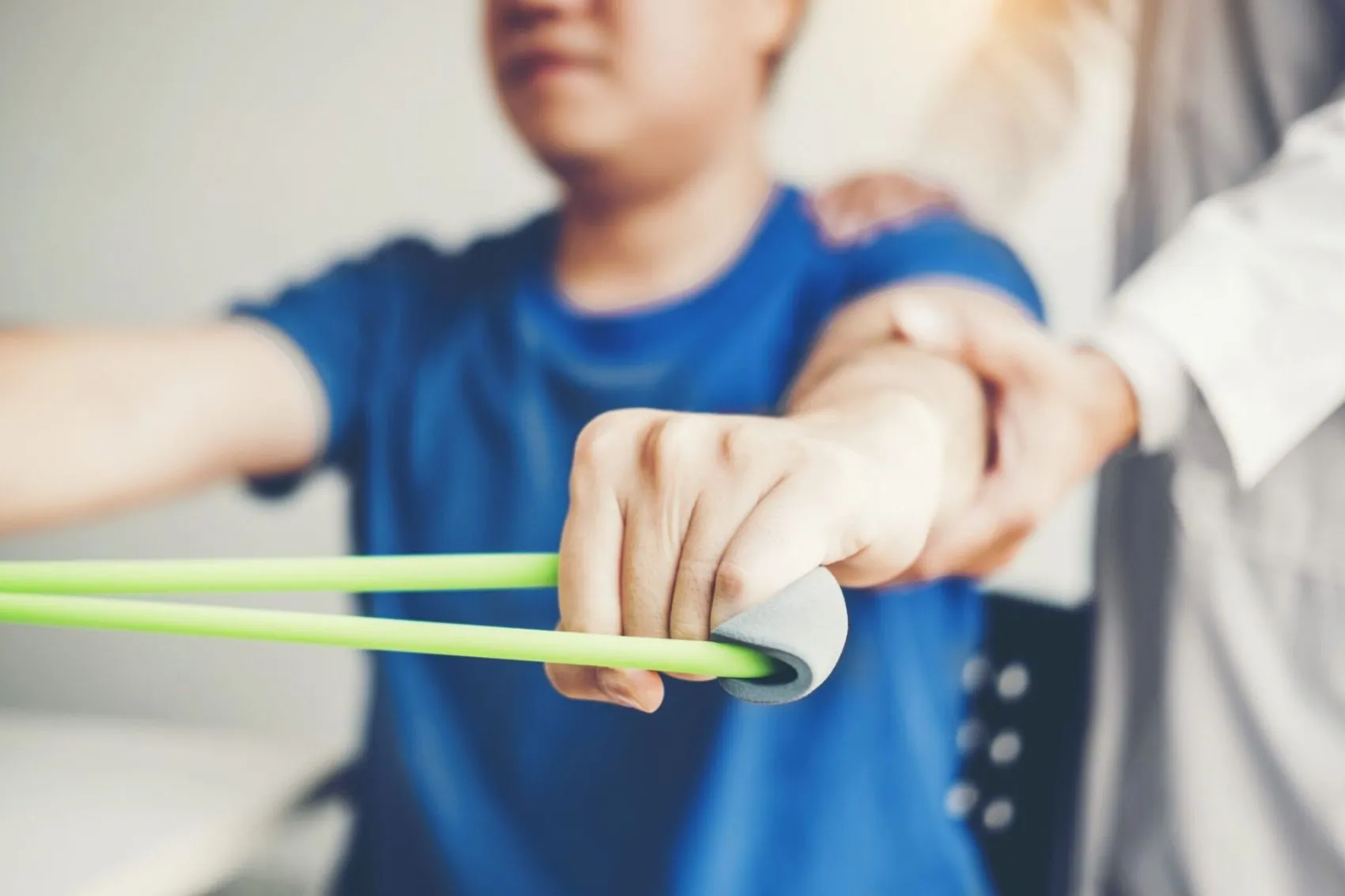
Exercise therapy for Musculoskeletal Injuries
Strengthening exercises, flexibility and controlled movements are the most common methods to reduce pain, increase muscle strength, improve joint range of motion and repair injuries in the musculoskeletal system (source).
For example, water therapy exercises (aquagymnastics) are a suitable option for people with arthritis or joint weakness, due to the reduction of pressure on the joints
Exercise therapy for cardiovascular diseases
Exercise therapy for cardiovascular patients using aerobic, resistance or combined exercises can improve cardiovascular function, increase lung capacity and endurance, and improve the quality of life in people with heart disease.
New studies have shown that combining resistance and aerobic exercise is more effective in managing heart disease (source).
Exercise therapy in respiratory problems
In respiratory or lung disorders (such as chronic lung problems), breathing exercises, hydrotherapy or light aerobic exercises can help improve lung function, strengthen respiratory muscles and increase breathing capacity, and thus improve the patient's quality of life (source).
Exercise therapy for chronic diseases and Metabolic
For diseases such as diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome or other chronic disorders, exercise therapy is known as an effective therapeutic intervention. Regular exercise can improve blood sugar control, blood lipids, and disease symptoms, and reduce the risk of side effects (sourcesource).
Exercise therapy for children and teenagers
At growing ages, exercise therapy can help prevent and treat musculoskeletal problems, improve mobility, strengthen muscles and promote general health; Especially if the child has frequent pain or movement disorders.
Studies have shown that regular exercise therapy in children and adolescents can reduce pain and musculoskeletal problems (source).
Types of exercises in sports therapy
Sports therapy exercises include a set of targeted activities that are designed according to the individual's needs and health status. These exercises can improve the strength, flexibility, balance, endurance and general performance of the body and play an effective role in the prevention and treatment of diseases.
Resistance exercises
These exercises are performed using weights, bands or body weight, and their main purpose is to strengthen muscles and increase strength. Resistance exercises help to improve daily performance, prevent muscle wasting and reduce pain in musculoskeletal problems.
Balance and coordination exercises
Balance exercises focus on improving body control, motor coordination and preventing falls. These exercises are especially necessary for the elderly or people with muscle weakness or neurological problems.
Stretching and flexibility exercises
Stretching exercises help increase joint flexibility and muscle length, and can reduce chronic pain, muscle cramps, and movement restrictions. Doing these exercises regularly improves the body's range of motion.
Aerobic and Endurance Exercises
These exercises include running, walking, cycling and swimming and help strengthen the heart and lungs, increase endurance and reduce body fat. Aerobic sports play an important role in the prevention and management of chronic diseases.
Exercises for special groups
These exercises are designed for children, the elderly, or people with special medical conditions and include specific programs to improve performance, prevent injury, and rehabilitate. Special exercises can include gentle activities, corrective movements or game-based exercises for children.
How does exercise therapy work?
Exercise therapy by stimulating the body's biological and physiological systems causes the body to regenerate, strengthen and adapt; Therefore, when a person regularly undergoes a therapeutic exercise program, improvements in physical function, tissue repair, and reduction in inflammation occur.
For example, studies have shown that regular exercise can accelerate tissue repair through the activation of stem cells and molecular signaling pathways (source).
In addition, exercise has a significant effect They affect the health of the heart and blood vessels: adjusting the balance of the automatic nervous system reduces the resting heart rate and blood pressure; Likewise, by strengthening the function of the endothelium and improving the flexibility of the vessels, blood circulation and oxygen delivery to the tissues will be optimized (source).
On the other hand, regular exercise causes the release of myokines, which have anti-inflammatory and protective effects, reduce oxidative stress, improve fat and glucose metabolism, and regulate the immune system; These mechanisms help reduce the chronic effects of diseases such as diabetes, atherosclerosis, and muscle wasting (source).
Stages of implementing exercise therapy
Executing exercise therapy is a structured and scientific process that is designed with the aim of promoting health, rehabilitation and disease prevention.
The success of this method depends on following strict principles, assessing the individual's condition and The program is designed according to physical and medical needs. The stages of implementing exercise therapy generally include evaluation, planning, implementation and continuous monitoring.
initial evaluation
In this stage, the physical condition, medicine and movement power of the person are carefully examined. The evaluation includes clinical examinations, measurement of muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and aerobic capacity to provide a scientific basis for designing a training program.
Setting goals and planning
Based on the evaluation results, short-term and long-term goals are determined. The exercise program is designed taking into account the type of disease, age, physical strength and individual limitations and includes the type of exercise, intensity, duration and number of sessions. Exercises gradually increase in intensity and complexity so that the body can adapt and prevent injury.
monitoring and modifying the program
The body's performance and response to the exercises are continuously monitored. Based on the monitoring results, the exercise program is modified and optimized to provide maximum effectiveness and safety. This stage includes periodic feedback, measuring progress and assessing possible side effects.
Requirements for exercise therapy
In order to achieve the desired results in exercise therapy, it is necessary to meet a set of conditions and requirements. این شرایط شامل آمادگی جسمی و ذهنی فرد، ارزیابی پزشکی و انتخاب محیط و ابزار مناسب میشود.
بدون رعایت این اصول، برنامه ورزش درمانی ممکن است تاثیر کامل خود را نداشته باشد یا حتی خطراتی برای سلامت فرد ایجاد کند.
- ارزیابی پزشکی کامل: بررسی سوابق بیماری، معاینات بالینی و ارزیابیهای تخصصی قبل از شروع برنامه تمرینی.
- مشاوره با متخصص: حضور فیزیوتراپیست یا مربی متخصص برای طراحی و نظارت بر تمرینات.
- انتخاب برنامه مناسب: برنامه تمرینی متناسب با سن، توان جسمی، نوع بیماری و محدودیتهای فردی.
- محیط و تجهیزات استاندارد: استفاده از فضای مناسب و ابزارهای ایمن و استاندارد برای تمرینات.
- رعایت شدت و حجم تمرین: شروع تمرینات با شدت مناسب و افزایش تدریجی برای پیشگیری از آسیب.
- پایش و اصلاح مستمر: نظارت بر پیشرفت و واکنش بدن و اصلاح برنامه در صورت نیاز.
- آمادگی ذهنی و انگیزه فرد: تعهد و انگیزه برای انجام منظم تمرینات برای دستیابی به نتایج مؤثر.
مراقبتها و نکات ایمنی ورزش درمانی
اجرای ورزش درمانی بدون رعایت نکات ایمنی میتواند منجر به آسیب، تشدید بیماری یا کاهش اثربخشی برنامه شود.
رعایت مراقبتها و اقدامات پیشگیرانه ضروری است تا فرد بتواند با اطمینان و آرامش تمرینات خود را انجام دهد و حداکثر بهره را از ورزش درمانی ببرد.
- مشورت با پزشک و متخصص: قبل از شروع هر برنامه ورزش درمانی، با پزشک یا فیزیوتراپیست مشورت کنید.
- گرمکردن و سردکردن بدن: انجام حرکات گرمکننده قبل از تمرین و حرکات سردکننده پس از تمرین برای جلوگیری از آسیب عضلات.
- رعایت شدت و حجم مناسب تمرین: شروع با شدت کم و افزایش تدریجی بر اساس توان بدن.
- استفاده از تجهیزات استاندارد: ابزار و تجهیزات ایمن و مناسب با کیفیت مناسب برای تمرینات.
- نظارت حرفهای: انجام تمرینات تحت نظر متخصص یا مربی مجرب، به ویژه برای افراد با بیماری یا آسیب.
- توجه به علائم بدن: در صورت احساس درد شدید، سرگیجه، تنگی نفس یا خستگی بیش از حد، تمرین را متوقف کنید.
- آبرسانی و تغذیه مناسب: تامین آب کافی و تغذیه مناسب قبل و بعد از تمرین برای حفظ انرژی و سلامت بدن.
- محیط ایمن و مناسب: انتخاب فضای مناسب، تهویه کافی و کفپوش مناسب برای جلوگیری از سقوط یا آسیب.
چه مدت طول میکشد تا اثرات ورزش درمانی ظاهر شود؟
اثرات ورزش درمانی معمولاً به نوع بیماری یا آسیب، شدت مشکل، سن و وضعیت جسمانی فرد، و استمرار اجرای برنامه بستگی دارد.
پژوهشهای معتبر نشان میدهند که بسیاری از انسانها میتوانند در عرض چند هفته بهبودهایی در درد، انعطاف یا دامنه حرکتی احساس کنند، و بعد از ۶ تا ۱۲ هفته (حدود ۲ تا ۳ ماه) تغییرات قابلتوجهی در قدرت عضلانی، عملکرد حرکتی یا کیفیت زندگی رخ دهد (منبع).
برای مثال، در مطالعهای پیرامون تمرین درمانی برای بازیابی تحرک برای افرادی با آسیب یا اختلال حرکتی، نتایج معنادار در تحرک و عملکرد جسمی بعد از چند هفته تا چند ماه مشاهده شد (منبع).
اما برای مشکلات مزمن یا شرایط پیچیدهتر (مثل درد مزمن، بهبود بعد از جراحی یا بیماری مزمن)، فرایند بهبود ممکن است چند ماه تا حتی بیشتر از سه ماه زمان ببرد.
ورزش درمانی چند جلسه لازم است؟
تعداد جلسات مورد نیاز برای ورزش درمانی بستگی به نوع مشکل، شدت بیماری یا آسیب، وضعیت جسمانی فرد و اهداف درمانی دارد. Typically, for mild musculoskeletal problems or transient pain, 8-12 sessions 2-3 times per week may be sufficient to see initial changes.
For more complex conditions such as post-surgical rehabilitation, chronic heart disease, metabolic problems or serious movement disorders, the number of sessions is usually more, sometimes up to 20-30 sessions or more, so that the long-term effects of exercise therapy in the form of
Is exercise therapy painful?
Exercise therapy can sometimes be accompanied by pain or temporary discomfort, but this pain is not necessarily a negative sign and is usually transient.
When muscles or joints are immobile for a while have been, their reactivation can cause muscle cramping or soreness, a phenomenon similar to delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS) that appears 12 to 72 hours after exercise.
400;">).
Scientific research has shown that in the treatment of chronic musculoskeletal pain, exercises that have a little pain can be more effective in the short term, but in the medium or long term, there is not much difference between painful and painless exercises (source).
So, exercise therapy may be a little painful, but this pain is often short-lived. and its main purpose is to strengthen and rehabilitate the body; Severe, prolonged or increasing pain should be taken seriously and a specialist should be consulted.